A-Diagrams are a crucial component of the life insurance industry, providing visual representations of complex processes and enhancing understanding among stakeholders. These diagrams serve multiple purposes, from illustrating the benefits and premiums associated with a policy to modelling the interactions between the insurance system and its environment. The use of diagrams ensures transparency and aids prospective policyholders in making informed decisions. They also guide insurance companies in effectively serving their clients, promoting expertise, and facilitating process improvements. By employing diagrams, the life insurance industry strives to balance the needs of consumers and providers, fostering an environment of trust and education.
What You'll Learn

Life insurance illustrations
The illustrations include estimates of the benefits entitled to a policyholder, the premiums required to maintain the benefit, the expenses related to policy issue and maintenance, and the benefit and premium periods. They also include information on the policy's guaranteed and non-guaranteed elements, such as policy benefits, premiums, values, credits, and charges.
There are three types of life insurance illustrations: basic, supplemental, and in-force. A basic illustration is used in the marketing of the policy and shows both guaranteed and non-guaranteed elements. A supplemental illustration depicts only the non-guaranteed elements permitted in the basic illustration and may differ in format. An in-force illustration is provided after the first policy anniversary and gives periodic updates on the policy's performance.
Life Insurance: Understanding the Typical Payout Amounts
You may want to see also

Life insurance underwriting
Medical underwriting involves examining an individual's health and lifestyle factors, such as age, medical history, habits, and occupation, to assess the risk they pose to the insurer. On the other hand, financial underwriting focuses on ensuring that the coverage amount aligns with the applicant's financial needs and circumstances. This includes reviewing income, assets, liabilities, credit history, and existing insurance coverage.
The life insurance underwriting process typically consists of several steps, including completing an application, undergoing a medical examination, information analysis, and insurance classification. The application process collects basic information such as name, address, occupation, and lifestyle choices. The medical examination confirms health details and helps identify any underlying health issues. The information analysis phase involves scrutinizing prescription history, medical records, motor vehicle records, credit history, and criminal background checks. Finally, during insurance classification, the underwriter assigns a rating that indicates the applicant's insurability based on health and lifestyle factors.
The premium an individual pays is usually based on risk and underwriting factors, including age, health status, occupation, gender, lifestyle, policy type, coverage amount, and credit standing.
Underwriting can be completed within 24 hours or may take up to several weeks, depending on the complexity of the application. It is an essential step in obtaining life insurance, as it helps insurers assess an individual's risk profile and provide them with accurately priced coverage.
Covid Shots and Life Insurance: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also

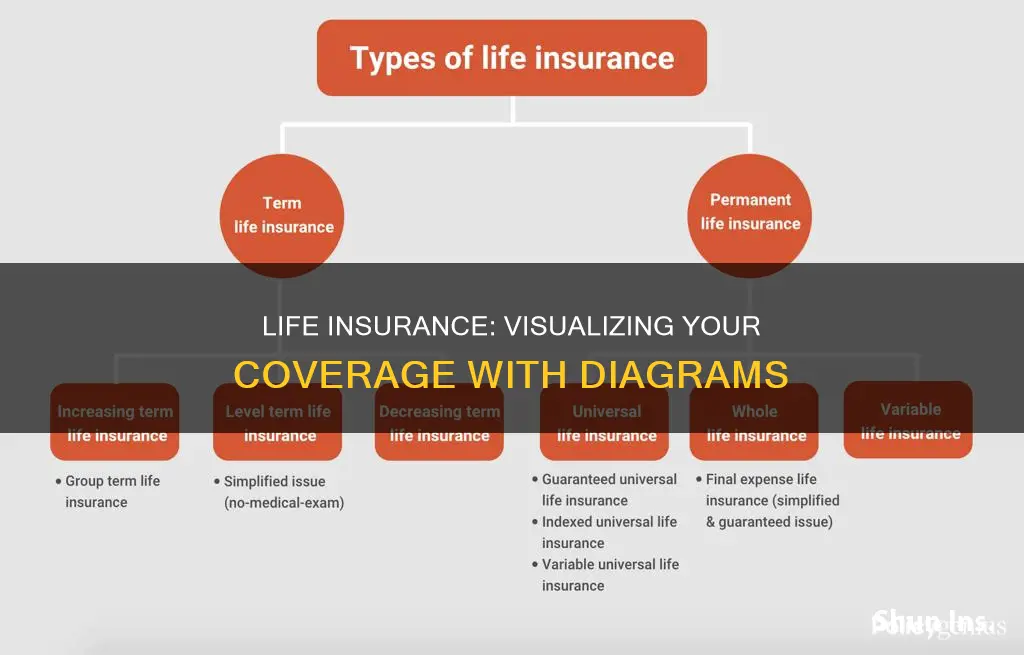
Types of life insurance
Life insurance is designed to reduce the financial burden on your loved ones when you pass away. There are several types of life insurance, each catering to specific needs and budgets. Here is a breakdown of the different types of life insurance:
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance is a temporary policy that provides coverage for a specified period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. It is a simple and low-cost option, ideal for those who only need coverage for a certain number of years. Term life insurance is often the most affordable type of life insurance and is sufficient for most people. However, if you outlive the policy, your beneficiaries will not receive a payout.
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides coverage for your entire lifetime, as long as you keep up with the premiums. It includes a savings component, known as the cash value, that grows over time at a fixed interest rate. Whole life insurance is typically more expensive than term life insurance but offers the advantage of lifelong coverage and the ability to build cash value.
Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is another form of permanent life insurance that offers flexibility. It allows you to adjust your premiums and death benefit within certain limits. Similar to whole life insurance, universal life insurance has a savings component, but the interest rate is not fixed and can change over time based on market conditions. Universal life insurance is generally less expensive than whole life insurance and can adapt to your changing needs.
Variable Life Insurance
Variable life insurance is a riskier type of permanent life insurance. It consists of a fixed death benefit and a variable cash value that rises and falls based on your payments and the performance of your selected investments. Variable life insurance offers a wider range of investment options, potentially providing greater benefits to your beneficiaries but also exposing you to higher risk, fees, and costs.
Final Expense Life Insurance
Also known as funeral or burial insurance, final expense life insurance is a type of whole life insurance with a smaller and more affordable death benefit. It is designed to cover end-of-life expenses such as funeral costs, medical bills, or outstanding debt. Final expense life insurance is often easier for older or less healthy individuals to qualify for, as it typically does not require a medical exam.
In addition to these main types of life insurance, there are also alternative forms such as indexed universal life insurance, simplified issue life insurance, and guaranteed life insurance, each catering to specific needs and circumstances. When choosing a type of life insurance, it is important to consider your current life stage, investment goals, budget, and the level of coverage you require.
Globe Life Insurance: Payouts and Policy Promises
You may want to see also

Life insurance application
Life insurance is a financial product that provides peace of mind and security for individuals and their loved ones. The process of applying for life insurance can seem daunting, but understanding the steps involved can make it more manageable. This guide will outline the key stages and requirements of the life insurance application process, helping applicants navigate it with confidence.
Understanding Life Insurance
Life insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides financial protection for the policyholder's beneficiaries in the event of their death. It ensures that loved ones are taken care of financially, helping to cover expenses such as funeral costs, mortgage payments, or ongoing living expenses. The policyholder pays regular premiums to maintain their coverage, and in return, the insurance company guarantees a payout, known as a death benefit, to the designated beneficiaries upon the insured's death.
Types of Life Insurance
There are several types of life insurance policies available, each with its own unique features and benefits. The most common types include:
- Term Life Insurance: This type of policy provides coverage for a specified term, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. It is often the most affordable option and is ideal for those with temporary insurance needs, such as covering a mortgage or providing financial support for dependents.
- Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance offers coverage for the policyholder's entire life, rather than a fixed term. It includes a savings component, known as cash value, which grows over time and can be borrowed against or withdrawn under certain circumstances.
- Universal Life Insurance: This type of policy provides more flexibility than whole life insurance, allowing the policyholder to adjust their coverage and premiums within certain limits. The cash value component earns interest and can be used to pay premiums or increase the death benefit.
The Application Process
The life insurance application process typically involves the following steps:
- Research and Comparison: Applicants should start by researching different insurance providers and the types of policies they offer. It is important to compare coverage options, premiums, and benefits to find the most suitable policy for your needs.
- Health and Lifestyle Assessment: Life insurance applications often require a health and lifestyle assessment, including a medical exam and questions about your medical history, lifestyle choices, and family health history. This information helps the insurance company assess your risk level and determine your premiums.
- Documentation: Applicants will need to provide various documents, including proof of identity, income verification, and medical records. It is essential to gather and organize these documents beforehand to ensure a smooth application process.
- Application Form: The application form captures personal information, such as name, date of birth, address, and contact details. It also includes questions about the applicant's health, occupation, and lifestyle. It is crucial to be honest and accurate when completing the form.
- Underwriting and Approval: Once the application is submitted, the insurance company will review it and assess the risk associated with the applicant. This process is known as underwriting, and it determines whether the applicant is approved for coverage and at what premium rate.
- Payment of Premiums: If the application is approved, the policyholder will need to start paying premiums to maintain their coverage. Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the policy's terms.
Choosing a Beneficiary
When applying for life insurance, it is essential to carefully consider who you want to designate as your beneficiary. The beneficiary is the person or entity that will receive the death benefit payout from the insurance company. Most people choose their spouse, children, or other family members as beneficiaries. It is important to provide accurate and up-to-date information about your beneficiary, including their full name, date of birth, and relationship to you.
In conclusion, applying for life insurance involves understanding the different types of policies available, undergoing a health and lifestyle assessment, completing the application form, and choosing a beneficiary. By following the outlined steps and providing the necessary documentation, individuals can secure financial protection for their loved ones and gain peace of mind for themselves.
Divorce and Life Insurance: What Happens to Your Policy?
You may want to see also

Life insurance claim
A life insurance claim can be made by following these steps:
Step 1: Contact the Insurance Company or Agent
The name of the insurance company will be clearly stated on the policy, so this is the first step to making a claim. If you remember the agent you worked with, ask for them specifically. They should be able to explain their process for filing a claim and act as an intermediary with the insurance company. If you don't have an agent, contact the company directly.
Step 2: Get Copies of the Death Certificate
Certified copies of the death certificate are required by insurance companies. You can get these from a local health department, and the funeral home may also be able to help. It is recommended to get at least 10 copies as these will be needed for other purposes, such as closing accounts and cancelling subscriptions.
Step 3: Fill Out the Paperwork
Most insurance companies make their forms available online. If not, simply call the insurance company or agent to find out what to do. They will likely ask you to send the death certificate in the mail with the completed forms.
Step 4: Choose How to Get the Payout
There are several ways to receive the payout:
- Lump sum: The beneficiary receives the entire death benefit in a single payment.
- Specific income: The company pays out the principal and interest according to a predetermined schedule.
- Life income: The beneficiary receives a guaranteed income for life, with the amount depending on the death benefit, age, and gender.
- Interest income: The company holds the proceeds and pays interest on them. The death benefit remains intact and is paid to a secondary beneficiary upon the beneficiary's death.
Step 5: Wait for the Payout
An insurance company can take up to 30 days to review and accept or reject a claim, but most will pay out within a week or two. If they take too long, they face interest charges.
Potential Problems
Although life insurance claims are rarely denied, it is useful to be aware of some potential issues:
- The policy owner stopped paying premiums.
- The insured lied on the application, for example, about being a smoker.
- The cause of death fell outside the scope of the insurance coverage, such as risky activities or a felony.
- The policy is less than two years old and the cause of death was suicide.
Life Insurance and Skydiving: What's Covered in Accidents?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A life insurance illustration is provided to prospective or new policy owners and estimates how the policy should perform under specific circumstances. It includes benefits entitled to a policyholder, premiums required to maintain the benefit, expenses related to policy issues and maintenance, and benefit and premium periods.
A use case diagram is a graphical representation of the interactions between a life insurance system and its actors. It helps to understand how the system interacts with its environment and describe the direct organisational environment.
A UML diagram is a type of diagram that describes a life insurance system and supports insurance processes. It includes use case diagrams and activity diagrams, which model the actors and their interactions with the system and outline processes such as new client registration, insurance claims, and insurance premium collection.