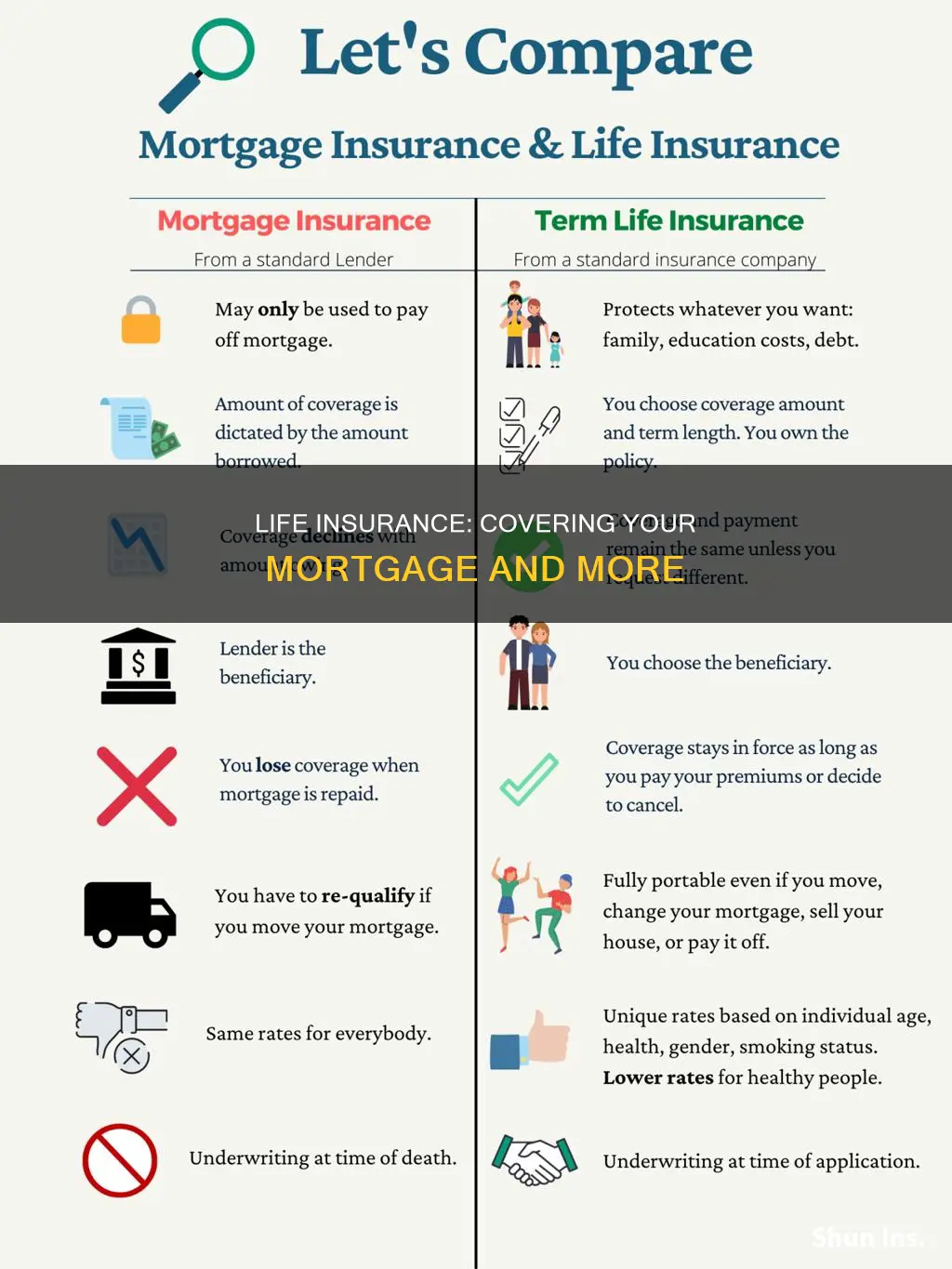
Life insurance can be used to cover a mortgage, but it's important to understand the differences between mortgage life insurance and other types of life insurance. Mortgage life insurance, also known as mortgage protection insurance, is designed specifically to repay mortgage debts if the borrower dies. The key difference is that the mortgage lender is the beneficiary of the policy, not the borrower's family or chosen beneficiaries. This means that the death benefit is paid directly to the lender to cover the remaining mortgage balance, and the family does not receive any proceeds. Standard term life insurance, on the other hand, offers more flexibility, as beneficiaries can choose how to use the payout, including paying off the mortgage or other expenses. While mortgage life insurance ensures the mortgage is covered, it lacks the versatility of other life insurance options.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is it? | A life insurance policy that pays your mortgage debt if you die. |
| Who is it for? | Homeowners who want to ensure their mortgage is paid off if they die. |
| Who is the beneficiary? | The mortgage lender. |
| Who sells it? | Banks affiliated with lenders, independent insurance companies, or the mortgage lender. |
| Who underwrites it? | The insurance company. |
| Who pays the premiums? | The homeowner. |
| How are the premiums paid? | Rolled into the loan or paid separately. |
| What happens if the homeowner dies? | The insurance company pays the remaining mortgage balance to the lender. |
| What happens if the homeowner becomes disabled or unable to work? | The insurance company may pay off the entire mortgage loan. |
| What are the disadvantages? | High premiums, lack of transparency, fluctuating premiums, and lack of flexibility in how the payout is used. |
What You'll Learn

Mortgage life insurance vs. term life insurance
When it comes to protecting your home and family, you have two main options: mortgage life insurance and term life insurance. Both can help secure your home in the event of your death, but they do so in very different ways. So, what's the difference?
Mortgage Life Insurance
Mortgage life insurance, also known as mortgage protection insurance, is a type of insurance policy that is designed specifically to pay off your mortgage debt if you die. The key feature of this policy is that the mortgage lender is the beneficiary, meaning the death benefit is used to wipe out the remaining mortgage balance. This ensures that your family can stay in their home, even if the primary income used for mortgage payments is lost.
Mortgage life insurance is typically sold by the mortgage lender or an affiliated insurance company, and the premiums can often be added to your monthly mortgage payments for convenience. The length of the policy coincides with the number of years left on your mortgage, and the benefit decreases over time as your mortgage amount gets smaller.
One of the advantages of mortgage life insurance is that it generally does not require a medical exam or detailed health questions, making it accessible to those with pre-existing medical conditions. It also offers peace of mind that your mortgage will be paid off, ensuring your family has a place to live.
However, the biggest drawback is the lack of flexibility. The death benefit goes directly to the lender, and your loved ones do not receive any money. Additionally, the policy only covers your mortgage and cannot be used for other expenses. The cost of mortgage life insurance can also be relatively high, especially for individuals in good health.
Term Life Insurance
On the other hand, term life insurance provides a lump-sum benefit to your chosen beneficiaries (usually your family) upon your death. This money can be used for various purposes, including paying off the mortgage, covering debts, and replacing lost income. Term life insurance is sold for a set length of time, such as 10, 15, 20, or 30 years, and the premiums are usually low for the initial term.
One of the biggest advantages of term life insurance is its flexibility. Your beneficiaries can use the payout to cover not just the mortgage but also other expenses such as funeral costs, childcare, and education. Additionally, the benefit amount remains the same and never decreases. Term life insurance is also portable, meaning it stays with you even if you move, pay off your mortgage, or change lenders.
However, term life insurance usually requires a medical questionnaire and exam as part of the underwriting process. The application process may be more extensive than mortgage life insurance, and the cost can be higher for those in poor health.
The choice between mortgage life insurance and term life insurance depends on your individual needs and circumstances. If your primary concern is solely protecting your mortgage and ensuring your family can stay in their home, mortgage life insurance may be a suitable option. However, if you want more flexibility in how the benefit is used and the ability to provide additional financial support to your loved ones, term life insurance may be the better choice.
Whole Life Insurance: Does It Expire With Age?
You may want to see also

Who receives the benefit payments?
The beneficiary or beneficiaries of a life insurance policy are the individuals or organisations that will receive the benefit payments. The policyholder designates the primary beneficiary or beneficiaries, and they can also choose to name a contingent beneficiary. This is a secondary recipient who will receive the benefit payments if the primary beneficiary dies before the policyholder.
The beneficiary of a mortgage life insurance policy is usually the mortgage lender. This means that the benefit payments are not received by the policyholder's loved ones, who are instead protected from losing the family home.
With a standard term life insurance policy, the policyholder can choose who will receive the benefit payments. The beneficiaries can use the money for anything, but the policyholder can state in their will that they would like it to be used to pay off the mortgage.
Who can be a beneficiary?
A beneficiary can be a single person or multiple people. It can also be an entity such as a charitable organisation.
Minors can be named as beneficiaries, but they cannot receive any benefits until they reach the age of majority based on state law and will need a legal guardian to manage the funds.
If there is no named beneficiary, the benefit payments may be paid to the policyholder's estate and become part of their taxable estate, potentially subjecting them to estate taxes.
Insurable Interest: Can You Insure Your Own Life?
You may want to see also

Pros and cons of mortgage life insurance
Mortgage life insurance is a type of insurance policy that pays off the balance of your mortgage when you die. It is often sold through banks and mortgage lenders, and its purpose is to ensure your home is paid off if you die with an outstanding balance on the loan.
Pros
- Guaranteed policy acceptance: You can't be denied an MPI policy based on your health condition, which is beneficial for those with pre-existing medical conditions.
- No underwriting required: Most MPI policies don't require a medical exam, which can be beneficial if you're sick or work in a dangerous/high-risk job.
- Peace of mind for your family: Your family won't be responsible for paying off your mortgage or losing the house due to foreclosure.
Cons
- Extra monthly payment: You'll be responsible for making an extra payment each month, which may be a strain on your budget.
- Limited payout options: The MPI payout only goes towards your mortgage debt and doesn't provide your family with money to cover taxes, bills, or funeral costs.
- Alternative policies may be better: Traditional life insurance policies can provide more of a financial safety net for your family, as the payout can be used for any purpose, not just the mortgage.
- Lack of flexibility: The payout from mortgage life insurance goes directly to the lender, so your family won't have the freedom to spend the money as they wish.
- Declining payout: While premiums stay the same, the payout decreases as you pay down your mortgage.
- Higher premiums: Premiums for MPI are often much higher than for term life insurance, especially if you're in good health.
Pension Benefits: Life Insurance Coverage for NYCers?
You may want to see also

How does mortgage life insurance work?
Mortgage life insurance, also known as mortgage protection insurance, is a type of insurance that pays out a lump sum to your loved ones if you die before you finish paying your mortgage. It is designed to ensure that your loved ones can pay off the remaining mortgage on your home and not have to worry about losing the property.
Mortgage life insurance is usually sold by the mortgage lender or an affiliated insurance company. The length of the policy coincides with the number of years left on your mortgage, and the premiums remain level throughout the term. However, the policy's value decreases over time as you pay off your mortgage. It is important to note that the mortgage lender is the beneficiary of the policy, not your spouse or any other individual you choose. This means that the insurance payout will go directly towards settling the remaining mortgage debt, and your loved ones will not receive any money.
There are two main types of mortgage life insurance policies:
- Decreasing term insurance: The most common type, where the payout reduces over time as you pay off your mortgage. This type of policy is designed for repayment mortgages and can be a cheap way to ensure your loved ones can pay off the remaining debt.
- Level term insurance: This type of policy provides a fixed payout if you die within a specified time frame. It tends to be more expensive but can be a better option if you want to leave a lump sum for your loved ones to cover other expenses or if you have an interest-only mortgage.
When considering mortgage life insurance, it is important to weigh the pros and cons. While it can provide peace of mind and ensure your loved ones can stay in their home, it may not provide enough money to cover other living costs. Additionally, your loved ones will not receive a death benefit, as the payout goes directly to the mortgage lender. An alternative option is a standard term life insurance policy, which gives your beneficiaries more flexibility in how they use the payout.
Before purchasing mortgage life insurance, be sure to shop around for the best deals and carefully review the terms, costs, and benefits of the policy. It is also worth considering whether you could get the same level of coverage for your family at a lower cost with fewer restrictions by buying term life insurance.
Life Insurance for Unborn Children: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

What happens if you don't have life insurance and you die with a mortgage?
If you don't have life insurance and you die with an active mortgage, your beneficiaries will be responsible for the remaining mortgage payments. This can be a significant financial burden for your loved ones, who may struggle to cover the monthly payments without your income.
In this scenario, your beneficiaries would have a few options:
- They could continue paying the mortgage as normal, covering the payments with their own income or assets.
- They could sell the property and use the proceeds to pay off the remaining mortgage.
- They could take out a new loan to cover the remaining mortgage payments.
- They could attempt to refinance the mortgage to lower the monthly payments.
If your beneficiaries cannot afford the mortgage payments and are unable to secure a new loan or refinance, they may be forced to sell the property or risk defaulting on the loan. This could result in a significant financial loss and potential damage to their credit score.
To avoid this situation, it is generally recommended that individuals with mortgages consider purchasing life insurance, specifically a term life insurance policy that covers the length of the mortgage. This will ensure that your beneficiaries receive a death benefit that can be used to pay off the remaining mortgage, providing them with financial security and peace of mind.
Life Insurance and Tax Credits: Missouri's Unique Benefits
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Mortgage life insurance is a life insurance policy that pays off your mortgage debt if you die. It is also known as mortgage protection insurance.
Mortgage life insurance is usually purchased when you buy your home or shortly after. The policy’s length coincides with the number of years you have to pay off your mortgage. The policy’s premiums remain level during the term, but its value decreases as your mortgage decreases.
Mortgage life insurance provides near-universal coverage with minimal underwriting. There is often no medical examination or blood sample required, which can be beneficial for those with pre-existing medical conditions. It also relieves the worry of your family losing their home if you die or are unable to work.
The biggest drawback of mortgage life insurance is the lack of flexibility. The death benefit goes directly to the mortgage lender, meaning your loved ones won't see any of the money. The premiums are also typically high, and it can be difficult to obtain transparent quotes online.







