Life insurance rates are determined by a variety of factors, including age, gender, health, and lifestyle choices. Age is a primary factor, with rates increasing as individuals get older due to the decreased life expectancy and increased likelihood of a payout. The type of policy, such as term or permanent life insurance, also impacts the cost, with term policies typically being more affordable. Health status, including pre-existing conditions, family medical history, and risky behaviours, can result in higher rates. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking or engaging in dangerous hobbies, can also drive up premiums. Additionally, the coverage amount and length of the policy affect the cost, with higher coverage and longer policies resulting in more expensive premiums.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average monthly cost of life insurance | $26 |
| Average monthly cost of life insurance for a 40-year-old with $500,000 in coverage | $50 |
| Average monthly cost of life insurance at age 25 | $31 |
| Average monthly cost of life insurance at age 65 | $593 |
| Average annual increase in life insurance rates | 8% to 10% |
| Average annual increase in life insurance rates for people over 50 | 9% to 12% |
| Average annual increase in life insurance rates for smokers | 218% |
| Average monthly cost of life insurance for a 30-year-old | $22 |
| Average monthly cost of life insurance for a 40-year-old | $32 |
| Average monthly cost of life insurance for a 50-year-old | $80 |
What You'll Learn

How gender impacts life insurance rates
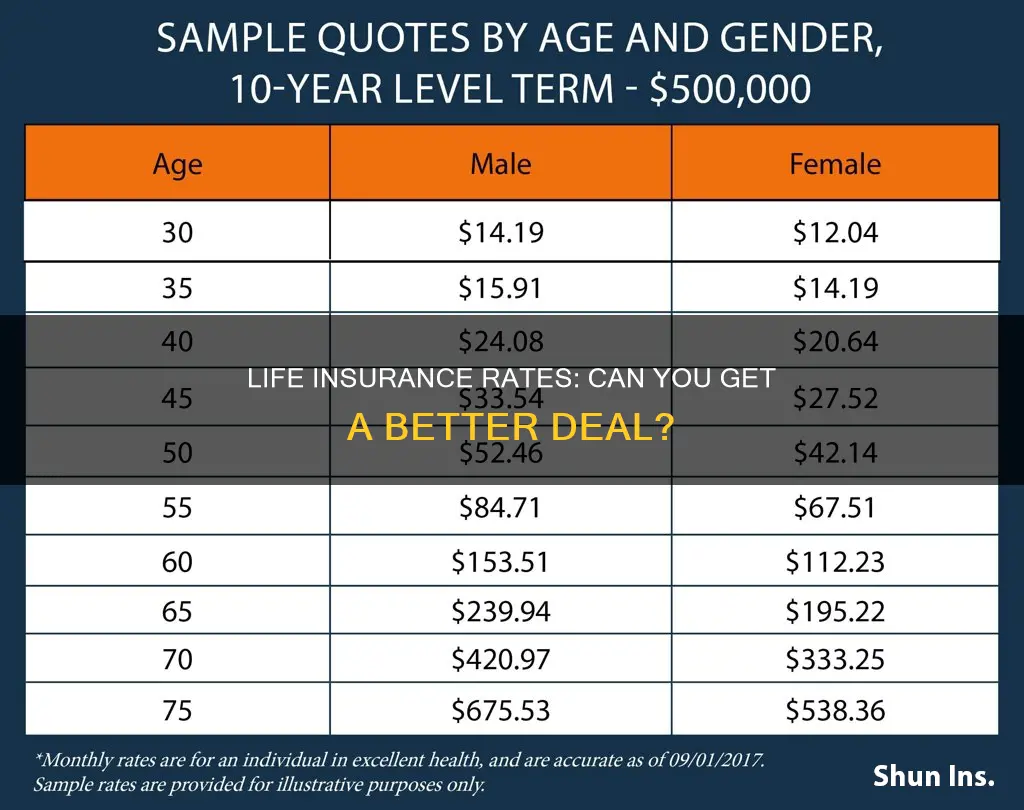
Life insurance rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including age, health, lifestyle choices, and gender. While multiple factors come into play, gender plays a significant role in determining the cost of life insurance. Here's how gender impacts life insurance rates:
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a crucial factor in determining life insurance rates. According to statistics, women tend to live longer than men. In the United States, the average life expectancy for women is approximately 80 years, while for men, it is around 74.5 years. This difference in life expectancy directly influences insurance rates. Since women are expected to live longer, insurance companies consider them a lower risk and, therefore, offer lower premiums. The likelihood of paying out a death benefit is higher for men due to their shorter life expectancy, resulting in higher insurance rates.
Health Factors
Men and women face different health risks throughout their lives. Men are generally more prone to certain health conditions that can increase their mortality risk, such as heart disease and hypertension. These gender-specific health conditions contribute to higher insurance rates for men. Additionally, men are statistically less likely to visit the doctor than women, which insurers view as a health risk, further impacting their insurance rates.
Occupational Hazards
Occupational hazards also play a role in gender-based insurance rates. Men and women tend to work in different industries, which may have varying levels of risk. Men are more likely to pursue careers in high-risk fields, such as construction, mining, or logging, which increases the chances of accidents and fatalities. This increased risk is reflected in their insurance premiums.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices and habits can significantly impact life insurance rates. Men are generally more inclined to engage in risky behaviors, such as smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, drug use, and high-risk hobbies like extreme sports. These lifestyle choices are associated with a higher likelihood of passing away prematurely, leading to higher insurance rates for men.
While gender is a factor in determining life insurance rates, it is important to note that other factors, such as age, health history, and lifestyle risks, often have a more significant influence on the cost of insurance. Additionally, for transgender and non-binary individuals, life insurance rates are based solely on risk level, and discrimination based on gender identity is illegal.
Life Insurance Options for Hyperhidrosis Sufferers
You may want to see also

How age impacts life insurance rates
Age is one of the most important factors that determines the rate of your life insurance premium. The older you are, the more expensive your life insurance premium will be. This is because the cost of life insurance is based on actuarial life tables that assign a likelihood of dying while the policy is in force. The older you are, the more likely you are to pass away while under coverage.
The premium amount increases by about 8% to 10% for every year of age. This increase can be as low as 5% annually if you're in your 40s, and as high as 12% annually if you're over 50. For example, a 45-year-old male will pay on average $1,125 for a new, 20-year term policy with $1,000,000 of coverage. The same policy purchased at age 46 will cost $1,225, and $1,345 a year if purchased at age 47.
The increase in monthly premiums as you age is much smaller when you are young compared to when you are older. For instance, the average life insurance quote only increases by 6% between ages 25 and 30, but it jumps by 86% between ages 60 and 65.
Age also affects whether a person will qualify for life insurance coverage at all, with qualifying medical exams getting more stringent as you get older. Most carriers only offer 20-year term policies to those aged 18 to 70. After that, you cannot get a term that long.
Life insurance will be less expensive when you are younger and healthier. If you will need life insurance coverage in the future, it may be more cost-effective to get it while you are younger to reduce your annual premiums.
Life Insurance Annuities: Smart Diversification Strategy?
You may want to see also

How health impacts life insurance rates
Life insurance rates are calculated based on several factors, and health is one of the most significant determinants. Here's how an individual's health can impact their life insurance rates:
Health Status and Medical History
An individual's current health status and medical history play a crucial role in determining their life insurance rates. Insurers typically require applicants to undergo a health assessment, which may include a medical examination and a review of medical records. This allows insurers to identify any pre-existing health conditions, such as high blood pressure, hypertension, or anxiety and depression. Applicants with health issues are often considered riskier to insure, as they are more likely to have a claim in the future. Consequently, they may be offered higher rates or, in some severe cases, be denied coverage altogether.
Lifestyle Choices and Risky Behaviours
Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, drinking, and drug use, can also influence life insurance rates. Smokers, for instance, tend to pay much higher premiums than non-smokers due to the associated health risks. However, it's important to note that quitting smoking can improve an individual's health rating and make them eligible for lower non-smoker rates in the future. Similarly, other risky behaviours, such as frequent marijuana use, can also lead to higher insurance costs.
Family Medical History
Insurers often consider the medical history of an applicant's immediate family, including parents and siblings. A family history of serious illnesses, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, or congenital heart disease, can result in higher premiums, as insurers may perceive a higher risk of the applicant developing similar health issues.
Weight and Body Mass Index (BMI)
In addition to medical conditions, insurers also take into account an individual's weight and BMI. Being overweight or obese can increase the chances of developing various health problems, which, in turn, can affect life insurance rates.
Health and Age
Age and health are closely linked when it comes to life insurance rates. As individuals get older, their health may deteriorate, leading to higher premiums. Therefore, applying for life insurance at a younger age, when one is generally healthier, can result in lower rates.
In summary, an individual's health can significantly impact their life insurance rates. Insurers assess health through medical examinations, medical records, and family history to determine the likelihood of future claims. Lifestyle choices, weight, and age-related health changes also play a role in calculating life insurance premiums. By understanding these factors, individuals can take steps to improve their health and, consequently, secure more favourable rates.
Group Life Insurance: Church Employee Benefits Explored
You may want to see also

How lifestyle impacts life insurance rates
Life insurance rates are calculated based on several factors, including age, gender, health, and lifestyle choices. While some factors such as age and gender are beyond one's control, lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on the cost of life insurance. Here are some ways in which lifestyle influences life insurance rates:
Smoking status: Life insurance rates are significantly higher for smokers compared to non-smokers. Smokers are considered high-risk due to the increased likelihood of developing respiratory diseases and other health issues. Quitting smoking can help lower your insurance premiums.
Health and weight: Pre-existing health conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, or diabetes, can increase your life insurance rates. Insurers assess your overall health, including weight, as it relates to height, and may place you in different health categories that impact your premiums. Maintaining a healthy weight and managing pre-existing conditions can help secure better rates.
Family medical history: A family history of serious health conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, or diabetes, can also affect your life insurance rates. While you cannot change your genetic predispositions, leading a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate the impact on your premiums.
Driving record: A history of DUIs, DWIs, or major traffic violations can result in higher life insurance rates. Insurers consider individuals with a poor driving record to be high-risk applicants. Improving your driving record over time can help lower your premiums.
Occupation and hobbies: Dangerous occupations and high-risk hobbies can also increase your life insurance rates. If your job involves hazardous duties or you engage in activities like skydiving, scuba diving, or racing, you may be subject to higher premiums. However, maintaining good health and safety practices can help offset these risks to some extent.
Leading a healthy and safe lifestyle, avoiding risky behaviours, and managing any pre-existing health conditions can all contribute to more favourable life insurance rates. It's important to remember that being transparent when applying for life insurance is crucial, as lying or omitting relevant information can have serious consequences.
Term Life Insurance: Renewable Option Explained
You may want to see also

How occupation impacts life insurance rates
Life insurance companies are all about risk. If there's a higher chance of your application resulting in a claim, the cost of your coverage will be higher. Occupations are judged on how hazardous they are, or how likely they are to lead to premature death. For example, a firefighter is deemed more dangerous than an accountant, and so, all other things being equal, a firefighter will pay higher life insurance premiums.
Insurance companies use statistical data to determine the risk posed by different jobs. They also use their own internal data, which may show higher-risk experience with certain occupations, even if they are not commonly known to be dangerous. For instance, truck drivers and on-the-road salespeople are considered high-risk because they spend long periods on the road, increasing the risk of accidents or falling asleep at the wheel.
When you apply for life insurance, insurance underwriters will evaluate your occupation, along with other factors such as your medical history, driving reports, financial statements, and even a background check. They will then assign you a specific risk class, which determines the cost of your policy. The most common risk classifications are preferred (for the healthiest individuals), standard (for people with average health and life expectancy), and substandard (for high-risk individuals).
If you work in a high-risk occupation, you will likely face higher premiums than those in less hazardous professions, but obtaining a policy is usually still possible. In fact, in the vast majority of cases, life insurance companies will approve a policy even for people in the most dangerous jobs. They will simply compensate for the higher risk by charging more.
Some companies will charge premiums based on the occupation itself, so there may be different rates depending on the career field. Other companies establish a flat rate that applies to any occupation deemed hazardous. For example, they may charge an extra $2 to $3 per $1,000 of coverage. On a $200,000 life insurance policy, with a flat rate charge of $2 per $1,000 of coverage, the extra charge would result in an additional $400 in annual premiums.
If you work in a high-risk field, it's recommended that you supplement any employer-provided group life insurance with a personal policy. This gives you and your loved ones additional financial security.
Who Can Be a Contingent Beneficiary for Life Insurance?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance companies use a few different criteria to calculate your premium, including your age, overall health, gender, lifestyle factors (e.g. your job or hobbies), the type of life insurance policy you need, and the amount of coverage you choose.
In addition to your age, life insurance companies also consider the type of coverage you choose (term life insurance plans generally have lower rates than whole life insurance policies), your health class (younger Americans in excellent health can expect to pay the lowest rates), your gender (since women have a longer average life expectancy than men, their rates are lower), and the amount of coverage you choose (the less coverage you buy, the lower the premiums).
The average cost of life insurance is $26 a month. This is based on data for a 40-year-old buying a 20-year, $500,000 term life policy. However, life insurance rates can vary dramatically among applicants, insurers, and policy types. The average monthly rate for life insurance is $22 for a 30-year-old, $32 for a 40-year-old, and $80 for a 50-year-old.
Yes, life insurance rates increase with age as health issues become more frequent and the likelihood of a payout increases. The older you are, the more likely you are to become ill or die, so insurance companies will charge higher premiums to offset this risk.







