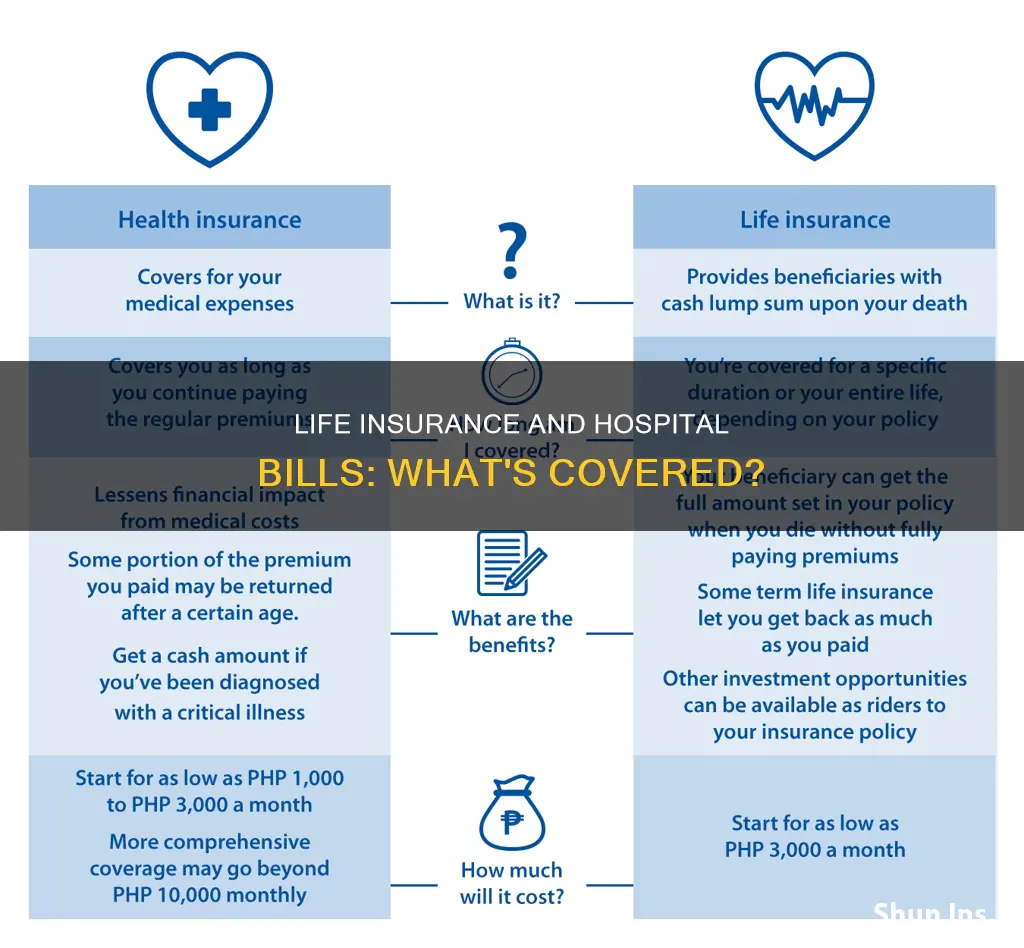
Life insurance and health insurance are two very different things. While health insurance covers medical expenses such as doctor's visits, hospital stays, medications, tests, and procedures, life insurance pays out a lump sum to your beneficiaries in the event of your premature death. However, there are some life insurance policies that now include living benefits, which allow the insured to file a claim against their death benefit and receive a portion of it before they die. This can be used to pay off hospital bills, health insurance deductibles, or other medical expenses.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Life insurance provides financial support for your loved ones after your death. Health insurance covers medical expenses such as doctor's visits, hospital stays, medications, tests, and procedures. |
| Payout | Life insurance pays out a lump sum to beneficiaries upon the policyholder's death. Health insurance covers a portion of medical expenses. |
| Coverage | Life insurance covers death and sometimes terminal illness. Health insurance covers medical treatment, drugs, and preventative check-ups. |
| Dependents | Life insurance is essential if you have dependents. Health insurance is also important for dependents but is not always necessary. |
| Age | Life insurance is more affordable for younger people. Health insurance is not always necessary for young adults. |
| Cost | Life insurance costs depend on age, health, lifestyle, and whether you smoke. Health insurance costs depend on the level of coverage and individual circumstances. |
| Exclusions | Life insurance usually excludes pre-existing conditions and risky activities. Health insurance may not cover pre-existing conditions, chronic illnesses, or alternative treatments. |
What You'll Learn
- Life insurance and health insurance: what's the difference
- Does life insurance cover hospital bills for pre-existing conditions?
- Does life insurance cover hospital bills for chronic illnesses?
- Does life insurance cover hospital bills for terminal illnesses?
- Does life insurance cover hospital bills for accidents?

Life insurance and health insurance: what's the difference?
Life insurance and health insurance are two distinct types of insurance that serve different purposes and offer different types of coverage. Here are the key differences between the two:
Purpose
The primary purpose of life insurance is to provide financial protection to your loved ones in the event of your death. It ensures that your family will have financial continuity and will not struggle with income loss, funeral costs, medical expenses, and other debts. On the other hand, health insurance is designed to cover medical expenses and help you afford medical care and stay healthy. It covers things like doctor's visits, hospital stays, medications, tests, and procedures.
Coverage
Life insurance provides a lump-sum death benefit to your beneficiaries upon your death. The amount paid out is typically based on the level of coverage you choose and can be used to cover specific payments like a mortgage. In contrast, health insurance covers a portion of medical expenses, including doctor's visits, hospital stays, medications, tests, and procedures. Basic health insurance usually covers most inpatient treatments and day-care surgery, while some policies may also cover outpatient treatments and provide a small fixed amount for each night spent in the hospital.
Term
Life insurance policies are typically for a fixed tenure and expire once the term is over. Term life insurance policies run for a specific period, such as 5, 10, or 25 years, and only pay out if the insured dies during the policy term. Whole-of-life policies, on the other hand, pay out regardless of when the insured dies, as long as premium payments are up to date. Health insurance policies, on the other hand, are usually short-term and need to be renewed annually to continue coverage.
Beneficiaries
Life insurance provides financial protection for your family and dependents in the event of your death. It ensures that they will have the financial resources to cover their expenses and obligations. Health insurance, meanwhile, covers the policyholder's medical expenses during their lifetime. Some health insurance policies, like family floater plans, may also cover the medical expenses of the policyholder's family.
Types
There are two main types of life insurance: term life insurance and whole-of-life insurance. Term life insurance is for a fixed period and only pays out if the insured dies during that term. Whole-of-life insurance, as the name suggests, covers the insured for their whole life and pays out regardless of when they die, as long as premiums are paid. Health insurance types include individual health insurance, which covers a single person, family floater health insurance, which covers all household members under one premium, and senior citizen health insurance, tailored to meet the needs of those over 60.
In summary, life insurance and health insurance serve different purposes and cater to different needs. Life insurance provides financial protection for your loved ones after your death, while health insurance helps you cover medical expenses during your lifetime. Both types of insurance are important, especially for individuals with dependents, and choosing the right coverage for each can provide valuable peace of mind.
Kansas Health Insurance: No Benefits for Life Partners
You may want to see also

Does life insurance cover hospital bills for pre-existing conditions?
Life insurance with pre-existing conditions can be more difficult and expensive to obtain, but it is not impossible. The specific policy types one qualifies for will depend on the particular medical problems, how well the condition is managed, and the insurer.
A pre-existing condition is a medical issue one was diagnosed with or treated for before applying for life insurance. Each insurer has its own underwriting process to assess applicants' risk profiles, and some insurers are more flexible about certain health conditions than others.
- The type of condition: The insurer evaluates the risk the condition entails and its likelihood of causing recurring issues. For example, cancer, heart disease, and other severe chronic illnesses are considered higher risk.
- Current health status: Even with a pre-existing condition, insurers evaluate how well the condition is being managed. If the condition is under control, one may more easily get approval and qualify for more favorable premiums.
- Age: Premiums can increase and approval chances can decrease with age, given the same pre-existing condition, as younger people generally have a longer life expectancy, reducing the insurer's risk.
- Lifestyle habits: Certain habits, such as smoking, can influence approval chances. On the other hand, a healthy lifestyle, such as regular exercise, can potentially increase approval chances.
There are several types of life insurance policies available for individuals with pre-existing conditions:
- Term life insurance: These policies have more favorable premiums and large death benefits, but coverage only lasts 10 to 30 years.
- Guaranteed issue life insurance: This type of policy never denies applicants, and there are no medical questions or exams. However, these policies don't offer a lot of coverage.
- Group life insurance: Group life insurance is often offered by employers for a highly affordable premium, and basic coverage is typically limited to one or two times the annual salary. The health conditions of the applicants are usually not considered, but the policy is only valid while employed at that job.
- Whole life insurance: People with pre-existing conditions could still qualify for whole life insurance, which offers lifelong coverage and a cash value growth component. However, the premiums can be much higher.
Additionally, hospital indemnity insurance can help cover out-of-pocket costs during a hospital stay. This type of insurance provides a lump-sum payment that can be used for various expenses, such as medical insurance deductibles, copayments, and household bills. It is worth noting that hospital indemnity insurance is not intended to replace medical coverage but rather to supplement it.
Life Insurance and HIPAA: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also

Does life insurance cover hospital bills for chronic illnesses?
Life insurance can be used to cover hospital bills for chronic illnesses, but it depends on the type of policy and the specific conditions covered. While life insurance typically pays out a lump sum upon the policyholder's death, some policies include "living benefits" that allow the insured to access funds while alive to cover medical expenses.
- Surrendering the policy: With permanent life insurance, you may be able to cash out the policy to pay medical bills. However, this will result in losing coverage, and there may be tax implications.
- Borrowing from cash value: If you have built up cash value in your permanent life insurance policy, you may be able to borrow from it to pay medical bills. Interest will apply, and failure to repay may result in a reduced death benefit or policy lapse.
- Riders: Various riders can be added to life insurance policies to provide additional coverage for chronic illnesses. These include:
- Accelerated death benefit rider: Allows early access to a portion of the death benefit if diagnosed with a terminal illness.
- Critical or chronic illness rider: Provides access to funds if diagnosed with a critical or chronic illness, though definitions and rules may vary.
- Waiver of premium rider: Allows you to stop paying premiums if you become totally and permanently disabled, freeing up money to pay medical bills.
- Long-term care insurance rider: Allows you to unlock a portion of the death benefit to pay for long-term medical care.
It is important to carefully review the terms and conditions of your life insurance policy to understand the specific coverage provided for chronic illnesses. Additionally, there may be tax and financial implications when accessing funds from your life insurance policy, so it is advisable to consult with a financial professional before making any decisions.
Nicotine Detection: Life Insurance's Blood Test Secrets
You may want to see also

Does life insurance cover hospital bills for terminal illnesses?
Life insurance policies can be used to cover hospital bills for terminal illnesses, but it depends on the type of insurance and the terms of the policy.
Some life insurance policies include a terminal illness rider, which provides financial coverage for the policyholder if they are diagnosed with a terminal illness during the policy term. This rider is sometimes included in the plan at no additional cost, while other policies allow it to be added as an extra. The rider typically includes a survival period of 12 months, after which the policyholder receives a lump sum payment. This can be used to cover hospital bills and other expenses.
If a policy does not include a terminal illness rider, it may still be possible to receive a payout for a terminal illness diagnosis through an accelerated death benefit rider. This allows the policyholder to withdraw part of the death benefit if they are diagnosed with a terminal illness and are projected to pass away within a certain timeframe, usually six to 24 months. The money received through this rider can be used for any purpose, including medical bills.
In some cases, individuals with a terminal illness may be able to purchase life insurance to cover their medical expenses. However, their options are limited, and they will likely have to choose a guaranteed issue life insurance policy, which has a modest face amount and is quite expensive compared to other types of policies. Additionally, these policies include a graded benefit period, typically two years, during which the full death benefit will not be paid out. If the policyholder dies during this period, their premiums will be returned with interest, or a percentage of the death benefit will be paid.
It is important to carefully review the terms and conditions of a life insurance policy to understand what is covered and what is not.
Cigna's Individual Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Does life insurance cover hospital bills for accidents?
Life insurance covers death due to natural causes, illness, and accidents. However, it is important to note that insurance companies can deny paying out your death benefit in certain circumstances, such as if you engage in risky behaviours or fail to pay your premiums.
In the case of accidents, life insurance policies generally cover deaths resulting from motor vehicle accidents, drowning, poisoning, fires, and other tragedies. It is worth noting that life insurance policies typically have a “suicide clause” that excludes coverage for suicide during the first two years of the policy. Additionally, if you participate in risky activities, your insurer may add an exclusion to the policy that prohibits payments for accidents occurring during these activities.
While life insurance provides financial protection for your loved ones in the event of your death, it is not designed to cover medical expenses during your lifetime. For coverage of hospital bills during your lifetime, you may need to consider additional insurance options such as health insurance or accident insurance.
Health insurance typically covers medical costs associated with accidents, including car accidents, regardless of who was at fault. However, the interplay between health insurance and other insurance policies, such as car insurance, can vary depending on the specific circumstances and state laws. In some cases, car insurance or other liability insurance may be responsible for covering accident-related medical expenses.
Accident insurance is another option that can provide financial protection in the event of an accident. Accident insurance plans offer benefits such as inpatient rehabilitation, hospital admission, and extended stays. These plans can help cover out-of-pocket costs associated with accidents, including deductibles, copayments, and extra costs for out-of-network care.
Farm Bureau Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can use your life insurance to pay for your hospital bills. Many companies allow you to use your death benefit while you're still alive, which can be helpful if you have outstanding medical bills that your health insurance doesn't cover.
Living benefits are built into many life insurance policies and allow the insured to file a claim against their death benefit and accelerate a portion of it. Simply put, you can use it before you die, but the monthly premium will decrease as a result.
The insured person receives the money from their life insurance policy and can then decide how to spend it. This could include paying off hospital bills, health insurance deductibles, or seeking alternative treatment.
There are two main types of life insurance: term life insurance policies and whole-of-life policies. Term life insurance policies run for a fixed period, such as 5, 10, or 25 years, and only pay out if you die during that period. Whole-of-life policies will pay out regardless of when you die, as long as you keep up with premium payments.
The cost of life insurance depends on various factors, including age, lifestyle, health, family medical history, occupation, and whether you smoke. The older you are and the riskier your lifestyle choices, the more expensive your policy is likely to be.







