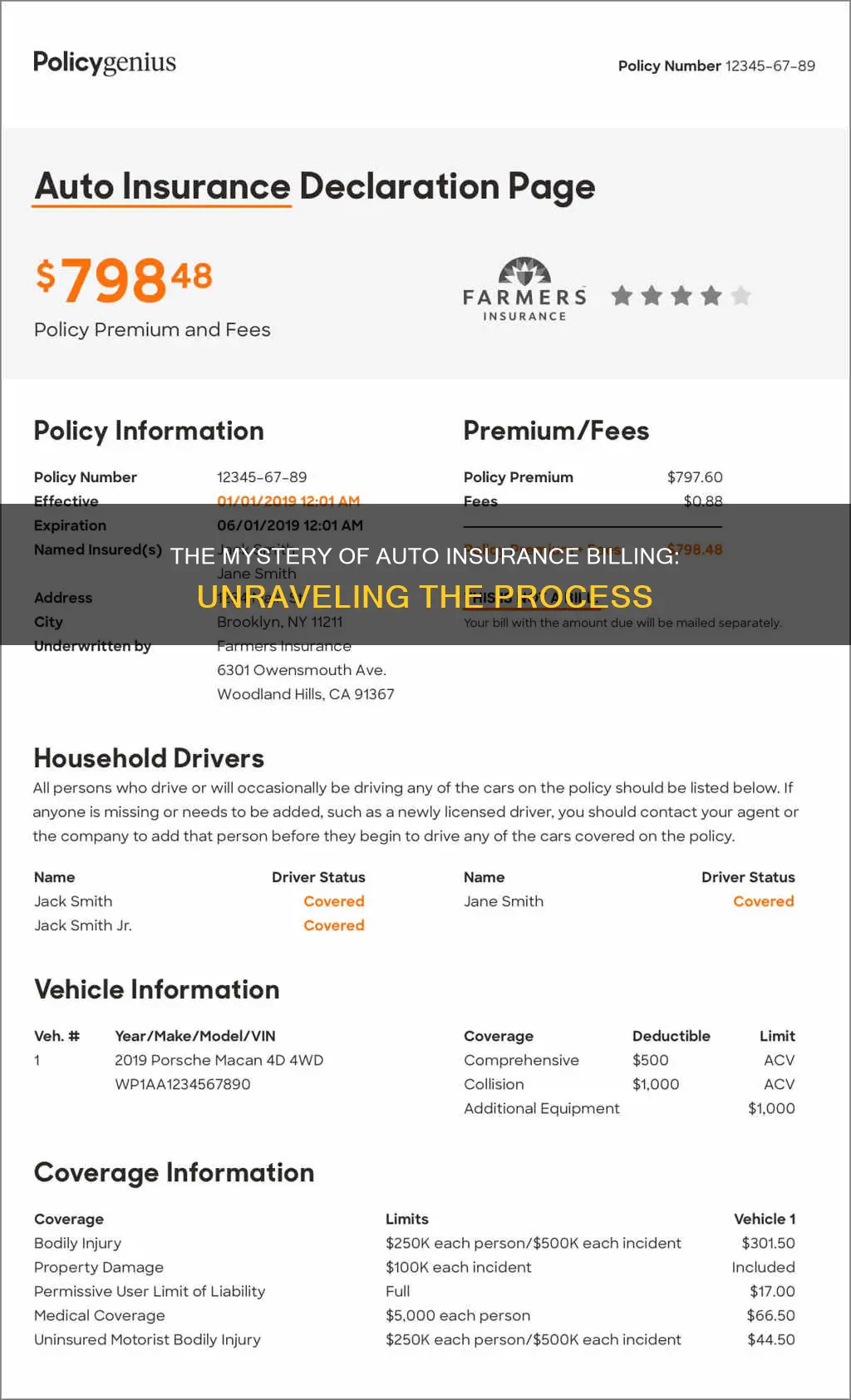
Auto insurance is designed to protect you financially in the event of an accident. It can help pay for vehicle repairs, medical expenses, and damage or injuries you cause to others while driving. The cost of auto insurance depends on various factors, including age, gender, location, driving history, and vehicle type. You can pay your auto insurance premiums upfront for the year or in monthly, quarterly, or semi-annual instalments. Understanding how auto insurance billing works is essential to ensure you have the right coverage and avoid surprises when making a claim.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Financial protection in the event of an accident, theft or other incidents |
| Required? | Yes, in almost every state |
| Coverage | Damage to your vehicle, your medical bills, damage to others, injuries to you and your passengers, protection from uninsured motorists |
| Payment Options | Monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, annually, upfront payment for the year |
| Calculation Factors | Age, gender, marital status, licensing status, driving history, vehicle usage, vehicle type, safety features, credit score, driving location |
| Add-ons | Rental car coverage, gap insurance, roadside assistance coverage |
What You'll Learn

Payment plans and billing frequency
Auto insurance payments are typically made on a regular basis, and there are several payment plans and billing frequencies to choose from. The frequency of payments will depend on the policy and the insurer, and can be made monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. Most auto insurance companies offer flexible payment plans to fit different budgets.
If you pay your premium in full upfront for the entire policy term, you won't have to make another payment until the renewal date. However, if you can't pay in full, you may be able to choose a different payment schedule. With most companies, you can pay monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually. Many companies also offer an automatic payment option where payments are deducted from your account each month.
When a payment is due, you will receive a bill that details the due date and the payment amount. Some companies charge a service fee for sending a paper bill, so you may want to consider going paperless and receiving email notifications instead.
It's important to make your payments on time to avoid cancellation of your coverage. Some insurers offer a grace period, but if the payment is not made within the specified time, your policy may be cancelled or suspended.
Auto Glass Insurance: Are Sensor Repairs Covered?
You may want to see also

Premium calculation
Auto insurance companies set their own rates, which vary depending on several factors. These factors include age, gender, marital status, licensing status, driving history, vehicle usage, driving habits, vehicle type, safety record, safety features, geographical location, and credit score.
- Age, Gender, and Marital Status: Typically, younger drivers below the age of 25 tend to pay higher premiums since they are considered to be more likely to be involved in accidents. Additionally, male drivers tend to pay more than female drivers, especially during their teenage years. Marital status also plays a role, as single drivers are seen as more likely to experience injuries in accidents compared to married drivers.
- Licensing Status and Driving History: A good driving record can lead to lower insurance rates. Conversely, a history of traffic violations, accidents, or a lack of continuous coverage can result in higher premiums.
- Vehicle Usage and Driving Habits: The frequency and purpose of driving can impact premiums. For example, those who work from home and drive less may pay less than those who commute daily.
- Vehicle Type, Safety Record, and Safety Features: The make, model, and variant of a vehicle influence the premium. Cars with high-tech safety features or higher repair costs may have higher insurance rates. Additionally, vehicles with approved anti-theft devices or safety features like airbags, ABS, and EBD may be eligible for discounts on premiums.
- Geographical Location: Urban areas with higher traffic density, crime rates, or natural hazards tend to have higher insurance rates compared to rural locations.
- Credit Score: In states where credit score is a factor, individuals with higher credit scores may receive lower insurance rates, as they are seen as less likely to file claims.
It's important to note that the calculation of insurance premiums is a complex process, and insurance companies use various algorithms and data points to determine the final rates offered to customers.
MassHealth Insurance and Auto Accidents: Understanding Medical Bill Coverage
You may want to see also

Deductibles and limits
When it comes to auto insurance, a deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket on a claim before your insurance covers the rest. For example, if you have a $500 deductible and $3,000 in damage from a covered accident, your insurer will pay $2,500, and you'll be responsible for the remaining $500.
Collision and comprehensive are the two most common car insurance coverages that include deductibles. Collision coverage helps pay for damage to your vehicle if it hits another car or object, or is hit by another car. Comprehensive coverage helps pay for damages that are not caused by a collision, like fire, theft, or weather. You may also have a deductible for personal injury protection or uninsured/underinsured motorist property damage in some states.
The amount of your deductible will influence your insurance rate. A higher deductible means a lower insurance rate, whereas a lower deductible means a higher insurance rate. For example, if you have a $1,000 deductible and $2,000 in covered damages, you're responsible for the first $1,000 of damages, and your insurance company is responsible for the other $1,000.
A limit, on the other hand, is the maximum amount your car insurance can pay out for a claim. Your limit is the maximum your insurance can pay out for a claim. For example, if your auto liability coverage has a $50,000/$100,000 limit on bodily injury for one accident, your insurance will not pay more than $50,000 for one person, and it will not pay more than $100,000 for one accident.
Your car insurance liability coverage limits are the most your insurance will pay to another party if you are legally responsible for an accident. Choosing a higher limit provides you with more protection if an accident occurs. Coverage limits may vary by coverage type and state.
High Auto Insurance Limits: Worth the Cost?
You may want to see also

Coverage types
Auto insurance policies are a combination of several coverage types. Some are mandated by law, while others are optional. Here is a list of some standard car insurance coverage options:
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance covers the cost of medical treatment for injuries and repairs for property damage caused by the policyholder to others. It can also cover legal costs such as attorney fees if the policyholder is sued for damages after an accident. The exact limit requirements vary by state.
Medical Payments or Personal Injury Protection Coverage
Medical payments coverage, sometimes called MedPay, or PIP insurance (PIP), can pay for injuries to the policyholder or their passengers, regardless of who is at fault for the accident. While these are similar, PIP offers more comprehensive coverage, including reimbursement for medical expenses, lost wages, funeral costs, and services to help the injured person complete regular tasks. The availability of MedPay and PIP varies by state.
Underinsured/Uninsured Motorist Coverage
Underinsured or uninsured motorist coverage protects the policyholder if they are in an accident with someone who doesn't have enough or any liability car insurance to cover the injuries or damage to the policyholder's vehicle.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage applies to the policyholder's own vehicle after a crash. It can help pay for the cost of repairs, and if the vehicle is totaled, collision coverage pays the policyholder the actual cash value of the vehicle, minus any deductible.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage protects against damage to the policyholder's car from incidents other than collisions, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. If the vehicle is a total loss, comprehensive coverage pays the policyholder for the value of the vehicle at the time of the incident, minus the deductible.
Additional Coverage Options
In addition to the standard coverage options, auto insurance companies may offer the following additional coverage options:
- Rental reimbursement coverage: Pays for a rental car while the policyholder's vehicle is being repaired after an accident.
- Gap insurance: Covers the difference between what the policyholder's car was worth and how much they still owe on the loan if the car is stolen or totaled.
- Roadside assistance: Provides help if the policyholder is stranded on the side of the road, such as towing services, lockout service, flat tire changes, and fuel delivery.
Gap Insurance: Nissan Lease Protection
You may want to see also

Policy activation
To activate your policy, you must make your first premium payment. This payment serves as "consideration" under contract law, an essential element that validates the agreement. Once this initial payment is made, your coverage begins, and you are protected per the terms of your policy.
It's worth noting that you have the option to pay your premiums in full upfront for the entire policy term. This approach can sometimes result in a discount or the avoidance of installment fees that come with monthly payments. However, if paying in full is not feasible, most auto insurance companies offer flexible payment plans.
With these payment plans, you can typically choose to pay your premiums monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually. Many insurers also provide the convenience of automatic payments directly from your account each month. If you prefer to make manual payments, you will receive a bill in the mail a few weeks before the due date, although this may incur a service charge.
Remember, your policy is not active until you make that initial premium payment. So, if you're shopping for insurance, be sure to select a plan that suits your needs and budget, and don't forget to factor in any additional fees associated with your chosen payment method and schedule.
Auto Insurance Premium: What's Covered?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Auto insurance payments are typically made on a regular basis, and the frequency depends on the policy and the insurer. Some common payment frequencies include monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
Insurance companies offer various payment methods for the convenience of policyholders. Common payment methods include electronic funds transfer (EFT) from your bank account, credit card payments, online payment portals, mailing a check, or paying in person at the insurance company's office.
Yes, many insurance companies offer the option to pay the auto insurance premium in full upfront for the entire policy term. Paying upfront can sometimes provide a discount or save on installment fees that may apply when choosing to pay in installments.
Missing an auto insurance payment can have different consequences depending on the insurance company and policy terms. Some companies may send a reminder or provide a grace period, but if the payment is not made within the specified time, the policy could be canceled or suspended, resulting in a loss of coverage.
In most cases, it is possible to request a change in the auto insurance payment schedule. Insurance companies may allow switching between monthly payments and paying in full upfront, depending on the policy and their terms.







