The cost of car insurance is determined by a variety of factors, including the type of car, the driver's age and gender, their driving record, and where they live. The amount of coverage and the deductible level also influence the premium. Car insurance companies use these factors to calculate the risk of the driver filing an insurance claim. While the price of car insurance can be high, there are ways to reduce costs, such as comparing multiple quotes, bundling policies, and improving one's credit score.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Driving record | The better your record, the lower your premium. Accidents or serious traffic violations will increase your premium. |
| How much you use your car | The more miles you drive, the more chance for accidents, so the more you'll pay. |
| Location | Urban drivers pay a higher price than those in small towns or rural areas due to higher rates of vandalism, theft and accidents. |
| Age | Mature drivers have fewer accidents than less experienced drivers, so insurers charge more if teenagers or young people below age 25 drive your car. |
| Gender | Women tend to get into fewer accidents and have fewer DUIs, so they often pay less than men. |
| The car you drive | The cost of your car is a major factor in the cost to insure it. Other variables include the likelihood of theft, the cost of repairs, engine size and the overall safety record of the car. |
| Credit | Your credit-based insurance score predicts the likelihood of your filing a claim and the likely cost of that claim. |
| Type and amount of coverage | The limits on your basic auto insurance, the amount of your deductible, and the types and amounts of policy options (such as collision) will affect how much you'll pay for coverage. |
| Payment method | Some insurance companies charge a fee for each monthly payment if you do not pay in full for the policy. |
| State | The average cost of car insurance varies between states for reasons such as accident and claim frequency, the cost of labour and vehicle parts, vehicle theft frequency, and road conditions. |
What You'll Learn

How age impacts insurance rates
Age is one of the most important factors in determining your car insurance rate. While there are good drivers in every age group, younger drivers are generally more likely to have accidents or take risks on the road. Experienced drivers are less likely to have accident claims, which means they cost less to insure.
In general, car insurance is most expensive for teens and young adults. This is because, statistically, drivers aged 16 to 19 get into almost three times as many fatal car accidents as any other age group. The cost of auto insurance coverage usually begins to drop by the time a driver reaches their early 20s. By 25, drivers might notice a significant reduction in their premiums.
Insurance rates are typically the lowest for middle-aged drivers. You'll get the best rates in your 50s and early 60s, assuming you have a good driving record. Then, auto insurance rates start to increase again around age 65. As drivers reach their 70s, car insurance rates start to increase again due to risk factors associated with senior drivers, such as vision or hearing loss and slowed response time.
It's worth noting that not all states permit age as a rating factor. For example, Hawaii and Massachusetts ban the use of age as a rating factor, and Michigan only factors in years of driving experience.
Grandchild on Your Auto Insurance
You may want to see also

The effect of gender on insurance costs
Gender is one of the factors that influence the price of auto insurance. While women tend to pay less for car insurance than men, this varies depending on age, location, and individual circumstances.
Gender and Auto Insurance Costs
In most states, gender plays a role in determining auto insurance rates, with males paying significantly more during their teenage and young adult years. However, as drivers get older, the gender gap in insurance rates narrows, and the rates become more similar for men and women. This is because insurance companies base their rates on risk assessment, and younger male drivers are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents, receive tickets, and be arrested for driving under the influence. Other factors considered by insurance companies include driving history, age, vehicle type, and individual credit scores.
The Impact of Gender-Neutral Regulations
It is worth noting that some states and countries have implemented gender-neutral regulations in insurance. In the United States, California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Michigan, Montana, North Carolina, and Pennsylvania ban insurers from using gender as a factor in setting rates. Similarly, since 2012, European Union law has prohibited insurers in member states from considering gender in health, life, and auto insurance premiums. As a result of these regulations, insurance companies adjust their rates based on other factors, which can lead to varying impacts on the premiums paid by men and women.
Factors Affecting Insurance Rates
While gender is a significant factor in insurance rates, other considerations also come into play. Age is a crucial factor, as younger drivers, regardless of gender, typically pay higher insurance rates due to their lack of driving experience and the associated higher risk of accidents. Additionally, factors such as driving history, vehicle type, and individual credit scores can influence insurance rates.
Consumer Perspective on Gender-Based Rates
The use of gender as a factor in insurance rates has been a topic of debate. Individuals, consumer advocates, and politicians often prefer that insurance premiums are based on factors that policyholders can control, such as their behaviour, rather than intrinsic characteristics like gender. On the other hand, insurance companies defend the use of gender as an actuarially sound criterion for establishing premiums.
Home and Auto Insurance: Separate Policies?
You may want to see also

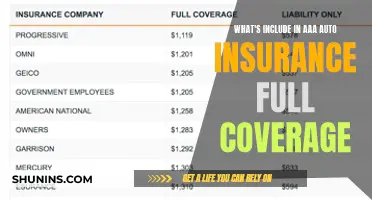
Full coverage vs. minimum coverage
When it comes to auto insurance, there are two main types of coverage to choose from: full coverage and minimum, or liability-only, coverage. Here's a detailed overview of the differences between the two to help you decide which option is best for you.
Minimum Coverage
Minimum coverage, or liability-only insurance, is typically the cheaper option and covers any injuries or damage you cause to other people or their property in the event of an accident. This type of insurance is required by law in most states, and the specific minimum coverage requirements vary by state. For example, some states mandate additional coverage types, such as personal injury protection (PIP) or uninsured motorist coverage. It's important to note that liability-only insurance does not cover damage to your own vehicle or injuries to yourself or your passengers.
Full Coverage
Full coverage insurance includes liability coverage, as required by your state, plus additional coverage for damage to your own vehicle. This typically includes collision coverage, which covers damage to your vehicle caused by collisions with other vehicles or objects, and comprehensive coverage, which covers non-collision incidents such as vandalism, weather damage, or theft. Full coverage is often required by lenders if you lease or finance your vehicle. It may also be required if you're found to be at fault in an accident and need to pay for repairs to your car. While full coverage offers more protection, it comes at a higher cost, with annual premiums averaging $2,329 in the US.
The decision between full coverage and minimum coverage depends on several factors, including your financial situation, the age and value of your vehicle, and your risk tolerance. If you have a loan or lease on your vehicle, full coverage is usually required. For older, paid-off vehicles, minimum coverage may be sufficient, as long as you're comfortable with the financial risk of repairing or replacing your car in the event of an accident. Additionally, consider your state's minimum coverage requirements and whether you want additional protection beyond that. Remember to review your insurance needs regularly, as they may change over time.
Vehicle Insurance Schedule: What's Covered?
You may want to see also

How to lower insurance costs
There are several ways to lower your auto insurance costs. Here are some detailed and direct strategies to help you save money on your car insurance:
Shop Around for Quotes
Before purchasing a car insurance policy, it is advisable to get quotes from multiple insurance companies. Prices can vary significantly between insurers, so obtaining at least three quotes can help you find the most cost-effective option. You can contact companies directly, use the internet, or consult your state insurance department for price comparisons. Additionally, consider the financial health and stability of the insurance company to ensure they can honour your claims.
Compare Insurance Costs Before Buying a Car
The cost of car insurance is influenced by the car's price, repair costs, safety record, and theft risk. Therefore, it is recommended to research insurance costs for different vehicles before making a purchase. This way, you can make an informed decision and choose a car with lower insurance premiums.
Increase Your Deductible
By opting for a higher deductible, you can substantially reduce your insurance costs. A deductible is the amount you pay before your insurance policy coverage begins. For example, increasing your deductible from $200 to $500 can lower your collision and comprehensive coverage costs by 15-30%. However, ensure that you have sufficient funds set aside to cover the higher deductible in case of a claim.
Reduce Coverage on Older Cars
If you own an older car, consider dropping collision and comprehensive coverages. These coverages may not be cost-effective if the value of your car is significantly lower than the premium. Review your insurance coverage periodically to ensure it aligns with your current needs.
Bundle Your Insurance Policies
Many insurance companies offer discounts if you purchase multiple types of insurance from them. You can bundle your homeowners and auto insurance or insure multiple vehicles with the same company to benefit from these discounts. This approach not only saves you money but also simplifies your insurance management.
Maintain a Good Credit Record
Establishing a solid credit history can positively impact your insurance costs. Insurance companies often use credit information to price auto insurance policies, as individuals with good credit tend to have fewer claims. Therefore, paying your bills on time, maintaining low credit balances, and regularly checking your credit report for accuracy can help lower your insurance premiums.
Take Advantage of Discounts
Insurance companies offer various discounts that can reduce your insurance costs. These include low mileage discounts for driving fewer miles per year, group insurance discounts through employers or associations, and safe driving discounts for maintaining a good driving record. Additionally, consider taking a defensive driving course, as some companies offer reductions for completing such programs.
Choose a Cheaper Car to Insure
The type of car you drive can significantly impact your insurance rates. Some vehicles are cheaper to insure due to their safety features, low repair costs, and lower likelihood of being stolen. When purchasing a new car, consider the insurance costs associated with different makes and models to find a more affordable option.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively lower your auto insurance costs and save money while still ensuring you have the necessary coverage.
Grand Theft Auto: Understanding Insurance Coverage
You may want to see also

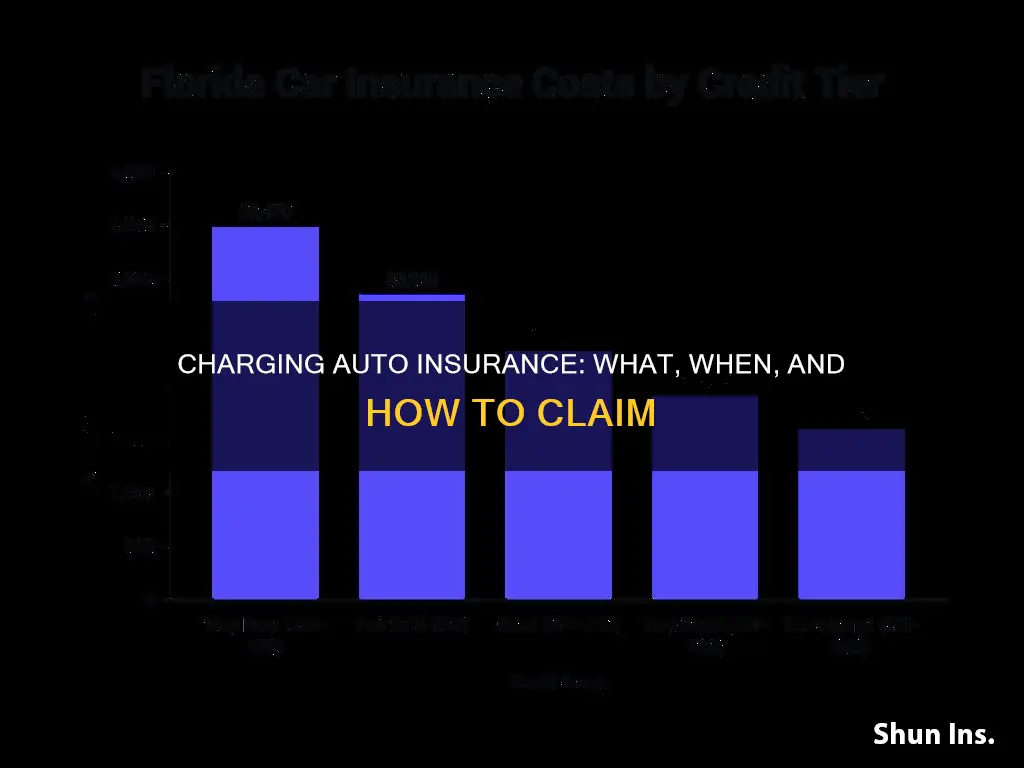
How credit scores affect insurance premiums
Credit scores can have a significant impact on insurance premiums, with higher credit scores often leading to lower insurance rates. This is because insurance companies use credit scores to assess the risk of doing business with a particular customer. A higher credit score indicates that a person is more likely to pay their bills on time and maintain their assets, reducing the likelihood of filing insurance claims.
In the context of auto insurance, a poor credit score can lead to substantially higher insurance rates. According to Forbes Advisor, an analysis of car insurance rates in 46 states that consider credit scores revealed an average rate increase of 76% for individuals with poor credit. This translates to an additional cost of nearly $1,180 per year. The impact of a poor credit score on auto insurance rates can be even more significant than that of a speeding ticket, an at-fault accident, or a DUI.
It is worth noting that the use of credit scores in insurance pricing is controversial. Critics argue that it is fundamentally discriminatory and disproportionately affects low-income individuals, even those with clean driving records. However, insurance companies defend their practice by citing research that finds a correlation between credit scores and the likelihood of filing insurance claims.
While the impact of credit scores on insurance premiums varies across states, it is important to note that some states have banned the use of credit scores in setting insurance rates. For example, California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan prohibit using credit scores to determine auto insurance rates. In these states, insurance companies base their rates on factors such as driving records, location, and other characteristics.
To improve their credit scores, individuals can take several steps, including paying their bills on time, reducing credit card debt, and regularly checking their credit report for accuracy. By improving their credit score, individuals can not only reduce their insurance premiums but also improve their overall financial health and credibility.
Progressive Auto Insurance: Understanding the Auto-Renewal Process
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The type of car you drive has a significant impact on your insurance rate. The price and availability of parts, the cost of labour, the statistical likelihood of accidents, the amount of damage your vehicle could inflict on another car in a collision, and the vehicle's safety and crash prevention features could all influence how much you pay for coverage.
In most states, your age significantly impacts how much you pay for coverage. Younger drivers tend to pay more for auto insurance compared to older drivers, as they are statistically more likely to be involved in an accident and engage in distracted driving.
In most states, women tend to pay lower premiums than men. This is because men generally engage in riskier driving behaviour and have a higher rate of accident severity.
The average cost of car insurance varies between states for many reasons, such as accident and claim frequency, the cost of labour and vehicle parts, vehicle theft frequency, and road conditions.
In most states, companies may legally use credit-based insurance scores when setting your rates. If your credit score is below average, you could pay more for your car insurance policy.