Understanding your vehicle insurance policy is an important skill for all drivers to have. While the legal jargon can be confusing, it's essential to know what your policy covers and what it doesn't, so you're not caught off guard in the event of an accident or incident.
Your auto insurance policy documents will outline the agreement between you and your insurer, detailing what you're covered for, what your insurer is obligated to do, and any limitations or exclusions. It's crucial to review this information periodically to ensure you have adequate coverage and to avoid costly surprises later on.
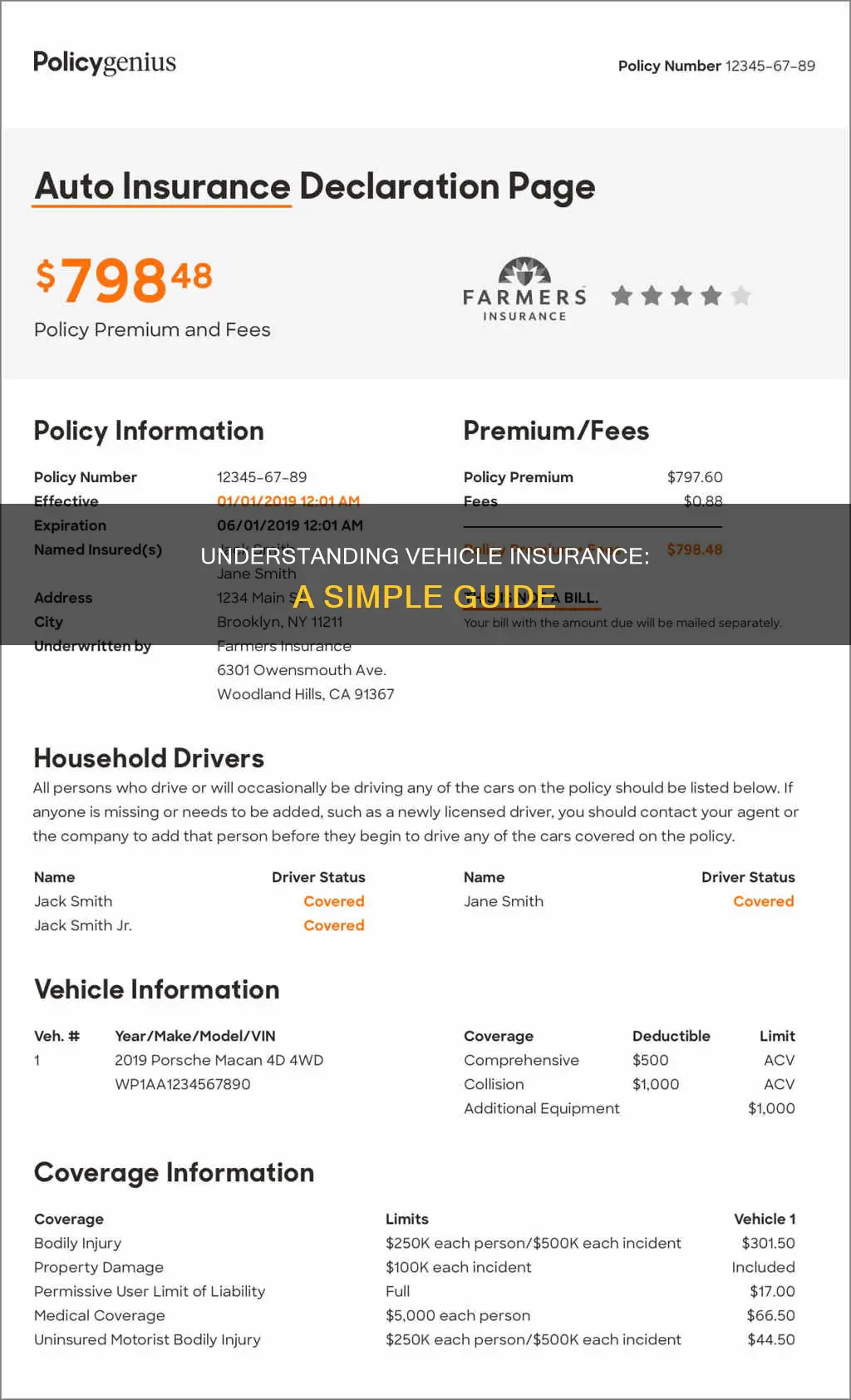
- Declarations Page: This is usually the first page, providing a summary of your coverages, limits of liability, premiums, deductibles, and personal information.
- Insurance Agreement: This section outlines the terms, conditions, and exclusions of your coverage.
- Definitions: This part clarifies any key terms used in the policy.
- Coverage Sections: These sections go into detail about the specific types of coverage you've selected, such as liability, collision, comprehensive, etc.
- Exclusions: This list outlines any situations or circumstances that are not covered by your policy.
- Endorsements: This outlines any optional add-ons or endorsements to your policy.
- Cancellation Terms: This explains the conditions under which your policy can be cancelled by you or the insurance company.
- Contact Information: Provides details on how to reach your agent and the insurance company for claims or assistance.
By understanding these components, you'll have a better grasp of your vehicle insurance policy and can make more informed decisions about your coverage needs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Financial protection in the event of an accident |
| Coverage | Damage to your vehicle, financial liability, medical expenses, theft, vandalism, windshield and glass damage, fire damage, flood damage, etc. |
| Policy Documents | Declarations page, insurance agreement, definitions, coverage sections, exclusions, endorsements, cancellation terms, contact information |
| Types | Liability, collision, comprehensive, uninsured/underinsured motorist, medical payments, personal injury protection (PIP), etc. |
| Premium | Amount paid for coverage, usually monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually |
| Deductible | Out-of-pocket expense before insurance payout; higher deductibles lead to higher rates |
| Limit | Maximum amount insurance will pay out per claim |
| Claim Filing | Directions on how to file a claim |
| Common Factors Affecting Premium | Vehicle type, annual mileage, driving record, location, age, sex, credit history, marital status, coverage and deductible choices, prior claims, insurance history, vehicle usage |
What You'll Learn

Understanding the declarations page
The declarations page is a summary of your auto insurance policy, usually the first page or pages of your insurance documents. It provides a concise summary of vital policy information, including:
- Policy number, period, and dates of coverage
- Insured drivers
- Covered vehicles, including make, model, year, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- Types of coverage, including their limits and deductibles
- Premium, including a breakdown of costs for each coverage type and vehicle
- Discounts
- Agency and company information
- Financial institution information
The declarations page is an important document that allows you to understand your policy at a glance. It is not, however, proof of insurance, and you should keep a physical or digital insurance card in your vehicle to show to law enforcement if you are pulled over.
Switching Auto Insurance: A Quick Guide
You may want to see also

Understanding key terms and definitions
Understanding the key terms and definitions in your vehicle insurance policy is crucial to knowing what you are and aren't covered for. Here are some of the most important terms and definitions to help you understand your policy:
Declarations Page: This is usually the first page of your policy document, summarising your coverages, limits of liability, premiums and deductibles. It will also include personal information, such as your name and address, and details of the insured vehicle(s), including their Vehicle Identification Numbers (VIN).
Insurance Agreement: This outlines what you and your insurer have agreed to regarding coverage. It includes the terms, conditions and exclusions of the policy.
Definitions: This section defines any key terms used in the policy. Defined words are often bolded, and it's important to refer back to this section to understand who and what is covered. For example, the definition of "family member" or "insured driver" can vary between policies, and it's important to know if your policy is restrictive or broad in this regard.
Covered Autos: Some policies may not cover damage to "substitute vehicles", such as rental or loaner cars.
Actual Cash Value (ACV): In the event of a total loss, collision and comprehensive policies usually pay out the actual cash value of the vehicle, which is the market value at the time of the loss. This amount may be less than what is owed on the vehicle, especially if it is newer, as new cars depreciate quickly.
After-Market Parts: These are parts made by a company other than the vehicle manufacturer. You may need to add an endorsement to your policy to ensure only Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts are used for repairs.
Exclusions: This section lists any situations or circumstances not covered by your policy. Common exclusions include intentional damage, normal wear and tear, accidents caused while performing illegal activity, and personal property not permanently attached to the vehicle.
Endorsements: This outlines any optional endorsements or add-ons you've chosen to include in your policy, such as roadside assistance, rental car reimbursement or accident forgiveness.
Premium: The amount you pay for your coverage, which can be paid monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually.
Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible typically results in lower rates, but you will pay more out-of-pocket if a claim occurs.
Coverage Amounts: How much your insurance will pay out per accident or claim.
Liability Coverage: This is required in most states and covers injuries, property damage, and lawsuits if you are found at fault in an accident. It includes bodily injury liability, which covers medical bills and other costs associated with injuries or death, and property damage liability, which reimburses others for damage to their vehicle or other property.
Collision Coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object, regardless of fault. It may also cover damage from potholes or rolling your car.
Comprehensive Coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle from incidents other than collisions, such as fire, flood, vandalism, hail, falling objects, earthquakes, windstorms, and animal contact. It also typically includes glass coverage for windshield damage.
Medical Payments or Personal Injury Protection (PIP): This covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, and sometimes lost wages and other related costs. PIP is broader and is required in no-fault states, covering expenses regardless of who is at fault.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage: This covers your injuries and vehicle damage if you are hit by a driver who is uninsured or doesn't have adequate coverage.
Labor Fees: Insurance Vehicle Repairs
You may want to see also

Understanding liability insurance
Bodily Injury (BI) Liability covers the medical bills for those injured during an accident, loss of income resulting from injuries, and costs associated with pain and suffering. This type of coverage also includes injuries and death that another driver causes while driving your car. Most states require drivers to carry a minimum amount of BI liability coverage, with specific amounts varying from state to state.
Property Damage (PD) Liability covers the costs to repair or replace items damaged in an accident, including damage to other vehicles and other types of property, such as homes, fencing, and storefronts. This coverage also includes damage caused by another driver operating your car. Like BI liability, most states require PD liability coverage, with specific minimum amounts that vary across states.
It is important to note that liability insurance does not cover damage to your own vehicle or injuries sustained by you or your passengers. Additionally, expenses that exceed your policy liability limit are typically not covered by liability insurance. To ensure you have adequate coverage, it is recommended to consider your state's minimum requirements, the value of your personal assets, and your ability to meet financial responsibilities after an accident.
To determine the specific liability insurance requirements and recommendations for your state, it is best to contact your state's Department of Motor Vehicles or Department of Insurance. Consulting with a qualified insurance agent or broker can also help you understand the amount and types of coverage that are right for your needs and budget.
Insurance: Transporting Vehicles
You may want to see also

Understanding comprehensive insurance
Comprehensive insurance is a type of vehicle insurance that covers damage to your car from causes other than a collision. It is optional and is sometimes referred to as "other than collision" coverage. It is not required by law in any state, but it is usually required by lenders if you are leasing or financing your vehicle. If you own your vehicle outright, you can decide whether to take out comprehensive coverage.
Comprehensive insurance covers damage to your vehicle caused by events outside of your control, such as:
- Theft
- Vandalism
- Glass and windshield damage
- Fire
- Accidents with animals
- Weather and natural disasters
- Explosions
- Falling trees, rocks, and other objects
Comprehensive insurance does not cover damage to other vehicles or people. It also does not cover damage caused by a collision with another vehicle or object, which is covered by collision insurance.
The cost of comprehensive insurance will depend on various factors, such as the state you live in, the value of your vehicle, and your driving record. The average cost ranges from approximately $134 per year to nearly double that. You can lower your premiums by raising your deductible.
Shop Smart: Vehicle Insurance Tips
You may want to see also

Understanding collision insurance
Collision insurance is a type of auto insurance that covers damage to your vehicle in the event of a collision with another vehicle or object. It is important to note that collision insurance only reimburses the insured for damage to their own vehicle and not for damage to other vehicles or objects, or for any bodily injuries sustained in the accident. This type of insurance is particularly useful if you are unable to pay for repairs or a replacement car in the event of a crash.
Collision insurance can cover a wide range of accident types, including accidents involving only your car (such as rolling over), accidents with another object (such as a telephone pole or a tree), and accidents with another vehicle (such as a traffic crash). It is important to note that collision insurance does not cover damage caused by theft, vandalism, or natural disasters, as these are typically covered by comprehensive insurance. Comprehensive insurance covers damage to your vehicle caused by non-collision-related events such as theft, vandalism, or hail.
In most cases, collision insurance is not required by law, but it may be required by your lender or leasing company if you are financing or leasing your car. Even if you own your vehicle outright, collision insurance can provide peace of mind and protect your investment, especially when paired with liability and comprehensive coverages. If you are a new or inexperienced driver, collision insurance can provide valuable protection in the event of an accident.
When considering collision insurance, it is important to weigh the costs and benefits. Collision coverage can be expensive, and you may want to choose a higher deductible to lower your premium. Additionally, the value of your car may also be a factor in your decision, as collision insurance will only pay out up to the current market value of your car, minus your collision deductible.
In summary, collision insurance is a valuable form of protection that can help cover the costs of repairing or replacing your vehicle in the event of a collision. It is important to understand the limitations of collision insurance and to consider combining it with comprehensive coverage for more comprehensive protection.
Vehicle Insurance: What's Covered?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The declarations page is the first page of your policy document and includes a summary of your coverages, limits of liability, premiums and deductibles. It is important because it outlines what your insurance policy covers and what it doesn't.
Liability insurance covers the injuries and damage you cause to others. It is required in most states and will protect you financially if you cause an accident.
Collision coverage pays for any damage to your car resulting from a collision with another car or object, regardless of whether you are at fault. Comprehensive coverage, on the other hand, covers damage to your vehicle that is caused by something other than a collision, such as fire, theft, vandalism or natural disasters.







