The cost of car insurance varies significantly from state to state. The national average cost of car insurance is $2,118 per year, but prices can range from as little as $1,021 in Idaho to as much as $4,769 in New York. The state in which you live is an important factor in determining how much you'll pay for car insurance. Differences among states affect car insurance costs based on what auto insurance is required, how much repairs cost, and more.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| States with the most expensive car insurance | New York, Florida, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, and Maryland |
| States with the cheapest car insurance | Idaho, Vermont, Ohio, Maine, and Iowa |
| States with the most expensive full-coverage car insurance | Louisiana, Florida, California, Colorado, and South Dakota |
| States with the cheapest full-coverage car insurance | Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Ohio, and Idaho |
| States with the most expensive liability-only car insurance | Florida, Louisiana, Nevada, Delaware, and South Dakota |
| States with the cheapest liability-only car insurance | Iowa, Vermont, Wyoming, South Dakota, and Nebraska |
What You'll Learn

No-fault states vs. tort states
No-fault states and tort states have different ways of handling insurance claims after a car accident. In no-fault states, drivers are required to first file a claim with their own insurance company to cover any medical expenses after an accident, regardless of who caused the crash. This is the case even if the driver was not at fault. In these states, drivers are also normally required to carry personal injury protection (PIP) insurance to help cover medical costs.
In at-fault, or tort, states, the driver who is deemed responsible for the accident (or their insurance company) is responsible for compensating the other driver for their losses, including bodily injury and property damage. The not-at-fault driver is not required to file a claim with their own insurance company.
There are 12 no-fault states: Florida, Hawaii, Kansas, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, and Utah. Three of these states (Kentucky, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania) have mixed systems, allowing drivers to choose between a no-fault policy and a standard tort policy.
One of the main differences between no-fault and tort states is the ability to sue the at-fault driver. In no-fault states, there are specified limits on when a driver can sue, whereas in tort states, the injured party can sue the negligent driver for economic and non-economic damages, such as pain and suffering.
Another difference is the cost of insurance. In general, car insurance is more expensive in no-fault states because drivers are required to purchase additional coverage, such as PIP. However, insurance premiums in no-fault states are expected to be lower due to reduced court loads and efficient payment of claims.
Canceling Oklahoma Auto Insurance: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Population density
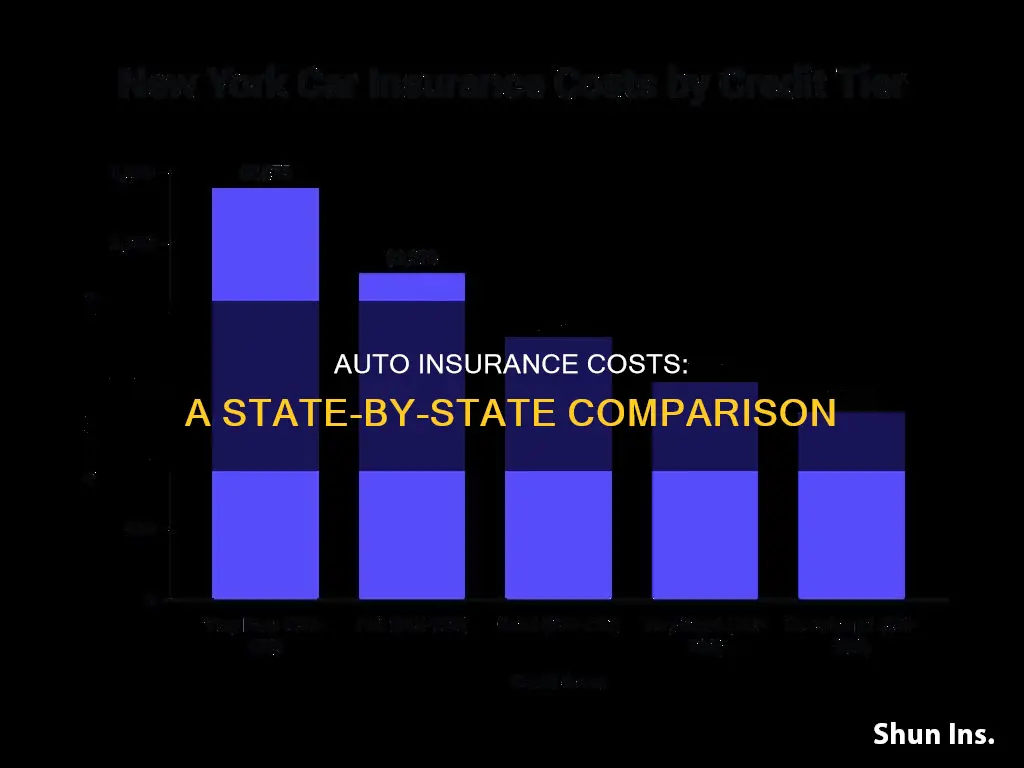
The impact of population density on auto insurance rates is particularly evident when comparing states with large cities to those with more rural areas. For example, Connecticut, a mostly urban state, has an average full coverage cost of $1,730 per year, while Iowa, a predominantly rural state, has an average annual full coverage cost of $1,238. Similarly, New York, a highly urbanized state, has the highest auto insurance premiums in the country, with an average annual cost of $4,769. In contrast, Idaho, a sparsely populated state, has one of the lowest average annual premiums at $1,021.
In addition to the state's overall population density, insurers also consider the specific city and ZIP code when determining rates. For instance, within New York, car insurance rates in New York City are even higher than in the rest of the state, with an average premium of $3,180 per year. On the other hand, less populated states like Idaho and North Dakota tend to have lower auto insurance rates.
Insurance Rates for Paid-Off Vehicles
You may want to see also

Weather conditions
Additionally, winter weather conditions can also impact insurance rates. States in the central U.S., like South Dakota, may face higher premiums due to hail damage. At the same time, northern states, including Minnesota and Wisconsin, could see increased rates due to the effects of winter weather on roads and vehicles.
The frequency and severity of weather events in a particular state influence insurance rates. For example, Florida and Louisiana, being in "hurricane alley", consistently face high winds, flooding, and property damage, leading to substantial insurance claims and increased premiums.
Furthermore, weather patterns can affect the cost of car repairs and replacements. States with higher costs for car repairs or replacements due to weather-related damages may have higher insurance rates. This is because insurance companies factor in the potential costs of paying out claims for weather-damaged vehicles when setting their rates.
In summary, weather conditions are a critical factor in determining auto insurance rates across states. States with a higher frequency of severe weather events, higher repair costs, and more weather-related claims tend to have more expensive insurance premiums. Conversely, states with milder climates and lower repair costs often benefit from lower insurance rates due to reduced weather-related impacts.
General Auto Insurance: Good or Bad?
You may want to see also

State laws and requirements
The state laws and requirements for auto insurance vary across the United States. While some states require drivers to have auto insurance, others mandate only a proof of financial responsibility.
Mandatory Auto Insurance
Almost all states require drivers to have some level of auto insurance. The states that do not require auto insurance are:
- New Hampshire
- Virginia
However, even in these states, drivers are required to show financial responsibility in some other way, such as with a surety bond, a cash deposit with the state, or a certificate of self-insurance.
Minimum Coverage
Each state has its own minimum requirements for auto insurance. These requirements usually include liability insurance, which covers bodily injury and property damage caused to others in an accident. Some states also require additional coverages, such as uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, personal injury protection, or medical payments.
The minimum liability limits are typically expressed as three numbers, such as 25/50/25, which correspond to the following:
- $25,000 of bodily injury liability per person
- $50,000 of bodily injury liability per accident
- $25,000 of property damage liability per accident
No-Fault States
Some states are considered no-fault states, which means that each party must first file a claim with their own insurance company after an accident, regardless of who was at fault. These states typically require drivers to carry personal injury protection (PIP) coverage to help cover medical costs.
Tort States
Most states are tort states, which means that the at-fault driver is responsible for paying for the damages and injuries caused in an accident. In these states, the injured party can file a claim with the at-fault driver's insurance company or sue the at-fault driver for compensation.
Auto Insurance in Michigan: How Much?
You may want to see also

Insurance claims
The cost of auto insurance varies widely across the US, with drivers in Louisiana and Florida paying the most for car insurance nationwide, and drivers in Maine and New Hampshire paying the least.
When it comes to making an insurance claim, there are a few things to keep in mind. Firstly, it's important to understand what a car insurance claim is and when to file one. A car insurance claim is a request for financial compensation that a driver files with an insurance company after their vehicle has been damaged or they have been injured in a car accident. It's generally recommended to file a car insurance claim if there has been an accident or injury involving another party as soon as possible. However, if the damage is minor and no one else is involved, you may not need to file a claim as the cost of repair may be less than your deductible.
- Contact your insurance company: Report the accident to your insurance company as soon as possible and provide them with information such as the location and time of the accident, the names and contact information of those involved, and any documentation related to the accident.
- File a police report: Your insurance company will request a police report number, so be sure to file a report with the local police, even if you didn't do so at the scene of the accident.
- Wait for an adjuster: The insurance company will assign an adjuster to your claim, who will gather information about the accident and inspect the damage to your vehicle.
- Get a report from the insurance adjuster: The adjuster will provide an initial estimate of the cost of repairs, which your insurance company will take into account when determining how much they will pay.
- Fix your vehicle: Once your claim is approved and you receive a payout, choose an auto shop to fix your vehicle. Your insurance company may have a list of preferred shops, but you are not required to use them.
It's important to note that filing a car insurance claim can result in an increase in your premium of between 3% and 32% on average for three to five years. This increase depends on several factors, including the type and amount of the claim, your insurance company, your claims history, and your location.
Old Vehicle, New Insurance: Geico Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The cost of car insurance is determined by a wide range of variables, including your driving record, deductible, credit history, age, marital status, location, state insurance minimums, gender, and vehicle type.
New York has the highest car insurance rates, with an average annual cost of $8,232 for full coverage and $2,490 for minimum coverage.
Maine has the lowest car insurance rates, with an average annual cost of $1,460 for full coverage.
The states with the highest car insurance rates after New York are Louisiana, Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Nevada.
The states with the lowest car insurance rates after Maine are Vermont, Hawaii, Idaho, and Ohio.







