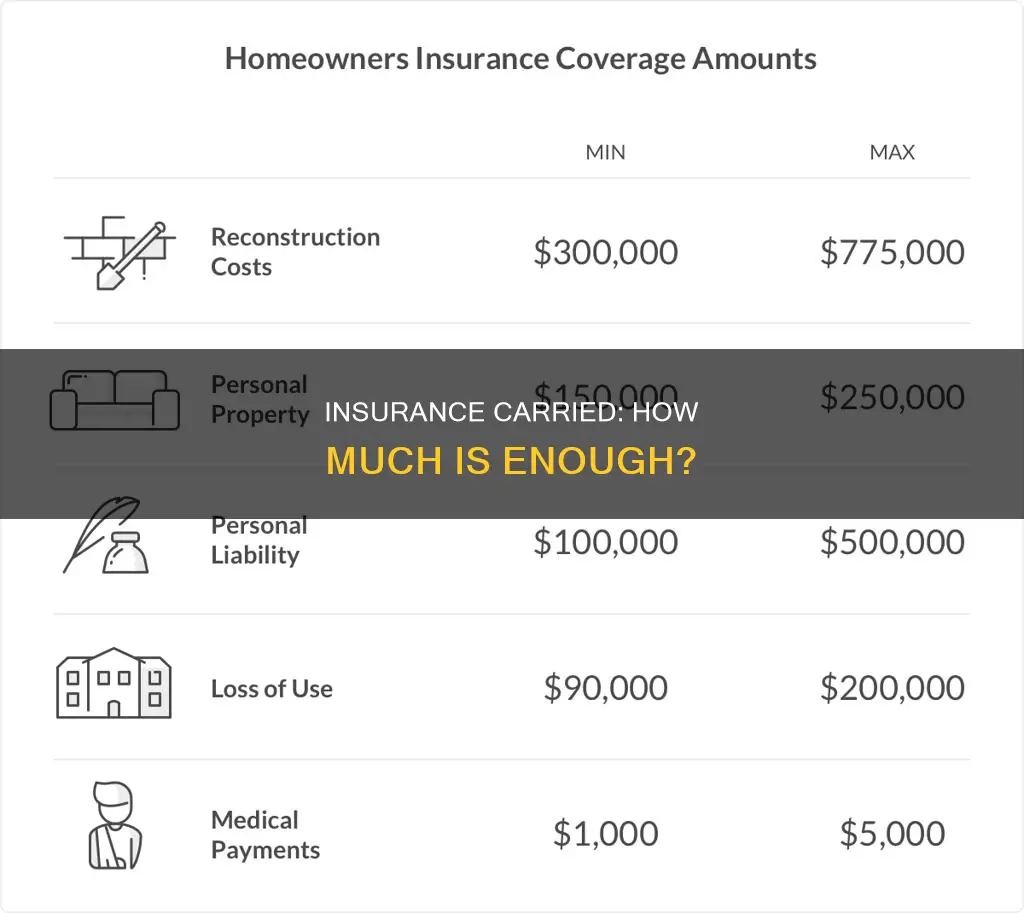
The amount of insurance is the sum of money that an insurance company agrees to provide coverage for, in relation to a specific policy. For instance, if a homeowner's insurance policy has a limit of $300,000, then the amount of insurance for this policy is $300,000. The policyholder is responsible for any losses that exceed this limit. The amount of insurance is influenced by factors such as the type of policy, individual circumstances, and the level of risk.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | The amount of money an insurance company is willing to provide financial coverage for a specific policy |
| Example | If a homeowner's insurance policy has a limit of $300,000, the amount of insurance for this policy is $300,000 |
| Responsibility | The policyholder is responsible for losses over the limit |
| Cost | Policies with a higher amount of insurance tend to cost more |
| Coverage | Policies with a higher amount of insurance tend to provide more coverage |
| Coinsurance | A clause in insurance contracts that ensures policyholders insure their property to an appropriate value |
| Coinsurance Requirement | Most coinsurance clauses require policyholders to insure to 80%, 90%, or 100% of a property's actual value |
| Home Insurance | Insureds are typically required to have coverage of at least 80% of the value of their home |
What You'll Learn
- The amount of insurance coverage is determined by the insurance company
- The amount of insurance is the maximum amount the insurance company will pay
- Insurance policies with higher coverage cost more
- The amount of insurance depends on individual circumstances
- The amount of insurance carried is linked to the risk retained by the insurer

The amount of insurance coverage is determined by the insurance company
The amount of insurance coverage is the sum of money that an insurance company agrees to provide financial coverage for, in relation to a specific policy. For instance, if your homeowner's insurance policy has a limit of $300,000, then the amount of insurance coverage for this policy is $300,000. Any costs that exceed this limit are the responsibility of the insured.
The amount of insurance coverage offered by a company is determined by the insurance provider and is influenced by several factors. For example, in the context of auto insurance, the amount of coverage will depend on the insured's driving record, the type of vehicle, and the level of risk associated with the driver's profile. Those with a history of accidents or speeding tickets may find it challenging to obtain a standard insurance policy and may need to explore alternative options like the California Automobile Assigned Risk Plan (CAARP).
Additionally, insurance companies typically offer policies with varying levels of coverage, allowing customers to choose the option that best suits their needs and budget. While policies with higher coverage amounts tend to be more expensive, they also provide more comprehensive protection for the policyholder. It is essential for individuals to carefully consider their circumstances and select an appropriate level of coverage. For instance, someone who drives frequently or believes they are accident-prone may opt for a higher amount of auto insurance coverage.
In the case of homeowner's insurance, most insurance companies adhere to the 80% rule, which states that the insurer will only cover the cost of damage if the homeowner has purchased insurance coverage equal to at least 80% of the house's total replacement value. If the coverage is less than this threshold, the insurance company will only reimburse a proportionate amount based on the minimum coverage that should have been purchased. This rule ensures that policyholders insure their property for an appropriate value, and it also guarantees a fair premium for the insurer given the level of risk they are assuming.
Uninsured: A Growing Concern
You may want to see also

The amount of insurance is the maximum amount the insurance company will pay
The amount of insurance is the maximum amount an insurance company will pay out for a specific policy. For example, if your homeowner's insurance policy has a limit of $300,000, the amount of insurance you have for this policy is $300,000. This means you are responsible for any losses that exceed this limit.
The amount of insurance is also referred to as the limit or coverage. It is the maximum financial coverage provided by an insurance company for a specific policy. The specific amount of insurance that a person needs depends on their individual circumstances. For instance, many people will purchase the state minimum amount of auto insurance, while others may choose a policy with a higher amount of insurance if they drive frequently or believe they are more accident-prone.
In the context of home insurance, most insurance companies adhere to the 80% rule. According to this rule, an insurer will only cover the cost of damage to a house or property if the homeowner has purchased insurance coverage equal to at least 80% of the house's total replacement value. If the coverage is less than 80% of the replacement value, the insurance company will pay a proportionate amount, as determined by the coinsurance formula.
The coinsurance formula calculates the reimbursement amount when a homeowner has failed to maintain coverage of at least 80% of the home's replacement value. In this case, the homeowner becomes a "co-insurer" and will share the loss with the insurance company according to the formula. The formula is relatively simple: the actual amount of coverage is divided by the amount that should have been carried (80% of the replacement value), and this value is then multiplied by the amount of the loss to determine the reimbursement amount.
ADP: Insurance Carrier or Not?
You may want to see also

Insurance policies with higher coverage cost more
The amount of insurance carried is the level of coverage or protection provided by an insurance policy. Insurance policies with higher coverage tend to cost more. This is because higher coverage means the insurance company will have to pay out more in the event of a claim.
Insurance companies determine the cost of insurance policies, or premiums, based on the level of risk they will need to cover. The higher the coverage, the higher the risk for the insurance company. For example, in the case of auto insurance, young male drivers are often deemed to be a higher risk than middle-aged married men with years of driving experience. As a result, insurance companies will charge higher premiums to young male drivers to offset the increased possibility of having to pay out money towards a claim. Similarly, drivers with a history of accidents or serious traffic violations may pay higher premiums as they are considered more likely to be involved in an accident and file a claim.
The same principle applies to other types of insurance, such as life insurance and homeowner's insurance. For life insurance, younger people tend to pay lower premiums since they are less likely to die than older people. Health is also a factor, as individuals in good health are considered lower risk and therefore pay lower premiums. For homeowner's insurance, the cost of premiums depends on factors such as the value of the home, the location, and the coverage amounts. Homes located in areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes or tornadoes, will typically have higher insurance premiums due to the increased risk of damage.
In addition to the level of coverage, insurance costs can also be influenced by factors such as the insured's age, gender, health status, driving record, location, and claims history. It is important to note that insurance companies use the underwriting process to evaluate and determine the level of risk for each individual or entity, which then sets the premium amount.
Insurance: When to Keep, When to Skip
You may want to see also

The amount of insurance depends on individual circumstances
The amount of insurance carried depends on individual circumstances. The core components of an insurance policy are the premium, deductible, and policy limits. The premium is the price of the policy, typically paid monthly. Insurers take multiple factors into account when setting a premium, such as the policyholder's history of claims, age, location, creditworthiness, and other factors that may vary by state.
The policy limit is the maximum amount an insurer will pay for a covered loss under a policy. Typically, higher limits carry higher premiums. The deductible is a specific amount the policyholder must pay out of pocket before the insurer pays a claim. For example, a $1,000 deductible means the policyholder pays the first $1,000 toward any claims. If their car's damage totals $2,000, they pay the first $1,000, and their insurer pays the remaining $1,000.
The amount of insurance carried can vary depending on the type of insurance. Here are some examples:
- Health insurance premiums are determined by factors such as age, sex, location, health status, and coverage levels. If you have chronic health issues, consider a policy with a lower deductible, as this will provide more affordable access to medical care throughout the year.
- Home insurance premiums are determined by factors such as the value of the home, personal belongings, location, claims history, and coverage amounts.
- Life insurance premiums are determined by factors such as age, sex, tobacco use, health, and amount of coverage.
- Auto insurance premiums are determined by factors such as the policyholder's history of property and auto claims, age, location, creditworthiness, and other factors.
It's important to note that different insurers may charge different premiums for similar policies, so it's worth shopping around to find the best price for your individual circumstances.
Hennessy Insurance: What Coverages Do They Offer?
You may want to see also

The amount of insurance carried is linked to the risk retained by the insurer
Insurers are legally required to maintain sufficient reserves to pay all potential claims from issued policies. Reinsurance allows insurers to underwrite policies covering a larger quantity or volume of risk without excessively raising administrative costs to cover their solvency margins. It also makes substantial liquid assets available to insurers in the event of exceptional losses.
There are two basic categories of reinsurance: treaty and facultative. Treaty reinsurance covers broad groups of policies, like all a primary insurer's auto business. Facultative reinsurance covers specific individuals or high-value or hazardous risks, such as a hospital, that wouldn't be acceptable under a treaty.
In the case of proportional reinsurance, the reinsurer receives a prorated share of all policy premiums sold by the insurer. For a claim, the reinsurer bears a portion of the losses based on a pre-negotiated percentage. The reinsurer also reimburses the insurer for processing, business acquisition, and writing costs. With non-proportional reinsurance, the reinsurer is liable if the insurer's losses exceed a specified amount, known as the priority or retention limit.
The amount of insurance carried is also linked to the risk retained by the insurer in the case of coinsurance. Coinsurance is a clause used in insurance contracts by insurance companies on property insurance policies. It ensures policyholders insure their property to an appropriate value and that the insurer receives a fair premium for the risk. Most coinsurance clauses require policyholders to insure their property for 80%, 90%, or 100% of its actual value. If a property owner insures their property for less than the amount required by the coinsurance clause, they become a "co-insurer" and will share the loss with the insurance company according to the coinsurance formula.
Vision Insurance: Cataract Care Covered?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The amount of insurance is the sum of money an insurance company agrees to provide financial coverage for, in relation to a specific policy. For example, if your homeowner's insurance policy has a limit of $300,000, then the amount of insurance for this policy is $300,000.
Insurance policies with a higher amount of coverage tend to be more expensive. However, they also offer more protection in the event of a claim.
The amount of insurance coverage you need depends on your personal circumstances. Many people opt for the state minimum amount of auto insurance, but those who drive frequently or consider themselves accident-prone may prefer a higher level of coverage.
Most insurance companies follow the 80% rule, which states that they will only cover the full cost of damage to a house if the homeowner has purchased insurance coverage equal to at least 80% of the house's total replacement value. If the coverage is less than 80%, the insurance company will only reimburse a proportionate amount.
Coinsurance is a clause used in property insurance policies, which ensures policyholders insure their property for an appropriate value, and the insurer receives a fair premium for the risk. Coinsurance is usually expressed as a percentage, often 80%, 90%, or 100% of the property's actual value. If a property owner insures their property for less than the amount required by the coinsurance clause, they become a "co-insurer" and will share the loss with the insurance company according to the coinsurance formula.







