A collateral agreement in life insurance is a legal contract that serves as a secondary agreement to the primary life insurance policy. It is an additional layer of protection for both the policyholder and the insurer, providing specific terms and conditions that can be enforced in the event of a dispute. This agreement often includes provisions related to the policy's terms, such as premium payments, policy changes, and the rights and obligations of both parties. Understanding the collateral agreement is crucial for policyholders to ensure they are aware of their rights and the insurer's responsibilities, offering a more comprehensive and secure insurance experience.
What You'll Learn
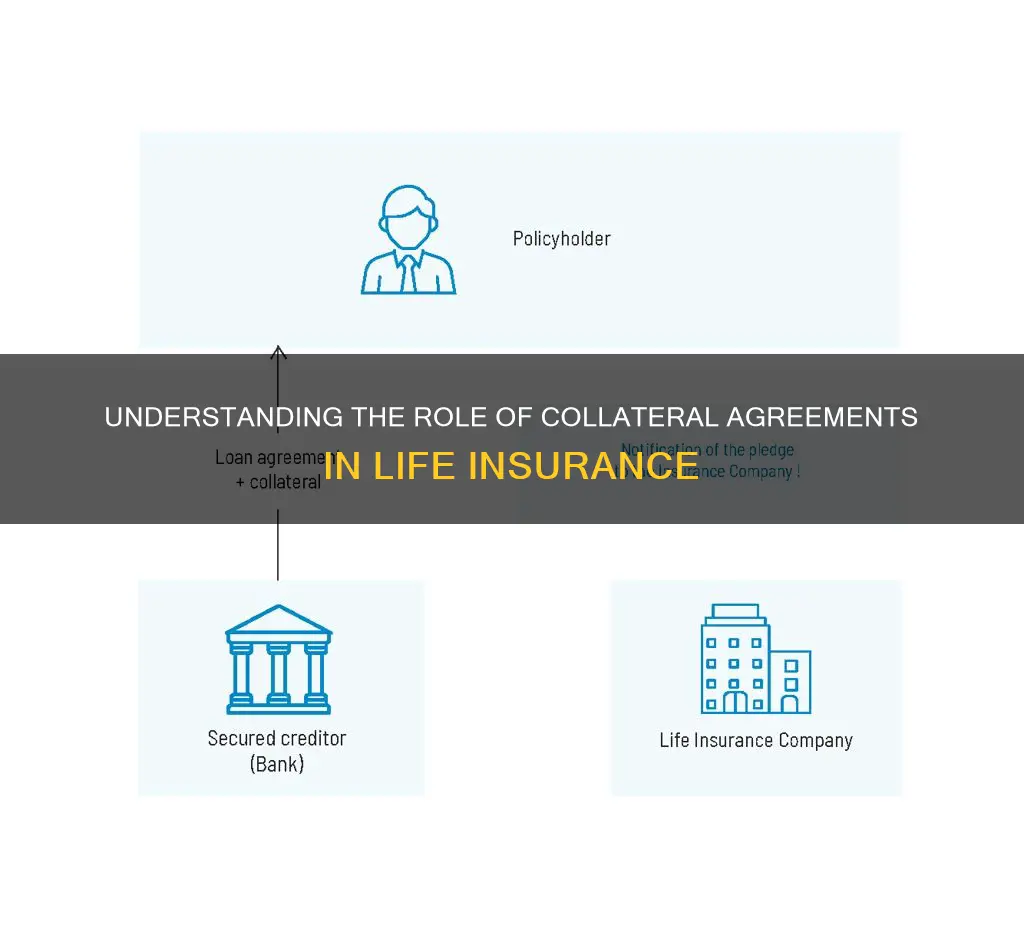
- Definition: A collateral agreement in life insurance is a separate contract that secures the loan taken to purchase the policy
- Purpose: It ensures the lender's interest in the policy's cash value if the borrower defaults
- Legal Implications: Collateral agreements can impact the policy's ownership and the lender's rights upon the insured's death
- Policy Conversion: These agreements may allow converting the policy to a different type without additional underwriting
- Beneficiary Designations: Policyholders can designate beneficiaries under the collateral agreement to receive proceeds

Definition: A collateral agreement in life insurance is a separate contract that secures the loan taken to purchase the policy
A collateral agreement in life insurance is a legal term that refers to a specific type of contract associated with life insurance policies. When an individual takes out a loan to purchase a life insurance policy, this additional agreement is put in place to secure the loan. It is a separate document from the main life insurance policy and serves as a form of protection for the lender.
In simple terms, the collateral agreement acts as a guarantee or security for the loan. It means that if the policyholder defaults on the loan payments, the lender has the right to take possession of the life insurance policy or any other asset(s) that have been pledged as collateral. This ensures that the lender has a means to recover their losses in the event of the policyholder's inability to repay the loan.
This type of agreement is often used in the context of term life insurance, where the policy is designed to provide coverage for a specific period. The loan taken to purchase the term policy may require a collateral agreement to ensure the lender's security. For instance, if an individual borrows money to buy a 10-year term life insurance policy, the lender might request a collateral agreement to safeguard their investment.
It is important to understand that the collateral agreement is a binding contract, and its terms should be carefully reviewed by the policyholder. The agreement will outline the specific collateral, the rights of the lender, and the consequences of defaulting on the loan. Policyholders should seek professional advice to ensure they fully comprehend the implications and to protect their interests.
In summary, a collateral agreement in life insurance is a separate contract that secures the loan used to purchase a life insurance policy. It provides lenders with a form of security and protection, allowing them to recover their losses if the policyholder fails to meet their loan obligations. This agreement is a crucial aspect of the loan process, ensuring that both the lender and the policyholder are protected.
Canceling RBC Life Insurance: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Purpose: It ensures the lender's interest in the policy's cash value if the borrower defaults
A collateral agreement in life insurance is a legal arrangement that serves a specific purpose in the context of securing a loan against a life insurance policy. This agreement is a crucial component when a borrower uses their life insurance policy as collateral for a loan, typically to access the cash value within the policy. The primary purpose of this agreement is to protect the lender's interest in the policy's cash value in the event of the borrower's default on the loan.
When a borrower takes out a loan and uses their life insurance policy as collateral, the lender wants to ensure that they have a claim on the policy's cash value if the borrower fails to repay the loan. This is where the collateral agreement comes into play. It is a legal contract that outlines the rights and responsibilities of both the borrower and the lender regarding the policy. The agreement specifies that if the borrower defaults, the lender has the right to access the policy's cash value to recover the loan amount. This ensures that the lender's interest in the policy is protected, providing them with a security measure to mitigate the risk of non-payment.
The agreement typically requires the borrower to notify the lender in the event of any changes to the policy, such as policy loans, withdrawals, or changes in beneficiaries. This transparency allows the lender to monitor the policy's value and ensure that it remains sufficient to cover the loan. In the event of the borrower's default, the lender can take control of the policy, receive the death benefit, or utilize the policy's cash value to settle the loan, thus safeguarding their financial interests.
This type of agreement is essential in life insurance lending, especially when the policy's cash value is substantial. It provides lenders with a clear understanding of their rights and the borrower's obligations, reducing potential disputes and ensuring a smooth process in the event of default. By having this agreement in place, both parties can have confidence in the arrangement, knowing that the lender's interest in the policy's cash value is protected.
Globe Life Burial Insurance: Legit or Scam?
You may want to see also

Legal Implications: Collateral agreements can impact the policy's ownership and the lender's rights upon the insured's death
A collateral agreement in the context of life insurance is a legal contract that serves as a secondary security measure for lenders. When an individual takes out a life insurance policy with a loan or mortgage component, the lender may require a collateral agreement to protect their interests. This agreement outlines the lender's rights and the policy's ownership in the event of the insured's death.
Upon the insured's passing, the collateral agreement comes into effect, and it can significantly impact the policy's ownership and the lender's rights. The agreement typically states that the lender has the right to receive the death benefit or proceeds of the life insurance policy as a form of repayment for the loan. This means that the lender's claim on the policy's value is secured, ensuring they receive compensation in the event of the insured's death.
In legal terms, the collateral agreement creates a lien or encumbrance on the life insurance policy. This lien gives the lender a legal claim or interest in the policy, which can be enforced to recover the loan amount. As a result, the lender's rights are protected, and they have a priority claim over other potential beneficiaries or heirs.
The implications of this agreement are crucial for both the insured and the lender. For the insured, it means that the lender has a vested interest in the policy's proceeds, which can be a significant financial burden if the insured were to pass away. The insured must ensure that the lender's rights are respected and that the collateral agreement is honored according to the terms of the policy.
For the lender, the collateral agreement provides a safety net and security. It allows them to recover their investment in the loan, especially in cases where the insured's death results in a substantial financial loss. However, it also means that the lender must carefully consider the terms of the agreement and ensure that the insured's rights are not compromised.
In summary, collateral agreements in life insurance policies have significant legal implications. They define the ownership and rights of the policy and the lender upon the insured's death. Understanding these agreements is essential for both parties to ensure compliance and protect their respective interests.
Acquisition Alert: a-capholdings Takes Over Sentinel Life Insurance
You may want to see also

Policy Conversion: These agreements may allow converting the policy to a different type without additional underwriting
The concept of policy conversion in life insurance is an essential feature that provides policyholders with flexibility and control over their insurance plans. This mechanism allows individuals to transform their existing life insurance policies into different types without undergoing a new underwriting process, which can be a time-consuming and potentially complex task. Policy conversion is particularly valuable as it enables policyholders to adapt their coverage to changing needs or circumstances without the hassle of starting the insurance application process from scratch.
Collateral agreements play a crucial role in facilitating policy conversions. These agreements are legal contracts between the insurance company and the policyholder, outlining the terms and conditions under which the policy can be converted. When a policyholder decides to convert their policy, the collateral agreement ensures that the insurance provider agrees to the new policy type, often with certain conditions or adjustments. This agreement acts as a safeguard for both parties, providing clarity and protection for the policyholder's interests.
The process of policy conversion typically involves the policyholder notifying their insurance company of their intention to convert. The insurance provider then reviews the collateral agreement to determine if the conversion is feasible and if any additional requirements need to be met. This may include providing updated financial information or medical records, especially if the new policy type has different coverage levels or risk factors. The key advantage is that the insurance company relies on the existing relationship and the collateral agreement to expedite the conversion process, saving time and effort for both the policyholder and the insurer.
For instance, a policyholder with a term life insurance policy might decide to convert it to a permanent life insurance plan as their financial situation improves. The collateral agreement would outline the terms of this conversion, including any adjustments to the policy's coverage amount or premium. This agreement ensures that the insurance company is aware of the policyholder's decision and can promptly process the conversion without the need for extensive new underwriting, which could be costly and time-consuming.
In summary, policy conversion, enabled by collateral agreements, offers policyholders a convenient way to adjust their life insurance coverage. This feature empowers individuals to make necessary changes to their policies without the typical lengthy underwriting process, providing a more efficient and flexible approach to managing one's insurance needs. Understanding the role of collateral agreements in policy conversion is essential for policyholders to make informed decisions and ensure their insurance coverage remains suitable and relevant over time.
Life Insurance: Covering Adult Children Under Your Policy
You may want to see also

Beneficiary Designations: Policyholders can designate beneficiaries under the collateral agreement to receive proceeds
When it comes to life insurance, the concept of a collateral agreement is an essential aspect of ensuring that your beneficiaries receive the intended proceeds. This agreement is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance policy will be honored upon the death of the policyholder. One crucial element within this agreement is the ability for policyholders to make beneficiary designations, which allows them to specify who will benefit from the insurance payout.
Beneficiary designations are a powerful tool for individuals to have control over their insurance policies. By designating beneficiaries, policyholders can ensure that the proceeds from the life insurance policy are distributed according to their wishes. This is particularly important as it provides a level of flexibility and customization that standard wills may not offer. When a policyholder names a beneficiary, they are essentially instructing the insurance company to pay out the policy's value directly to the designated individual or individuals upon their passing.
The process of making beneficiary designations is straightforward. Policyholders typically have the option to name primary and contingent beneficiaries. A primary beneficiary is the first in line to receive the proceeds, and this person can be an individual, a trust, or even an organization. Contingent beneficiaries are secondary recipients who will only receive the proceeds if the primary beneficiary is unable or unwilling to accept the payment. This feature ensures that the insurance company has a clear understanding of who should receive the funds.
It is worth noting that beneficiary designations can be changed at any time, providing policyholders with the flexibility to adapt their wishes as their circumstances change. This is a significant advantage over other inheritance methods, as it allows for quick and direct distribution without the need for legal proceedings. When making these changes, it is essential to inform the insurance company to update the records accordingly.
In summary, the collateral agreement in life insurance empowers policyholders to take charge of their beneficiaries' financial future. Through beneficiary designations, individuals can ensure that their loved ones receive the intended financial support upon their passing. This aspect of life insurance provides a sense of security and control, allowing individuals to leave a lasting legacy for their beneficiaries.
Beneficiary of My Own Life Insurance: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A collateral agreement is a separate legal document that accompanies a life insurance policy. It is an additional contract that provides more specific terms and conditions regarding the insurance coverage, especially in cases where the policy has unique or complex features. This agreement ensures that both the insurer and the policyholder have a clear understanding of the policy's provisions, including any restrictions, exclusions, or additional benefits.
The main life insurance policy outlines the basic coverage, premiums, and general terms of the insurance. In contrast, a collateral agreement delves into the finer details, addressing specific circumstances or conditions that may not be covered by the standard policy. It can include provisions for accelerated death benefits, waiver of premium, or other rider benefits, ensuring that the policyholder's needs are met in various life events.
A collateral agreement is crucial as it provides clarity and customization to the insurance policy. It allows policyholders to tailor their coverage to their specific requirements, ensuring they receive the exact benefits they desire. This agreement also helps in managing expectations and reducing potential disputes between the insurer and the policyholder, especially in cases where the policy has unique or non-standard features. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the policy's terms, protecting both parties involved.







