Life insurance is a financial product designed to provide financial protection and support to beneficiaries in the event of the insured individual's death. It is a crucial tool for managing risk and ensuring financial security for loved ones. However, not all insurance products fall under the category of life insurance. For instance, health insurance, auto insurance, and home insurance are distinct from life insurance and serve different purposes. Understanding the differences between these insurance types is essential for individuals to choose the right coverage for their needs. This paragraph aims to explore the specific characteristics that set certain insurance products apart from traditional life insurance, highlighting the unique aspects of each.
What You'll Learn
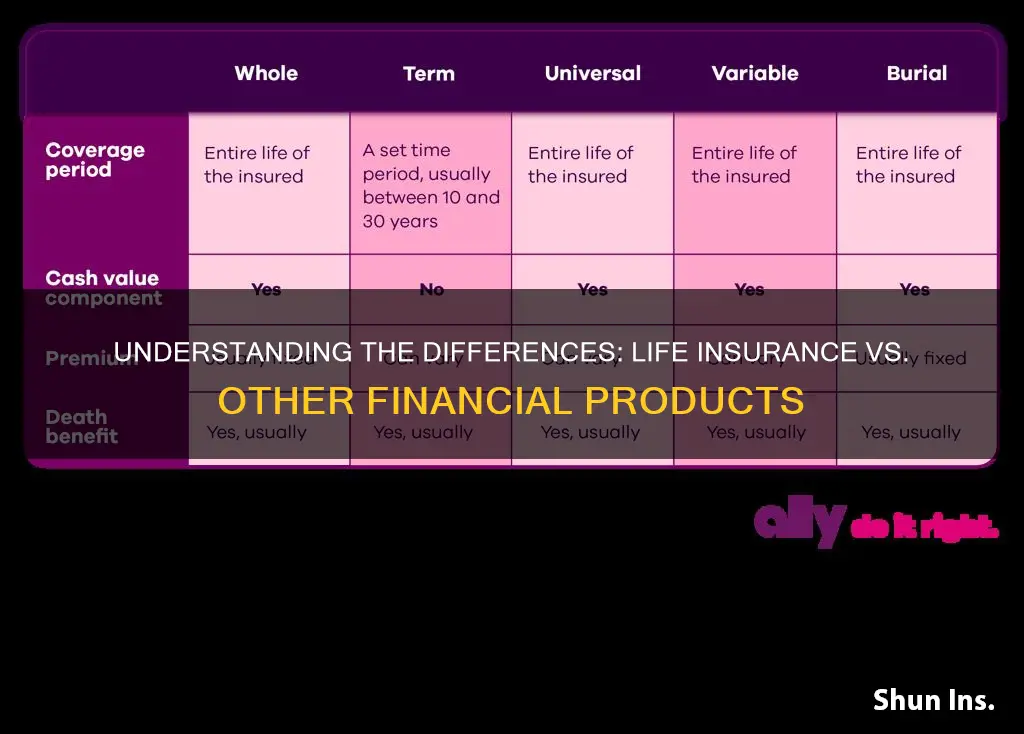
- Term Life Insurance: Coverage for a specific period, offering protection against financial loss
- Whole Life Insurance: Permanent coverage with a savings component, providing lifelong protection
- Universal Life Insurance: Flexible coverage with adjustable premiums and potential investment options
- Variable Life Insurance: Offers investment options, providing potential for higher returns but also higher risk
- Annuities: Income-generating contracts, not typically classified as life insurance

Term Life Insurance: Coverage for a specific period, offering protection against financial loss
Term life insurance is a type of coverage that provides financial protection for a specific period. It is a straightforward and cost-effective way to ensure that your loved ones are financially secure in the event of your untimely death. This insurance policy is designed to offer peace of mind, knowing that your family will have a financial safety net during challenging times.
The term "term" in term life insurance refers to the duration for which the policy is in effect. It is a temporary arrangement, typically lasting for 10, 15, 20, or 30 years. During this period, the insurance company promises to pay out a predetermined death benefit to your beneficiaries if you pass away. This benefit can help cover various expenses, such as mortgage payments, children's education, or daily living costs, ensuring your family's financial stability.
One of the key advantages of term life insurance is its simplicity and affordability. It is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance because it does not accumulate cash value over time. Instead, it focuses solely on providing coverage for a defined period. This makes it an excellent option for individuals who want to protect their loved ones without the added complexity and cost of building cash value.
When choosing a term life insurance policy, it is essential to consider your specific needs and circumstances. You should evaluate the duration of coverage required, ensuring it aligns with the time frame during which your family would need financial support. Additionally, assessing the amount of coverage needed is crucial. This involves calculating potential expenses and determining the policy's death benefit to guarantee adequate protection.
In summary, term life insurance is a valuable tool for providing financial security for a specific period. It offers a straightforward and affordable way to protect your loved ones, ensuring they have the necessary support during challenging times. By understanding the term and duration of coverage, as well as the policy's benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their insurance needs.
Employer Life Insurance: Borrowing from Your Policy?
You may want to see also

Whole Life Insurance: Permanent coverage with a savings component, providing lifelong protection
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a range of benefits, including lifelong coverage and a savings component. It is designed to provide financial security and peace of mind for individuals and their families. This type of insurance is a long-term commitment, ensuring that the policyholder and their beneficiaries are protected throughout their lives.
One of the key features of whole life insurance is its permanent nature. Unlike term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specified period, whole life insurance remains in force for the entire lifetime of the insured individual. This means that the policyholder and their beneficiaries are protected even if the insured person passes away, ensuring financial security for the loved ones left behind. The policy guarantees a death benefit, which is a fixed amount paid out upon the insured's death, providing a financial safety net.
In addition to the death benefit, whole life insurance also includes a savings component. A portion of the premium paid by the policyholder goes into an investment account, allowing the policy to accumulate cash value over time. This cash value can be used for various purposes, such as loaning money to the policyholder, paying for college expenses, or even taking out a tax-free loan against the policy's cash value. The savings aspect of whole life insurance provides an opportunity for long-term wealth accumulation, making it a valuable financial tool for those seeking both insurance and investment benefits.
The benefits of whole life insurance extend beyond the financial security it provides. It offers a sense of stability and peace of mind, knowing that your loved ones will be taken care of, regardless of life's twists and turns. This type of insurance is particularly valuable for those with financial dependents, such as children or a spouse, as it ensures their financial well-being in the event of the insured's passing. Furthermore, whole life insurance can be a valuable asset for estate planning, allowing individuals to leave a financial legacy for their beneficiaries.
In summary, whole life insurance is a comprehensive financial product that combines insurance and savings. It provides permanent coverage, ensuring lifelong protection for the insured and their beneficiaries. The savings component allows for long-term wealth accumulation, making it a versatile tool for financial planning. By understanding the features and benefits of whole life insurance, individuals can make informed decisions about their financial security and the well-being of their loved ones.
Life Insurance for 23-Year-Olds: Necessary or Not?
You may want to see also

Universal Life Insurance: Flexible coverage with adjustable premiums and potential investment options
Universal life insurance offers a unique and flexible approach to life coverage, providing policyholders with a range of features that set it apart from other insurance products. One of its key advantages is the ability to customize the policy to fit individual needs. Unlike traditional term life insurance, where the coverage amount and premium remain fixed for a specified period, universal life insurance provides a dynamic and adaptable solution.
With universal life insurance, policyholders can adjust their coverage amount over time. This flexibility allows individuals to start with a higher coverage amount during their younger years, ensuring adequate protection when it is most needed. As they age and their financial situation changes, they can increase or decrease the coverage, ensuring that the policy remains relevant and aligned with their evolving circumstances. This adjustability is particularly beneficial for those who want to maximize their insurance coverage during their most productive years while also having the option to reduce it as they approach retirement.
Another distinctive feature of universal life insurance is the potential for investment growth. Policyholders can allocate a portion of their premiums to investment accounts, which are managed by the insurance company. These investment options can offer the potential for long-term growth, allowing the policy's cash value to accumulate over time. This feature is attractive to those seeking to grow their money while also having the security of life insurance. The investment aspect provides an opportunity to potentially increase the overall value of the policy, making it a more comprehensive financial tool.
The adjustable nature of universal life insurance premiums is another advantage. Premiums can be tailored to the policyholder's financial situation and risk tolerance. During the initial years, higher premiums may be paid to build up the cash value quickly. As the policy matures, premiums can be adjusted downward, providing more affordable coverage. This flexibility ensures that the insurance remains accessible and affordable throughout the policy's duration.
In summary, universal life insurance stands out for its adaptability and customization. It offers policyholders the freedom to adjust coverage amounts, providing tailored protection at various life stages. The potential for investment growth and the ability to customize premiums make it a versatile and attractive option for those seeking a comprehensive financial strategy that includes both insurance and investment benefits. This type of insurance is particularly well-suited for individuals who want to take control of their financial future and ensure that their insurance needs evolve alongside their changing lives.
Custom Whole Life Insurance: Tailored Financial Security
You may want to see also

Variable Life Insurance: Offers investment options, providing potential for higher returns but also higher risk
Variable life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a unique combination of insurance protection and investment opportunities. Unlike traditional life insurance, which primarily focuses on providing a death benefit to beneficiaries, variable life insurance allows policyholders to invest a portion of their premiums in various investment options. This feature sets it apart and makes it distinct from other forms of life insurance.
The key characteristic of variable life insurance is its flexibility. Policyholders can choose from a range of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, to grow their policy's cash value. This investment aspect is what sets it apart from the more straightforward nature of term life insurance or whole life insurance, where the primary function is to provide financial protection in the event of the insured's death.
One of the advantages of variable life insurance is the potential for higher returns. By investing in the market, policyholders can benefit from the performance of the chosen investment options. This can be particularly attractive to those seeking to grow their wealth over time. However, it's important to note that this investment approach also comes with higher risk. The value of the investments can fluctuate, and there is a possibility of losing some or all of the invested amount.
Additionally, variable life insurance provides policyholders with control over their investments. They can adjust their investment strategy based on market conditions and their financial goals. This level of customization is a significant advantage for those who want to actively manage their insurance and investment portfolio.
In summary, variable life insurance stands out due to its investment component, offering policyholders the opportunity to potentially increase their returns. However, this also means that it is not solely a form of life insurance but rather a financial product that combines insurance with investment strategies. Understanding the investment nature of variable life insurance is crucial for individuals considering this type of coverage to ensure they are making informed decisions about their financial security and wealth management.
Joint Life Insurance: How Long Does It Last?
You may want to see also

Annuities: Income-generating contracts, not typically classified as life insurance
Annuities are financial products that are often confused with life insurance, but they serve very different purposes and are not typically classified as such. While life insurance is designed to provide financial protection and a death benefit to beneficiaries in the event of the insured's passing, annuities are income-generating contracts that offer a steady stream of payments to the annuitant, the individual who purchases the annuity.
Annuities are structured as a long-term investment, often with a guaranteed income stream for the annuitant's lifetime. They are typically offered by insurance companies and can be either fixed or variable. Fixed annuities provide a predetermined interest rate and income, while variable annuities offer potential for higher returns but also carry more risk. The key difference lies in the primary objective: life insurance is about risk management and providing financial security, whereas annuities focus on generating income and growing wealth over time.
When considering the classification, life insurance policies are designed to pay out a death benefit, which is a lump sum or regular payment made to the designated beneficiaries upon the insured's death. This payout is a critical aspect of life insurance and is not a feature of annuities. Annuities, on the other hand, provide income to the annuitant during their lifetime, which can be useful for retirement planning or as a steady source of cash flow. The income generated from annuities can be used to cover living expenses, pay for healthcare, or simply provide financial security.
Furthermore, the tax treatment of annuities differs from life insurance. Life insurance proceeds are generally tax-free, providing a significant benefit to beneficiaries. In contrast, annuity payments are typically taxable income for the annuitant, and the tax implications can vary depending on the type of annuity. This difference in tax treatment further emphasizes that annuities are not life insurance and are instead a distinct financial instrument.
In summary, annuities are income-generating contracts that offer a steady stream of payments to the annuitant, making them a valuable tool for retirement planning and income generation. While they may be confused with life insurance, they serve a different purpose and are not typically classified as such due to their unique features and tax implications. Understanding the distinction between these financial products is essential for individuals seeking to make informed decisions about their long-term financial security.
Obese People: Getting Life Insurance, Is It Possible?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance is a contract between an individual and an insurance company, where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a sum of money upon the insured's death. It is specifically designed to provide financial protection and support to loved ones in the event of the insured's passing. Other types of insurance, such as health, auto, or home insurance, typically cover risks like illness, accidents, property damage, or liability, and do not focus on the insured's death.
No, disability insurance is not the same as life insurance. Disability insurance provides income replacement if the insured becomes unable to work due to illness or injury. It ensures financial stability during periods of disability, whereas life insurance offers financial security for the beneficiary in the event of the insured's death.
Yes, some people might confuse long-term care insurance with life insurance. Long-term care insurance helps cover the costs of long-term medical care, such as nursing home or assisted living expenses, which can be a significant financial burden. While it provides financial protection, it is not specifically designed to pay out upon the insured's death.
No, term life insurance and whole life insurance are two different types of life insurance policies. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, or 'term', and is generally more affordable. Whole life insurance, on the other hand, offers lifelong coverage and includes a savings component, where a portion of the premiums is invested, allowing for potential cash value accumulation over time.







