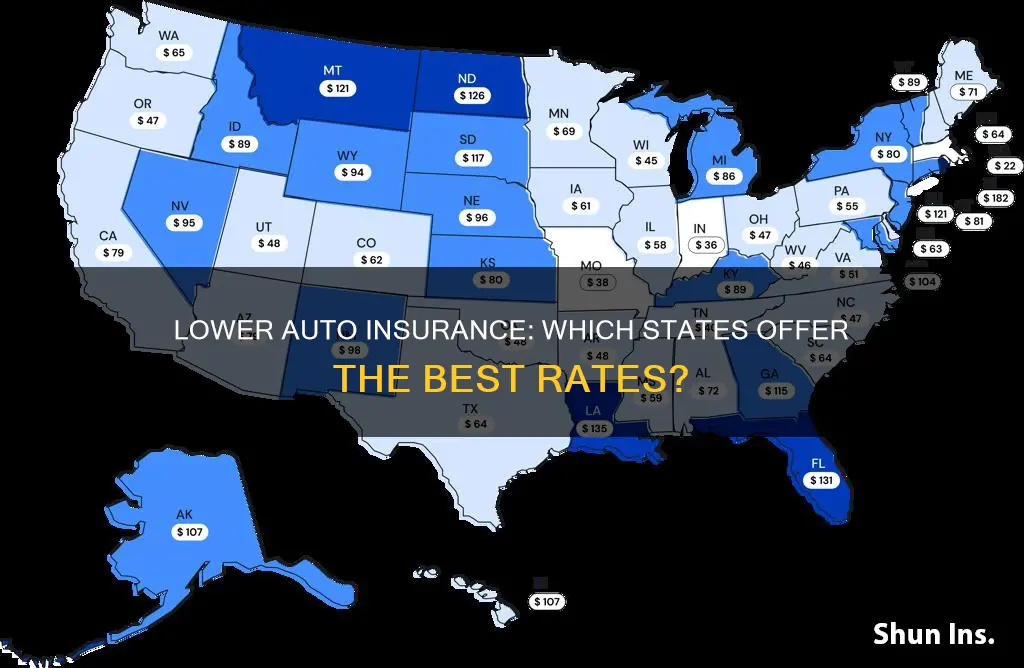
The cost of auto insurance varies from state to state, with some states offering lower rates than others. The national average cost for car insurance is $2,118 per year, but this can range from as low as $1,021 in Idaho to as high as $4,769 in New York. The state where you live is an important factor in determining how much you’ll pay for car insurance, as differences among states affect car insurance costs based on what auto insurance is required, how much repairs cost, and more.
Some of the cheapest states for auto insurance include Maine, Vermont, Ohio, Idaho, and Iowa. On the other hand, the most expensive states for auto insurance include New York, Florida, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, and Maryland.
Factors that influence the cost of auto insurance in each state include the number of auto insurance claims, the cost of car repairs and medical care, the frequency of lawsuits, and the state's minimum insurance requirements. Additionally, states with higher population densities and more congested cities tend to have higher insurance rates due to the increased risk of accidents and claims.
It's worth noting that auto insurance rates can also vary within a state, with more populated cities typically having higher insurance rates than less populated areas. When determining auto insurance rates, insurance companies consider various factors such as age, driving history, gender, vehicle type, and credit score, in addition to location.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| States with the lowest full-coverage car insurance rates | Maine, Vermont, Ohio, Idaho, Hawaii, New Hampshire, Indiana, Iowa, Tennessee, Wisconsin, North Carolina |
| States with the highest full-coverage car insurance rates | Louisiana, New York, Michigan, Pennsylvania, Nevada, Florida, Kentucky, Missouri, Delaware, Rhode Island, California, Colorado, South Dakota |
| States with the lowest liability-only car insurance rates | South Dakota, Wyoming, Idaho, Vermont, Iowa |
| States with the highest liability-only car insurance rates | Florida, Louisiana, Nevada, Delaware, New Jersey |
What You'll Learn

Population density
Living in a densely populated area typically leads to higher car insurance premiums. This is because accidents are more frequent in these areas, as a higher number of vehicles are on the road. Population density also influences the type and frequency of claims filed, as well as the costs of repairing vehicles.
For example, in Texas, full coverage in Houston, a large city, is about $32 more per month than in Corpus Christi, a smaller city with less traffic. Similarly, within Houston, the monthly insurance rates vary by up to $171 per year between different ZIP codes.
States with lower population densities, such as Wyoming, Idaho, Vermont, and Iowa, tend to have cheaper insurance rates. In contrast, states with higher population densities, like New York, Nevada, Delaware, Florida, and Rhode Island, have more expensive insurance rates.
However, population density is not the only factor influencing insurance rates. Other considerations include road conditions, the number of licensed drivers, the cost of living, weather conditions, local claims history, and state laws.
Does Auto Insurance Protect Against Flash Floods?
You may want to see also

Weather conditions
For instance, areas with harsh winters and snowy, icy roads tend to have higher insurance rates because of the increased risk of accidents in such conditions. Similarly, states with volatile weather patterns, such as Louisiana, tend to have higher insurance rates to account for the potential damage and claims arising from these events.
On the other hand, states with milder weather conditions generally experience a lesser impact on their auto insurance rates. For example, North Carolina, known for its mild weather, has lower-than-average insurance rates.
It is worth noting that weather-related claims typically fall under comprehensive auto insurance, which covers a range of perils, including natural disasters, fallen objects, theft, and accidents involving animals. While these weather events can increase the chances of vehicle damage or accidents, they do not directly influence insurance rates, and any rate increases are due to the higher frequency of claims in those areas.
Additionally, weather conditions can indirectly affect insurance rates by influencing road risks and traffic congestion. For example, busier roads and more congested cities tend to have higher insurance rates because the increased traffic volume correlates with a higher likelihood of accidents.
Best Auto Insurance Options: Top Policies for Your Car
You may want to see also

Cost of living
The cost of living is a significant factor in determining auto insurance rates. States with a lower cost of living tend to have cheaper auto insurance rates. This is because the cost of repairs and labour is generally lower in these states, which leads to lower insurance premiums.
For example, Alaska has a low cost of living and a low population density, contributing to relatively low auto insurance rates. On the other hand, California's sky-high cost of living and poorly ranked infrastructure make finding cheap auto insurance a challenge for residents.
Other factors that contribute to the cost of living and, consequently, auto insurance rates include the following:
- Population density: States with higher population densities tend to have higher insurance rates due to increased congestion and a higher risk of accidents.
- Weather conditions: States prone to severe weather events, such as hurricanes or flooding, often have higher insurance rates as these events can cause substantial damage to vehicles.
- Crime rates: States with higher crime rates, particularly car theft and vandalism, will have higher insurance rates as insurers view insuring vehicles in these areas as riskier.
- Number of uninsured drivers: A high number of uninsured drivers can increase insurance rates for all drivers in the state.
- State insurance requirements: States that mandate additional coverage types, such as personal injury protection, tend to have higher insurance costs.
Additionally, factors such as age, gender, driving record, and credit score can also impact auto insurance rates and vary from state to state.
To Snitch or Not to Snitch: The Ethical Dilemma of Reporting Your Roommate to Auto Insurance
You may want to see also

Number of licensed drivers
The number of licensed drivers in a state is one of the factors that can influence insurance rates. States with a high number of licensed drivers tend to have higher insurance rates.
In 2021, there were almost 233 million licensed drivers in the United States, with California issuing the highest number of licenses at around 27 million. This is unsurprising, as California is the most populous state in the country, representing close to 12% of the country's total population.
Other states with a high number of licensed drivers include:
- Texas
- Florida
- New York
- Pennsylvania
- Illinois
- Ohio
- Georgia
- North Carolina
- Michigan
On the other hand, states with a low number of licensed drivers tend to have lower insurance rates. These include:
- Idaho
- Vermont
- Wyoming
- North Dakota
- South Dakota
- Montana
- Maine
- Hawaii
- West Virginia
Auto Insurance Requirements for a Lien: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Percentage of uninsured drivers
The percentage of uninsured drivers varies across the United States, with Mississippi having the highest uninsured motorist rate at 29.4% in 2019, followed by Michigan (25.5%), Tennessee (23.7%), New Mexico (21.8%), and Washington state (21.7%). New Jersey, Massachusetts, and New York had the lowest percentages of uninsured drivers, at 3.1%, 3.5%, and 4.1%, respectively.
The number of uninsured vehicles on the road has decreased in recent years, but there are still around 28-29 million uninsured drivers in the US, meaning that about one in seven or eight drivers doesn't have car insurance. The rate of uninsured motorists on the road hasn't changed much in recent years, with a national average of 12.3% in 2010 and 12.6% in 2019.
The cost of insurance by state does not necessarily correlate with the number of uninsured motorists. For example, in 2019, Alabama had the seventh-highest percentage of uninsured motorists in the nation (19.5%), but the average cost of insurance was $906.36, putting them 29th for average insurance costs in the US. In contrast, insurance in New Jersey, which had the lowest uninsured motorist rates in the country, cost $1,395.53 in 2019.
Some states have implemented "no-pay, no-play" laws, which limit how much uninsured drivers can collect if they are in an accident with an insured driver. These laws aim to encourage uninsured drivers to get a policy, but they have had a slightly negative effect, with states with these laws having a slightly higher rate of uninsured drivers (13.7% compared to 12.2%).
Understanding Comprehensive Auto Insurance Claims and Coverage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Maine has the lowest car insurance rates in the US, with an average annual premium of $1,175.
Louisiana has the highest car insurance rates, with an average annual premium of $2,883.
The cost of car insurance in a state is influenced by factors such as population density, weather conditions, road risks, and the number of uninsured drivers.
To get cheaper car insurance, consider improving your credit score, maintaining a good driving record, and comparing rates from multiple insurance providers.







