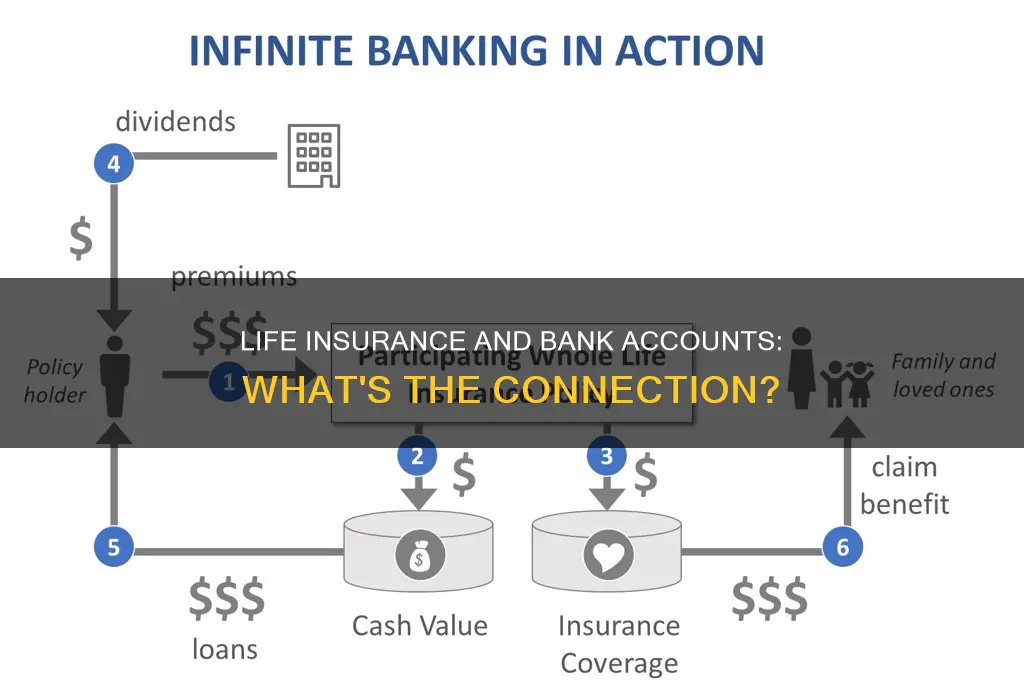
Life insurance is a type of insurance contract between a policyholder and an insurance company that pays out a death benefit when the insured person passes away. There are several kinds of life insurance, including term and permanent plans. Term life insurance provides coverage for a set period, such as 15, 20, or 30 years, while permanent life insurance provides coverage that typically does not expire. Permanent life insurance includes whole life, universal life, and variable universal life insurance. While life insurance products are available for purchase through most banks, they are rarely included for free in bank accounts.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Do all bank accounts include life insurance? | No |
| Is life insurance available to buy through most banks? | Yes |
| What type of life insurance can you buy from your bank? | Simple term life insurance, decreasing mortgage life insurance, funeral plans, critical illness insurance, and income protection cover |
| Who underwrites and administers the policy? | A trusted third-party insurer |
| Do banks sell the best life insurance policies or offer the cheapest monthly payments? | No |
What You'll Learn

Bank-owned life insurance (BOLI)
BOLI is a permanent life insurance policy often purchased for high-earners and/or board members of a bank. The bank pays for the policy and receives the benefits after the insured individual's death. Banks do not take out BOLI for every employee but only for key players whose death could cause a financial loss for the bank.
BOLI is a tax-efficient method to offset employee benefit costs. The bank purchases and owns an insurance policy on an executive, becoming the beneficiary. Cash surrender values grow tax-deferred, providing the bank with monthly bookable income. Upon the executive's death, tax-free death benefits are paid to the bank.
There are three types of BOLI products offered to banks: General Account, Separate Account, and Hybrid Account. The General Account is the oldest and most common type, where the bank's investment deposit becomes part of the insurance carrier's general account, mainly invested in bonds and real estate. The Separate Account allows the insurance provider to segregate the holdings into investments managed by fund managers, providing detailed reporting of the bank's portfolio. The Hybrid Account combines the benefits of both the General and Separate Accounts, offering a guaranteed crediting rate and transparency into investment holdings.
BOLI is a long-term asset that offers banks a highly-rated investment option with significant tax advantages. It helps banks compete with other employers' benefit plans and provides a way to fund benefit plans. However, it is important to note that BOLI is not available for individuals to purchase for themselves.
Millionaires' Secret: Building Wealth with Life Insurance
You may want to see also

Permanent life insurance
There are two main types of permanent life insurance: whole life insurance and universal life insurance. Whole life insurance policies have fixed premiums that never change, and the cash value grows at a guaranteed rate over time. Universal life insurance policies, on the other hand, offer flexible premiums that can be adjusted over time. However, this flexibility may negatively impact the cash value of the plan and could lead to higher premiums in the future.
To get the most out of a permanent life insurance policy, policyholders should choose the right type of policy, pay premiums on time, monitor and adjust the policy as needed, and consider working with a financial professional to optimize their coverage.
Humana's Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Term life insurance
There are several types of term life insurance plans, including fixed term, increasing term, decreasing term, and annual renewable. The fixed-term option is the most popular and basic version, offering coverage for 10, 20, or 30 years with static premiums. Increasing term life insurance allows for scaling up the value of the death benefit over time, while decreasing term life insurance reduces the premium payments. Annual renewable term life insurance provides coverage on a yearly basis and must be renewed by the end date, often resulting in higher premiums over time.
When choosing a term life insurance policy, the insurance company determines the premium based on factors such as the policy's value, age, gender, and health of the policyholder. Additionally, the insurance company may inquire about driving records, current medications, smoking status, occupation, hobbies, and family history. These factors help assess the risk and set the premium accordingly.
Life Insurance: Navy Federal's Comprehensive Coverage Options
You may want to see also

Whole life insurance
There are several main types of whole life insurance, categorized based on how premiums are paid. Level Payment policies are the most common, with premiums remaining unchanged throughout the duration of the policy. With Single Premium policies, the insured pays a one-time large premium, which funds the policy for life. Limited Payment policies involve a limited number of payments, with higher premiums than Level Payment policies. Modified Whole Life Insurance policies offer lower premiums than standard policies in the first two or three years, and higher-than-standard premiums in the later years and are more expensive in the long run.
Life Insurance: Haram's Financial Risk and Uncertainty
You may want to see also

Universal life insurance
The cash value in a universal life insurance policy earns interest, which is set by the insurer and can change frequently. While there is usually a minimum interest rate guaranteed by the insurer, underperforming investments or underpayment of premiums can lead to a decrease in cash value and an increase in premiums. It is important for policyholders to monitor their cash value to avoid large payment requirements or policy lapse.
Overall, universal life insurance can be a valuable tool for individuals seeking lifelong protection, the ability to adjust their coverage over time, and the opportunity to build tax-efficient cash value.
Flight Emergencies: Insurance Coverage for Flight-for-Life Services
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, banks don't generally offer free life insurance to their customers, but life insurance products are available for purchase through most banks.
Life insurance is a type of insurance contract between a policyholder and an insurance company. The policyholder pays premiums to keep their coverage, and upon their death, the insurance company pays out a death benefit to the named beneficiaries.
There are two main types of life insurance: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a set period, such as 15, 20, or 30 years. Permanent life insurance, including whole life and universal life, offers coverage for the entirety of the policyholder's life.
'Packaged' bank accounts usually attract a monthly fee and include general insurance types such as travel, mobile phone, and breakdown insurance. However, they rarely include life insurance.
Banks often sell life insurance products provided by trusted third-party insurers. These can include term life insurance, decreasing mortgage life insurance, funeral plans, critical illness insurance, and income protection cover.







