Life insurance is a type of insurance policy designed to help cover your loved ones' financial needs after your death. The price you pay for life insurance is usually set when you first buy your policy, based on your health, age, and other factors. While it is uncommon for your rate to increase once you've bought your life insurance, it can happen in certain situations. For example, if you choose a policy with increasing term life insurance, the benefit increases over time, and payments often do too. Additionally, permanent or whole life policies tend to be more expensive than term life policies. Other factors that can cause your insurance premium to increase include your credit score, driving record, address, and vehicle.
What You'll Learn

Life insurance rates and age
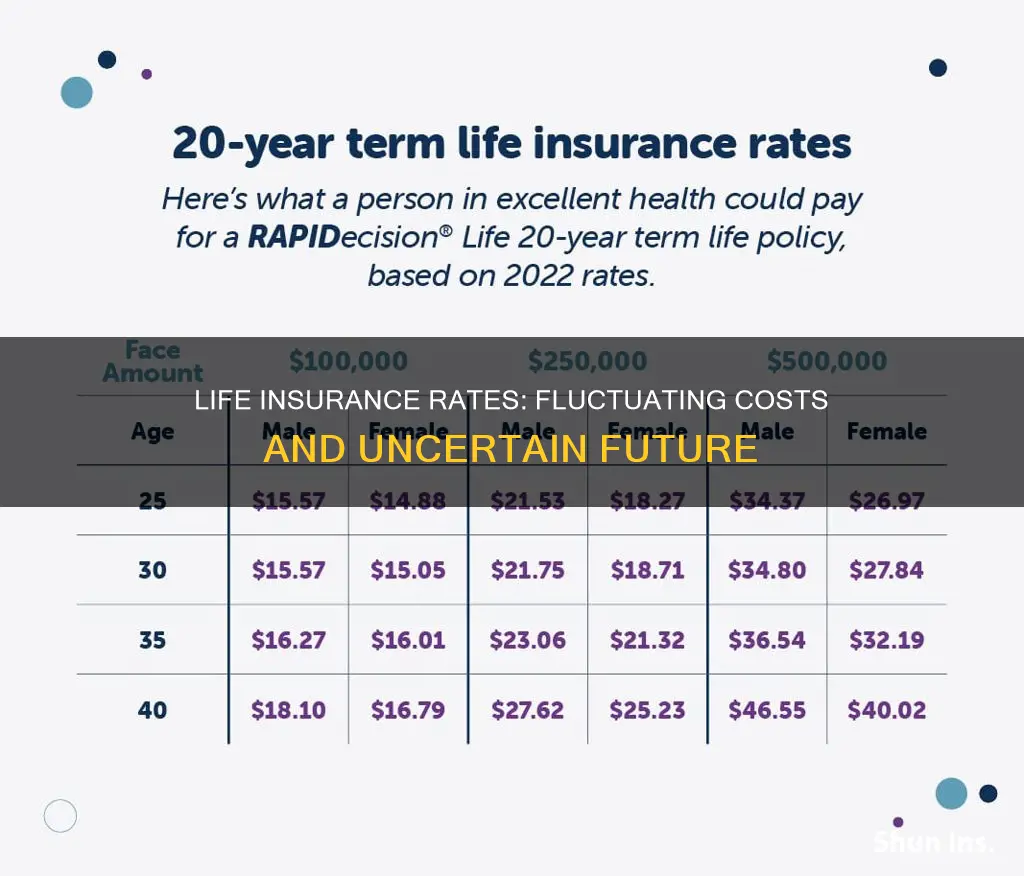
Age is one of the primary factors influencing your life insurance premium rate, whether you're seeking a term or permanent policy. The older you are when you purchase a policy, the more expensive the premiums will be. This is because the cost of life insurance is based on actuarial life tables that assign a likelihood of dying while the policy is in force. The likelihood of dying increases with age, hence the higher premium rates for older people.
Typically, the premium amount increases, on average, about 8% to 10% for every year of age; it can be as low as 5% annually if you're in your 40s, and as high as 12% annually if you’re over 50. With term life insurance, your premium is established when you buy a policy and remains the same every year. With some permanent life insurance policies, the premium rises annually.
Age also affects whether a person will qualify for life insurance coverage at all, with qualifying medical exams getting increasingly stringent as people get older.
The annual premium, or “rate,” for a term life insurance policy is determined at the time of purchase and set for the duration of the policy. For example, a 45-year-old male will pay on average $1,125 for a new, 20-year term policy with $1,000,000 of coverage. The same policy purchased at age 46 will cost $1,225, and $1,345 a year if purchased at age 47.
The reason every year inches up the cost of term life insurance is simple math. Every birthday puts you one year closer to your life expectancy and thus, you are more expensive to insure. Rates increase every year by 5% to 8% in your 40s, and by 9% to 12% each year if you’re over 50.
To hold term life insurance prices steady, insurers spread the premiums you would pay over 10, 20, or 30 years and average them into one payment. Instead of paying low premiums when you’re young and very high premiums when you’re older, you pay the same amount every year.
Once the term of your current term policy expires, you could face very steep rates based on your age. If the insured outlives the initial term, the insurance carrier must adjust the premium to reflect their new age.
Permanent life policy rates may be either level (fixed) or they may vary. If they vary, they usually rise as you age. The premiums are determined by the insurance carrier each year based on actuarial tables and they increase at each successive age because each year there is a bigger drain on the cash value due to rising mortality charges.
Life Insurance: Where to Purchase and What to Consider
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and health
Life insurance rates are influenced by several factors, and health is one of the most significant determinants. Here is an overview of how life insurance rates and health are interconnected:
Impact of Health on Life Insurance Rates:
- Overall Health: Insurance companies consider an individual's overall health, including weight and the presence of pre-existing conditions. The healthier you are, the lower your premiums are likely to be.
- Medical History: Insurers may inquire about your medical history, such as previous or current health conditions, and their severity.
- Health Risk Factors: Factors like smoking, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol can negatively impact your insurance rates.
- Family Medical History: A family history of serious health issues, such as heart disease, cancer, or diabetes, may also be taken into account when determining your premiums.
- Health Examinations: The results of medical exams, including blood and urine tests, can influence your risk classification and, consequently, your insurance rates.
- Risk Classification: Insurance companies assign applicants to different risk classes based on their health. Being in a lower risk class can result in lower premiums.
- Lifestyle Choices: Engaging in risky hobbies or occupations can impact your health risk classification and, thus, your insurance rates.
Improving Health to Lower Rates:
Improving your health can have a positive impact on your insurance rates. For example, losing weight, quitting smoking, or changing to a less hazardous occupation can contribute to a better insurance risk classification and lower premiums.
Health and Term Life Insurance:
Term life insurance rates are influenced by health in a similar manner to permanent life insurance. However, term life insurance rates are typically lower than permanent life insurance because they do not build cash value.
Health and Whole Life Insurance:
Whole life insurance rates are also impacted by health. Since whole life insurance includes a cash value component, the rate of return on this cash value will drive the premium up or down. A higher rate of return can help keep premiums lower.
Group Life Insurance:
Group life insurance policies offered through employers typically have level premiums for all members and do not discriminate based on age, gender, or health. However, these policies usually have limited coverage and are not portable if you leave the company.
In conclusion, health plays a crucial role in determining life insurance rates. The healthier you are, the more favourable rates you are likely to receive. Improving your health and making positive lifestyle choices can have a positive impact on your insurance premiums.
Life Insurance for Bipolar: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and gender
Life insurance rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including age, gender, health, and lifestyle choices. While age is a primary factor, with premiums increasing by about 8% to 10% for every year of age, gender also plays a significant role in determining rates.
Men generally have higher life insurance rates than women, mainly because women have a longer life expectancy. According to the latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the life expectancy in the US is 79.3 years for women and 73.5 years for men. This difference in life expectancy is reflected in the cost of life insurance, with women paying on average 24% less than men.
Actuarial tables, which are used by insurance companies to assess insurance risk and assign rates, have historically shown that men tend to die earlier than women. However, recent research suggests that life expectancy by gender may be more complex, but there isn't enough data to change existing insurer guidelines.
It's important to note that gender is just one factor among many that insurers consider when determining rates. Medical history and lifestyle choices often have a more significant impact on the cost of coverage. Health and lifestyle risks, such as smoking, can lead to higher premiums, regardless of gender.
In conclusion, while gender does influence life insurance rates, it is not the only factor, and other aspects such as age, health, and lifestyle choices also play a crucial role in determining the cost of coverage.
Borrowing Against Your Guardian Life Insurance: Is it Possible?
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and risk factors
Life insurance is designed to pay out a death benefit to the person or persons you name as beneficiaries when you pass away. In exchange for this coverage, you pay a premium to the life insurance company. The older you are when you purchase a policy, the more expensive the premiums will be. This is because the cost of life insurance is based on actuarial life tables that assign a likelihood of dying while the policy is in force. In other words, the older you are, the more likely you are to pass away while under coverage.
Your age is one of the primary factors influencing your life insurance premium rate, whether you're seeking a term or permanent policy. Typically, the premium amount increases on average by about 8% to 10% for every year of age. This can be as low as 5% annually if you're in your 40s and as high as 12% annually if you're over 50.
Aside from age, there are several other factors that influence life insurance rates. These include:
- Overall health, including weight and the presence of pre-existing conditions
- Participation in risky hobbies, such as skydiving or hang-gliding
- Smoking status
- Gender
- Occupation
- Salary
When calculating how much you'll pay for life insurance, your risk class comes into play. Life insurance companies assign applicants to various risk classes based on these factors. If you're assigned to the lowest risk class, you'll typically pay lower premiums. On the other hand, if you're assigned a substandard rate based on health, smoking status, age, or other risk factors, you may pay more for life insurance.
In addition, if you're considering a whole life or universal policy, the rate of return on the cash value will drive the premium up or down. A higher rate of return on cash value can help keep policy premiums low. Conversely, a lower-than-expected return on cash value will require a higher funding amount to keep the policy in force longer.
Life insurance rates can also be affected by market conditions and investment portfolio performance. For example, whole life policies are based on dividends that are loosely tied to interest rates. If interest rates go down, dividends may be reduced, impacting how long you have to pay premiums, how much cash value will accrue, and potentially the size of your death benefit.
Variable universal life policies, on the other hand, are based on stock market returns, which can be volatile. As a result, the actual performance of these policies may not align with the initial illustrations provided by the insurance company.
It's important to note that life insurance rates can vary between different insurance providers, so it's recommended to shop around and compare rates before choosing a policy. Additionally, life insurance rates can change over time, so it's a good idea to periodically review and evaluate your policy to ensure it still meets your needs and aligns with your financial goals.
Who Are Your Life Insurance Beneficiaries? Inform Them Now!
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and policy type
Life insurance rates and policies can vary depending on several factors, including age, health, and policy type. When it comes to policy type, there are two primary categories: term life insurance and permanent life insurance.
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, such as 5 or 30 years. The premium, or rate, for term life insurance is typically established when the policy is purchased and remains fixed for the duration of the term. While term life insurance rates do not increase annually, they can increase significantly when the term ends and the policy is renewed at an older age. Term life insurance generally offers lower premium rates compared to permanent life insurance.
Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides coverage for the insured's entire life as long as premiums are paid. Within permanent life insurance, there are several types of policies, including whole life insurance and universal life insurance.
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance offers coverage for a lifetime, provided that premiums are paid. It also includes a cash value component, where a portion of the premium payments goes towards building a cash value that can earn interest and grow over time. Whole life insurance policies typically have set premiums that do not change. The cash value grows at a fixed interest rate or a rate based on more complex investments, depending on the policy.
Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance provides more flexibility than whole life insurance. Policyholders can adjust their premiums and death benefits to meet their changing needs. The cash value growth in universal life insurance policies depends on the insurer's performance but usually has a minimum guaranteed rate. The cash value accumulation can fluctuate according to market interest rates, causing the amount earned per year to vary.
Factors Affecting Life Insurance Rates
Regardless of the policy type, several factors can influence life insurance rates. Age is a significant factor, with premiums increasing by about 8% to 10% for each year of age. Health is another important consideration, with insurance companies assessing overall health, pre-existing conditions, and participation in risky activities. Additionally, life insurance rates can be impacted by gender, with women generally paying lower premiums than men due to their higher average life expectancy.
Finding Unclaimed Life Insurance: A Free, Easy Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, life insurance rates can change over time. While it is uncommon for rates to increase once you've bought a policy, it can happen in certain situations. For example, if you choose a policy with increasing term life insurance, the benefit increases over time and payments often do, too.
Several factors can cause your life insurance rates to increase. These include your age, health, credit score, driving record, address, and vehicle. Additionally, if you convert your policy from term life insurance to whole life insurance, your rates may increase as whole life policies are typically more expensive.
To keep your life insurance rates low, focus on maintaining a good driving record and a good credit score. You can also compare rates from different providers to find the most suitable policy for your needs.
While life insurance rates generally tend to increase, there may be some instances where they decrease. For example, improving your health and lifestyle habits, such as quitting smoking, can lead to lower rates. Additionally, as you get older, your rates may decrease as insurers consider age as a predictor of driving experience and accident risk.







