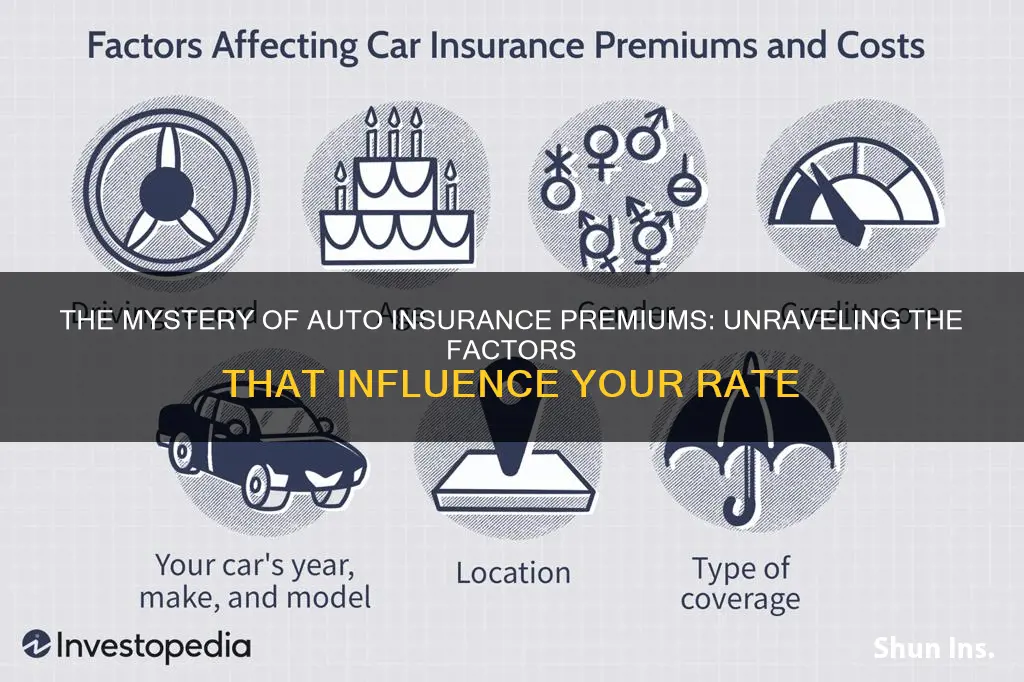
Auto insurance premiums are determined by a multitude of factors, and each insurance provider has its own way of calculating them. However, they generally follow the same principles. The most significant factor is the location of the insured, with urban drivers paying higher premiums due to higher rates of vandalism, theft, and accidents. The likelihood of natural disasters such as wildfires, floods, and earthquakes also plays a role. The age of the driver is another key consideration, with younger and older drivers deemed more likely to have accidents and therefore attracting higher premiums. The type of coverage and the amount of coverage also influence the premium, with more comprehensive coverage and higher coverage limits resulting in higher premiums. An individual's driving record is also taken into account, with a history of accidents or serious traffic violations leading to higher premiums. Other factors include gender, the car being insured, credit score, and whether the policy covers dependents.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Age | Premiums increase as people age and have a higher chance of needing more medical services. |
| Gender | Women often pay less for auto insurance than men as they tend to get into fewer accidents. |
| Marital status | Marital status can affect insurance premiums. |
| Lifestyle | Lifestyle choices such as smoking can increase insurance premiums. |
| Driving record | The better the driving record, the lower the premium. |
| Claims history | A history of insurance claims can result in higher premiums. |
| Credit history | A high credit score may result in lower premiums. |
| Location | Urban drivers pay higher premiums than those in small towns or rural areas. |
| Car type | The cost of the car and the likelihood of theft influence the premium. |
| Type of coverage | The more comprehensive the coverage, the more expensive the premium. |
| Amount of coverage | The less coverage, the cheaper the premiums. |
| Deductibles | A higher deductible results in lower premiums. |
| Out-of-pocket maximum | A higher out-of-pocket maximum results in lower premiums. |
What You'll Learn

Driving record
A driver's record is a major factor in determining car insurance premiums. A good driving record generally results in lower premiums, while a history of accidents or serious traffic violations will lead to higher premiums. This is because a driver with a history of accidents or violations is considered a higher risk to insure.
Insurance companies will review a driver's history, including moving violations and accidents, to estimate the level of insurance risk. The frequency and severity of recent driving violations and collisions are taken into account. For example, a speeding ticket can increase insurance rates by 20-26%, an at-fault accident can increase rates by 49%, and reckless driving can increase rates by 91%. A serious offence such as a DUI or reckless driving charge can result in a driver being labelled as high-risk, which can increase premiums by 30-300%.
The length of time that accidents and violations remain on a driving record varies depending on state law and the insurance company. Generally, this period is between three and five years, but it can be longer for more serious offences. For example, in California, a DUI remains on a driver's record for ten years, while an accident has a look-back period of three years. Once infractions are older than the look-back period, they will no longer impact insurance premiums.
In addition to a driver's history, insurance companies may also consider other factors such as credit score, age, location, and the type of car driven when determining insurance premiums.
Foremost Auto Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Age and gender
Age
Younger drivers, especially teens, tend to pay the highest premiums. This is because they are considered to be the riskiest drivers to insure due to their inexperience behind the wheel. Statistically, drivers aged 16 to 19 get into almost three times as many fatal car accidents as any other age group.
Auto insurance rates start to decrease when drivers reach their early 20s, with a significant reduction in premiums often occurring at age 25. Rates continue to drop as drivers gain more experience, with drivers in their 50s and 60s paying the least.
However, auto insurance rates begin to increase again around age 65 or 70. This is due to age-related factors such as vision or hearing loss and slower response times, which can make seniors more prone to accidents.
Gender
In most states, gender also plays a role in determining auto insurance rates, with males typically paying more than females, especially during their teen and young adult years. This is because men are generally considered riskier to insure. They are more likely to engage in risky driving behaviours, such as speeding, driving under the influence, and not wearing seat belts. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), men also tend to drive more miles than women.
However, the gender gap in rates narrows as drivers age and gain more experience, with rates becoming roughly equal by age 35. After age 50, females may start paying slightly less again, but the difference is usually minimal.
It is worth noting that some states, including California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Michigan, North Carolina, and Pennsylvania, prohibit the use of gender as a factor in determining auto insurance rates. In these states, rates should be similar for men and women with the same rating factors, such as vehicle type and driving history.
Auto Insurance: A Fair Hiring Question?
You may want to see also

Type of coverage
The type of coverage you choose is a significant factor in determining your auto insurance premium. The more comprehensive your coverage, the higher your premium will be.
Auto insurance policies typically include multiple types of coverage, each serving a specific purpose. While some types of coverage are mandated by law, others are optional.
Mandatory Coverage Types
The two types of liability insurance are mandated in almost every state:
- Bodily injury liability insurance covers the medical costs of the other driver and their passengers in the event of an accident caused by you.
- Property damage liability insurance covers the cost of repairs to vehicles, buildings, fences, mailboxes, etc., that are damaged in an accident caused by you.
Optional Coverage Types
Optional coverage types can increase your premium but may be invaluable in specific situations. Some common optional coverage types include:
- Collision insurance covers damage to your car after an accident, regardless of who was at fault.
- Comprehensive insurance covers damage to your car from events other than a collision, such as theft, storms, floods, vandalism, etc.
- Personal injury protection (PIP) covers medical expenses, funeral costs, child care, and lost wages for you and your passengers after an accident, regardless of who was at fault.
- Uninsured motorist coverage pays for expenses incurred due to an accident caused by an uninsured driver.
- Underinsured motorist coverage pays for expenses that exceed the at-fault driver's insurance limits.
- Gap insurance covers the difference between your car's value and the amount you owe on your loan if your car is totalled.
- New car replacement insurance provides funds for a new car of the same make and model if your car is totalled.
- Rental reimbursement insurance covers the cost of a rental car while your vehicle is being repaired.
- Rideshare insurance covers expenses incurred while driving for a rideshare company, such as Uber or Lyft, during the period between rides.
- Roadside assistance insurance covers the cost of services like towing, fuel delivery, and jump-starting your vehicle if it breaks down.
Georgia Drivers: Avoid Underinsurance
You may want to see also

Location
Auto insurance premiums are determined by a variety of factors, one of the most significant being location. The location of the insured individual is a critical determinant of the cost of car insurance, with urban residents often facing higher premiums than those in rural areas. This disparity is influenced by several factors, including:
Higher Rates of Vandalism and Theft: Urban areas typically experience higher rates of vandalism, theft, and accidents. As a result, insurers consider city dwellers to be at greater risk of making claims, leading to higher premiums.
Parking Situations: The specific location where an individual parks their car also matters. Street parking or a lack of covered or protected parking in urban areas increases the likelihood of theft or vandalism, which is reflected in higher insurance rates.
State Regulations: Car insurance is regulated at the state level, and each state has its own set of requirements. Some states, like Michigan, mandate unlimited Personal Injury Protection (PIP) coverage, which significantly increases insurance costs. Differences in state laws and requirements directly impact the premiums charged by insurers.
Risk Factors Within a State: Within a state, insurance companies also consider specific ZIP codes or locales. Areas with higher population densities, prone to natural disasters, or with higher rates of crime and vandalism, will face higher insurance rates. For example, locales susceptible to floods, wildfires, or crimes will likely have elevated premiums.
Cost of Repairs and Medical Care: The cost of car repairs and medical care varies across different locations. Insurers take these regional differences into account when setting premiums, as the potential payouts for claims will differ based on location.
Weather-Related Risks: Certain locations are more prone to weather-related risks, such as wildfires or windstorms, which can cause damage to vehicles. Insurers factor in these risks when determining premiums, as they anticipate higher claim rates in these areas.
The impact of location on auto insurance premiums is significant, with individuals in high-risk urban areas or specific ZIP codes facing notably higher costs. This factor, along with others such as driving record, age, and vehicle type, collectively contribute to the final premium amount determined by insurance companies.
Auto Insurance Card: Spouse's Name?
You may want to see also

Credit score
Insurers consider several factors when calculating credit-based insurance scores, including outstanding debt, credit history length, credit mix, and payment history. They use these scores to assess the risk of offering coverage, with higher scores indicating lower risk and potentially resulting in lower premiums. This practice is, however, prohibited in certain states like California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan, where rates are primarily based on driving records and other factors.
Improving your credit score can positively impact your insurance premiums. Paying bills on time, maintaining a low credit utilisation ratio, and keeping old lines of credit open can all contribute to a better credit score. Additionally, it's important to monitor your score regularly and minimise hard credit inquiries. While getting an insurance quote may not affect your credit score, consistently demonstrating financial responsibility can lead to better insurance rates.
West Auto Insurance: The Best Coverage for Your Car
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Auto insurance premiums are determined by a multitude of factors, including an individual's driving record, age, gender, location, and the type of car they drive. Premiums are calculated based on the likelihood of the insured experiencing a loss and the predicted cost of that loss.
The cost of auto insurance is influenced by several variables, including an individual's driving record, age, gender, location, and the type of car they drive. A person with a clean driving record will generally pay less than someone with a history of accidents or traffic violations. Mature drivers tend to have fewer accidents, so younger and less experienced drivers may pay more for insurance. The type of car also matters; more expensive cars with powerful engines tend to be more costly to insure.
There are several ways to lower your auto insurance premium. Firstly, you can improve your driving record by avoiding accidents and traffic violations. Secondly, you can choose a car that is cheaper to insure, typically a vehicle with a less powerful engine and good safety features. Additionally, you can consider increasing your deductible, which is the amount you pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. By accepting a higher deductible, you reduce the insurer's risk, which can result in lower premiums.







