Auto insurance companies make money through the premiums paid by their clients. The average annual cost of auto insurance coverage in the United States varies depending on the type of coverage and the state. The average cost of car insurance in California, for example, is $2,667 per year for full coverage and $651 per year for minimum coverage. Auto insurance agents can also earn an income through commissions, which are usually a percentage of the total premiums.
What You'll Learn

Auto insurance agents' income
Auto insurance agents are industry professionals who represent insurance companies and help them reach out to clients. They explain the insurance policies, their key features, and benefits to the clients.
There are several factors that affect how much auto insurance agents make. Based on employment and industry websites, the average annual salary falls between the $43,000 and $60,000 range. An agent's earnings can be significantly higher or lower, depending on different variables, including commission rates, experience level, and partner insurers. Most auto insurance agents have average salaries between the 25th and 75th percentile, or about $31,500 to $75,500. Figures above or below this salary range are considered outliers.
Auto insurance agents can earn an income through several methods. The most common way is through commissions. For captive agents, the commission rate is from 5% to 10% of the total premiums in the first year and about 2% to 5% for every renewal. The figure is slightly higher for independent agents at 15% for new policies. For existing plans, the typical rate is also 2% to 5%. Many captive auto insurance agents work full-time as salaried employees for the insurance companies they partner with. They may earn a fixed wage and receive commissions on top of their monthly salary, depending on the terms of their contract with the insurer. Some insurers that reach a specific profit target share the benefits by giving agents bonuses. These income-generating methods are not mutually exclusive. Auto insurance agents can receive a monthly wage from their partner insurers, along with commissions for every policy they sell and bonuses if an insurer's sales exceed the yearly target.
Mississippi Valley Credit Union: GAP Insurance Offerings
You may want to see also

Commission rates
Auto insurance agents are typically paid a commission when selling a policy and at renewal time. The commission rates vary depending on the type of agent, the insurance company, the type of policy, and the agent's experience level.
Captive Agents vs. Independent Agents
Captive agents work directly for a specific insurance company, while independent agents can sell insurance from various companies. Captive agents usually receive a base salary and company support, but their commission rates are lower, typically ranging from 5% to 10% of the premium sold. On the other hand, independent agents have more flexibility in choosing carriers and earn higher commissions, generally ranging from 10% to 15%, or even up to 20% in some cases.
Factors Affecting Commission Rates
- Location: Agents in states with extensive minimum coverage requirements and higher insurance premiums will earn higher commissions due to the percentage-based nature of commissions.
- Client's Risk Factor: Agents who specialize in high-risk drivers with bad driving records, suspended licenses, or teen drivers will likely earn higher commissions due to the higher insurance premiums charged to these clients.
- Level of Coverage: Agents who sell full coverage or encourage additional coverage options will earn higher commissions as the cost of the insurance policy increases.
Average Salary and Income
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median salary for insurance sales agents was $49,840 per year in 2021. However, this varies significantly depending on the agent's experience, the company they work for, and the number of new clients and policies they bring in. The lowest-paid 10% of insurance agents earned less than $29,970, while the highest-paid 10% earned over $126,510 per year.
GEICO: Insuring Low-Speed Vehicles?
You may want to see also

Required coverage types
Auto insurance companies make money through a variety of coverage types that are often mandated by state laws. While the specific requirements vary across different states, here is an overview of the commonly required coverage types:
Liability Car Insurance
Liability car insurance is the primary mandated coverage in most states. It covers injuries and property damage caused to others in an accident deemed to be your fault. This type of insurance includes bodily injury liability and property damage liability. The bodily injury liability covers medical expenses for the driver and passengers in the other vehicle, as well as any injured pedestrians. The property damage liability covers the cost of repairing damage to another person's property, such as their vehicle or any structures that may have been hit, like fences or buildings. It is recommended to purchase liability insurance that exceeds the state-mandated minimum to adequately protect your assets.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured motorist coverage protects you if you are in an accident with a driver who does not have insurance or does not have sufficient insurance to cover the damages. This coverage typically includes bodily injury liability and property damage liability, similar to the basic liability insurance. It ensures that your medical expenses and property damage are covered even when the at-fault driver does not have the necessary insurance.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal injury protection covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault for the accident. PIP also extends beyond medical payments to cover lost wages, funeral expenses, and replacement services that you may need due to injuries sustained in the accident, such as cleaning services or childcare. Some states mandate PIP as part of their "no-fault auto insurance" laws, while in other states, it is offered as an optional coverage type.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive insurance covers losses due to incidents other than collisions. This includes damage caused by fire, falling objects, explosions, natural disasters like earthquakes or floods, vandalism, riots, or contact with animals. Comprehensive coverage also typically includes repairs for cracked or shattered windshields. This type of coverage usually comes with a separate deductible, and in some cases, the glass portion of the coverage may be offered without a deductible.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage is often sold together with comprehensive coverage. It covers the cost of repairing or replacing your vehicle if it is damaged in a collision with another vehicle or object, including trees, telephone poles, or potholes. Even if you are at fault for the accident, collision coverage will reimburse you for the repair costs, minus the deductible. If you are not at fault, your insurance company may pursue reimbursement from the other driver's insurance, and you will also be compensated for your deductible.
While these are the most common types of required coverage, it is important to note that specific requirements may differ based on your state's laws and regulations. Additionally, if you lease or finance your vehicle, your lender or leasing company may have additional insurance requirements, such as collision and comprehensive coverage.
Gap Insurance: Limited or Unlimited?
You may want to see also

Premium relief
Auto insurance companies make money through premiums, which are the regular payments that customers make to maintain their insurance coverage. In 2020, auto insurance companies were criticised for reaping windfall profits of at least $29 billion as a result of the pandemic. This was because miles driven, vehicle crashes, and auto insurance claims dropped significantly due to lockdowns and other government actions. Despite this, insurance companies only provided $13 billion in "premium relief", with the remaining third of the profits going to payouts for senior management and stockholders.
The Consumer Federation of America (CFA) and the Center for Economic Justice (CEJ) analysed insurers' 2020 premium and claims results and concluded that insurers should have returned $42 billion in premium overcharges to consumers. The CFA and CEJ also pointed out that insurers' "premium relief" short-changed consumers by over $125 per insured vehicle.
In response to the pandemic, many large insurers provided refunds or credits to consumers in April and May 2020. However, very little excess premium was returned after that, and even this two-month payback was only about half of what should have been refunded. California, Michigan, New Jersey, and New Mexico were the only states to require premium refunds during the spring of 2020, with California being the only state to continue requiring refunds beyond the initial months of the pandemic.
The CFA and CEJ sent letter after letter to insurance regulators throughout 2020, urging them to take action and reduce illegally excessive auto premiums. They also called on state insurance commissioners to address the $30 billion overcharge to auto insurance consumers and to begin the process of returning pandemic premium overcharges to customers.
In summary, while auto insurance companies did provide some premium relief during the pandemic, it was not enough to offset their windfall profits. As a result, consumers were short-changed, and insurance companies pocketed the majority of the excess profits.
Smart Ways to Save on Auto Insurance
You may want to see also

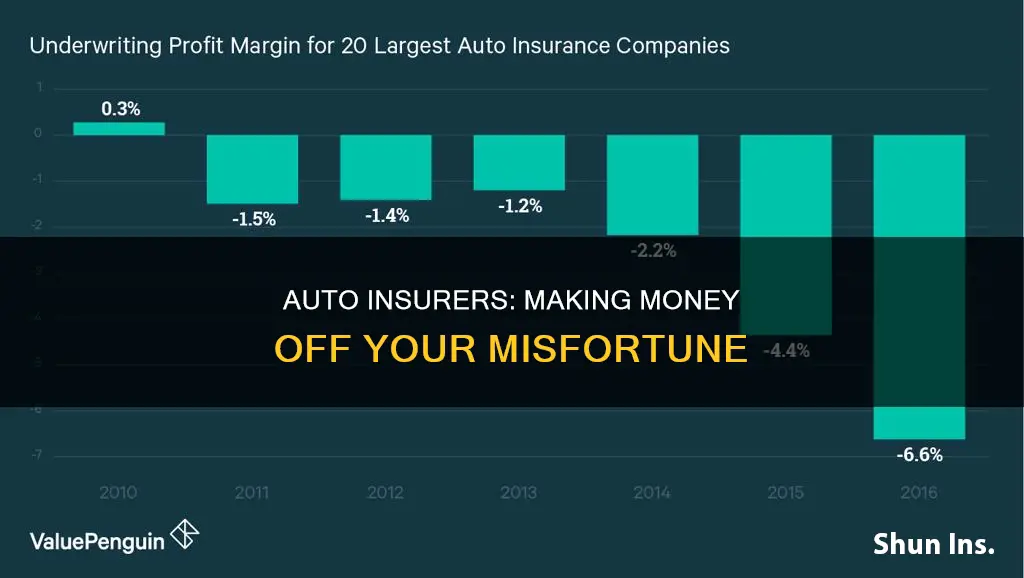
Profit targets
Auto insurance companies make money through premiums, which are the regular payments made by customers for their insurance policies. The company pools this money and uses it to pay out claims when customers file them. The company also invests this money to generate profits.
Insurance companies maintain a profit margin of around 5%, with 68% of premiums applied to paying claims, 25% spent on overhead, and 2% set aside for taxes. In 2020, auto insurance companies in the US made a profit of at least $29 billion, largely due to reduced driving and accidents during the pandemic.
Insurance agents, who sell policies on behalf of insurance companies, can earn through commissions, salaries, and bonuses. Captive agents, who represent a single insurer, typically earn commissions of 5-10% on the total premiums in the first year and 2-5% on renewals. Independent agents, who represent multiple insurers, can earn higher commissions of 15% on new policies and 2-5% on existing plans. Some insurers also pay their captive agents a fixed salary and provide commissions on top. Bonuses are also common if the insurer meets its profit targets.
Drunk Driving: Auto Insurance Coverage?
You may want to see also







