Life insurance is a contract between a policyholder and an insurance company that pays out a death benefit when the insured person passes away. The purpose of life insurance is to help provide financial security to your loved ones upon your death. The insurance company pays a lump sum, known as a 'death benefit', to the people you choose as beneficiaries if you pass away. This is designed to offer peace of mind, knowing that this can help financially protect your loved ones after you're gone.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of contract | Legally binding |
| Parties to the contract | Policyholder and insurance company |
| Purpose | Financial protection for loved ones after death |
| Coverage | Depends on the type of policy |
| Payment | Regular premiums |
| Payout | Death benefit or lump sum |
| Beneficiaries | Individuals, trusts, or organizations |
| Uses of payout | Funeral costs, mortgage payments, education expenses, etc. |
What You'll Learn

The role of beneficiaries
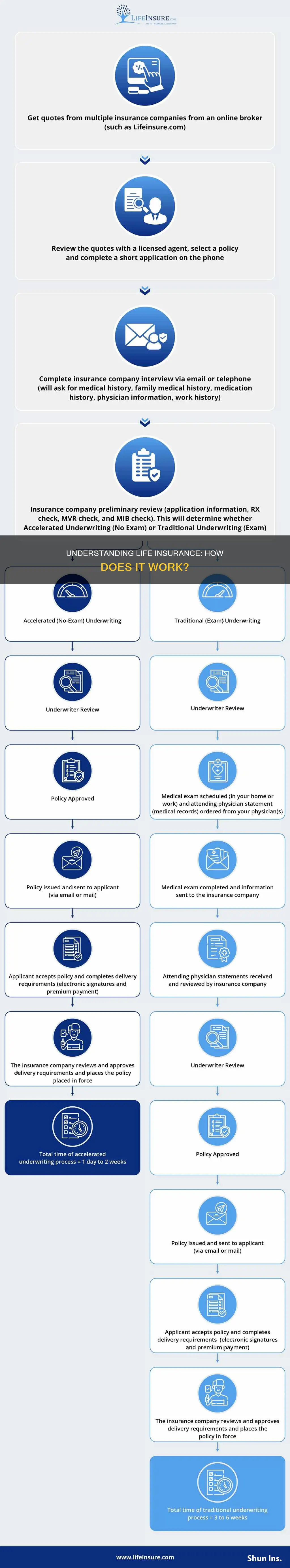
Life insurance is a contract between an insurance company and a policyholder. The policyholder makes regular premium payments and follows the terms within the plan, and the company provides the policyholder's beneficiaries with a death benefit or payout when they pass away. The purpose of life insurance is to help provide financial security to the policyholder's loved ones upon their death.
There are two main types of life insurance beneficiaries: primary and contingent. A primary beneficiary is the first in line to receive the death benefit payout after the policyholder's passing. The policyholder can name more than one primary beneficiary. A contingent beneficiary, on the other hand, is a backup beneficiary who will receive the payout if the primary beneficiary is unavailable or deceased. The policyholder can also name multiple contingent beneficiaries.
It is important to keep beneficiary designations up to date, especially after major life changes such as marriage, children, or divorce. While it is not mandatory to name a beneficiary, it is usually the primary reason people purchase life insurance—to provide financial support to their loved ones. If no beneficiary is named, it may be unclear who is entitled to the funds, which can delay the benefit payment. In such cases, the payout will typically be paid to the policyholder's estate or held in probate.
To ensure a smooth process, beneficiaries must file a claim with the life insurance company, as benefits are not automatically paid out. They will need to verify the death of the policyholder, their identity, and their relationship to the insured. While there is no time limit for filing a death claim, the sooner the claim is filed, the sooner the benefit can be paid.
USDA Commercial Loans: Life Insurance Requirements Explained
You may want to see also

The different types of life insurance
Life insurance is a contract between the policyholder and an insurance company. In exchange for regular premium payments, the insurance company agrees to pay a sum of money to one or more named beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder. The purpose of life insurance is to provide financial security to your loved ones upon your death.
There are two broad categories of life insurance: term and permanent. Term life insurance provides coverage for a set number of years, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If the policyholder dies during the coverage period, the policy will pay benefits to the named beneficiaries. However, if the policyholder lives past the selected period, the policy will expire. On the other hand, permanent life insurance does not expire and provides coverage for the entire life of the policyholder.
Permanent life insurance can be further divided into three main types: whole, universal, and variable. Whole life insurance has no expiration date and a portion of the premiums paid build cash value over time. Universal life insurance also provides lifetime coverage and can build cash value, with the added flexibility of adjusting premium payments. Variable life insurance is another type of permanent life insurance that can build cash value, with the potential for greater growth over time by increasing the value of certain subaccounts within the policy.
In addition to these main types, there are also other variations of life insurance, such as burial or final expense insurance, group life insurance, mortgage life insurance, and credit life insurance. Burial insurance is a type of whole life insurance with a smaller death benefit designed to cover funeral and burial costs. Group life insurance is typically offered by employers as a workplace benefit, while mortgage life insurance covers the balance of a mortgage and pays out to the lender, not the family, in the event of the policyholder's death. Credit life insurance, on the other hand, pays off a specific loan, such as a home equity loan, upon the death of the policyholder.
Understanding Life Events: Impact on Health Insurance Options
You may want to see also

The cost of life insurance
Factors that Affect the Cost of Life Insurance
Two of the biggest factors that influence life insurance rates are age and gender. Younger people tend to pay less than older people as they are less likely to have health problems, and women usually pay less than men because they have longer life expectancies. The cost of life insurance also tends to be higher for males because they often have more dangerous jobs and shorter lifespans.
Other factors that can impact the cost of life insurance include:
- Health: Insurers consider height, weight, and medical history, especially any chronic or serious illnesses.
- Tobacco use: Smokers typically pay higher rates due to the associated health risks.
- Hobbies: High-risk hobbies, such as skydiving or racing cars, can increase premiums.
- Criminal history: A history of DUIs, arrests, or criminal convictions may affect rates or disqualify you from coverage.
- Occupation: Risky jobs, such as police officers, firefighters, pilots, or construction workers, may result in higher premiums.
- Financial history: Bankruptcies or other risk factors in your credit report may impact your rate.
- Coverage amount: The more coverage you want, the higher the cost.
Term Life Insurance vs. Permanent Life Insurance
Term life insurance is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance as it is considered a temporary policy with a set coverage period. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, usually lasts a lifetime and includes a cash value component, making it more expensive.
Cost-Saving Tips for Life Insurance
There are several ways to lower your life insurance rate, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Managing any medical conditions
- Quitting smoking
- Avoiding high-risk hobbies
- Applying early for a policy, as rates tend to increase with age
Whole Life vs Term Life: What's the Better Insurance Option?
You may want to see also

How to choose a life insurance policy
Life insurance is a contract between an insurance company and a policyholder. In exchange for regular premium payments, the insurance company agrees to pay a sum of money to one or more named beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder. The purpose of life insurance is to help provide financial security to your loved ones upon your death.
There are two main types of life insurance: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Term life insurance covers a set number of years, such as 10, 20, or 30 years, while permanent life insurance covers the policyholder for their entire life.
When choosing a life insurance policy, there are several factors to consider:
Your needs and budget:
The type of life insurance you choose will depend on your specific needs and financial situation. Term life insurance is typically more affordable and suitable for those with a limited budget, while permanent life insurance offers lifelong coverage and access to cash value but comes with higher premiums.
Coverage amount:
Determine how much coverage you need based on factors such as income replacement, college tuition, and burial expenses. The coverage amount will impact the cost of the policy.
Length of coverage:
Consider how long you need the life insurance coverage to last. If you have specific financial obligations, such as a mortgage or children's education, term life insurance can be tailored to match the length of these commitments. Permanent life insurance provides coverage for as long as you live.
Cost and payment flexibility:
Compare the costs of different policies, including the premiums and any additional fees or charges. Also, consider the flexibility of payment options, as some permanent policies allow you to adjust premium payments or skip payments if you have enough cash value built up.
Available riders and benefits:
Review the riders and additional benefits offered by different insurance companies. Riders can provide access to your death benefit while you are still alive, covering expenses related to a terminal illness or nursing home care.
Conversion options:
Some term life insurance policies can be converted into permanent life insurance, which can be useful if your financial needs change or if you want to avoid shopping for a new policy later in life.
Company reputation and customer service:
Research the reputation and customer satisfaction of the insurance company. Look for a company with a strong financial standing and positive reviews for their handling of claims and customer service.
When choosing a life insurance policy, it is important to carefully consider your personal circumstances, financial goals, and the level of protection you want for your loved ones. It may be beneficial to consult with a financial professional or insurance agent to help you navigate the different options and choose the policy that best suits your needs.
Understanding Whole Life Insurance: Unlocking Cash Value
You may want to see also

How to claim life insurance
Life insurance is a contract between the policyholder and the insurance company. The policyholder makes regular premium payments, and the insurance company pays a sum of money to the beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder.
- Identify the insurer: The first step is to identify the policyholder's insurance company. This information should be available in the policy documents. If the policy documents are not accessible, the policyholder's financial advisor or estate planning attorney may have this information.
- Obtain the death certificate: The next step is to obtain multiple certified copies of the policyholder's death certificate from the relevant local government agency, such as the local vital records office. The death certificate is required by the insurance company to verify the policyholder's death.
- Contact the insurer: Once you have the necessary documents, contact the insurance company to initiate the claims process. They will provide you with a claim form to fill out. Most insurers allow you to file the claim online or in person.
- Submit the required documentation: Along with the completed claim form, submit the policy number (found on the policy documents) and the policyholder's death certificate. It is essential to carefully review and triple-check your answers before submitting to avoid any delays in the process.
- Choose the payout option: Insurers typically offer several payout options, including a lump sum, life income annuity, specific income annuity, or a retained asset account. Each option has different tax implications, so it is recommended to consult a tax professional for guidance.
- Receive the death benefit payout: Once the insurer approves the claim, they will disburse the death benefit according to the selected payout method. It is important to maintain communication with the insurer throughout the process to ensure a smooth transaction and address any delays.
It is important to note that there is no deadline for filing a life insurance claim, and the process can take anywhere from 3 to 60 days for the payout to be received.
Banner Life Insurance: Is It Worth the Hype?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance is a contract between a policyholder and an insurance company that pays out a sum of money, known as a death benefit, to the policyholder's beneficiaries after their death. The purpose of life insurance is to provide financial security to loved ones after the policyholder's death.
Life insurance works by allowing beneficiaries to claim a financial payout, often equal to the coverage amount, after the death of the policyholder. The payout can be used for funeral costs, mortgage payments, education expenses, or any other financial needs.
There are two main types of life insurance: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Term life insurance covers the policyholder for a set number of years, while permanent life insurance covers the policyholder for their entire life. Permanent life insurance also has a cash value component that can be borrowed against.
The cost of life insurance depends on several factors, including the type of policy, the insurance company, the policyholder's age, health, and family history. Term life insurance is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance.







