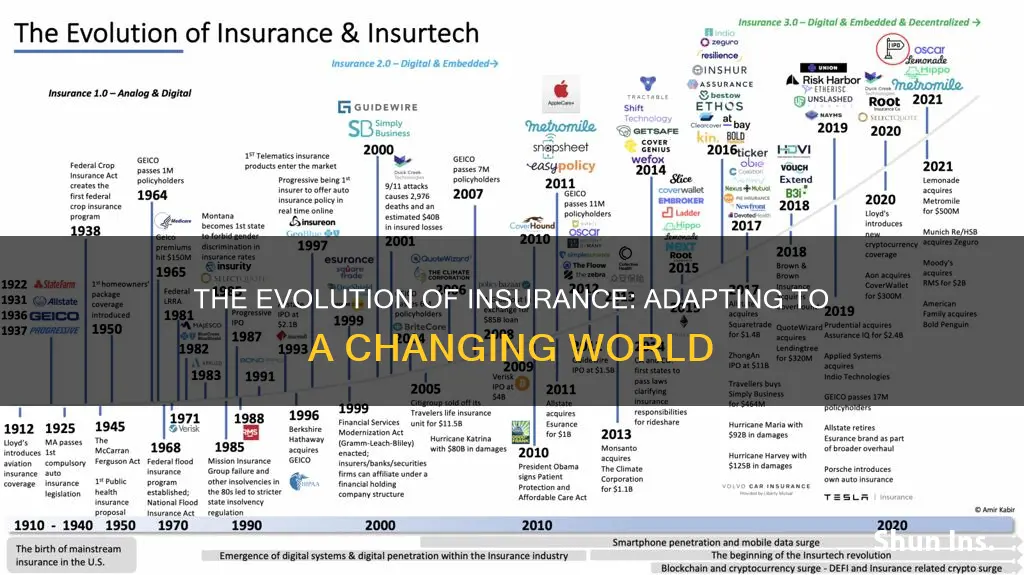
The insurance industry has changed significantly over the years, with digital transformation playing a pivotal role in its evolution. The sector has shifted from a stable and predictable business to one that embraces innovation and technology. Historically low rates, riskier investments, and an increase in claims due to the pandemic have all contributed to the changing landscape. Digital capabilities have enabled insurers to enhance product development, improve customer engagement, streamline operations, and drive growth. The use of Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data, the Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics has revolutionized the industry, with advanced technologies impacting every aspect of insurance, from underwriting and pricing to claims processing. The industry continues to adapt to new challenges and opportunities, shaping the future of insurance towards a more digital, efficient, and customer-centric approach.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Stability | The insurance industry is no longer stable and predictable |
| Profitability | Growth without sacrificing profitability is challenging |
| Climate Change | Climate change is impacting certain risk profiles |
| Customer Expectations | Customers expect products tailored to them |
| Technology | Technology has continued to advance |
| Competition | Competition has intensified |
| Customer Service | Digital self-service tools have improved |
| Efficiency | Automation of manual processes has increased efficiency |
| Cost | The cost of insurance has increased |
| Claims | Claims have increased |
What You'll Learn

Increased use of digital technologies
The increased use of digital technologies has transformed the insurance industry in numerous ways, and this trend is expected to continue in the coming years. Here are some key aspects of this transformation:
Enhanced Data Analytics and Personalization:
Digital technologies, particularly data analytics, have enabled insurers to better understand their customers' needs, preferences, and behaviours. This has resulted in more personalized products, improved customer retention, and increased competitiveness in the market. Data analytics also aids in identifying new opportunities for growth and innovation.
Improved Operational Efficiency:
Digital tools, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), have helped automate repetitive tasks, streamline claims processing, and reduce costs associated with manual processing. This has led to increased operational efficiency and improved overall customer experience.
Digital Customer Engagement:
Insurers have embraced digital channels, such as online portals, mobile apps, and social media, to enhance customer engagement. Customers can now easily access policy information, make changes, and file claims through these digital platforms. Additionally, digital self-service tools and chatbots have improved response times and provided customers with faster and more convenient ways to interact with their insurers.
Innovative Products and Services:
The adoption of digital technologies has led to the development of innovative insurance products and services. For example, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has enabled insurers to offer pay-as-you-go insurance products based on real-time data. Insurers are also leveraging telematics and usage-based insurance (UBI) to provide personalized pricing and encourage safer driving habits.
Digital Collaboration and Partnerships:
Insurers are increasingly collaborating with technology partners, startups, and other industries to develop and implement digital solutions. This includes partnerships with InsurTech companies, which are challenging traditional insurance business models and driving digital transformation in the industry.
Advanced Risk Assessment and Management:
Digital technologies, such as predictive analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), have revolutionized risk assessment and management. Insurers can now use real-time data and advanced analytics to identify risk factors, price their products accordingly, and even shift from a "`detect and repair'" model to a "predict and prevent" approach.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Security:
As insurers embrace digital transformation, they must also navigate the regulatory environment to ensure compliance. This includes addressing concerns related to data privacy and security, especially as more sensitive customer data is stored in the cloud and exposed to potential cyber-attacks.
The increased use of digital technologies has had a profound impact on the insurance industry, and it will continue to shape how insurers operate and interact with their customers in the future.
Incident-to Billing: Unraveling the Insurance Allowance Mystery
You may want to see also

More complex risk profiles
The insurance industry has witnessed tremendous changes over the years, with digital transformation and customer expectations being key drivers. One notable evolution is the development of more complex risk profiles, which has significant implications for the industry.
A risk profile is a quantitative analysis of the threats faced by an individual or organization, and it plays a crucial role in the insurance industry. It helps insurance companies assess the level of risk associated with insuring individuals, properties, or businesses, and determine appropriate premiums. Risk profiling is particularly relevant in commercial insurance transactions, where it ensures adequate insurance coverage. The absence of risk profiling can lead to under-insurance or non-insurance, undermining the value and reputation of the industry.
Risk profiles are becoming more complex due to various factors. Firstly, climate change is irrevocably impacting certain risk profiles, making it essential for insurance executives to make aggressive strategic choices to adapt. Secondly, the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated changes in customer and employee expectations, putting immense pressure on the industry to adjust. Thirdly, the increasing digitization of the economy and the rise of new technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), have transformed the way insurance companies do business. They now have access to vast amounts of data, enabling more sophisticated risk analysis.
The use of advanced technologies, such as AI and deep learning, is expected to play a significant role in shaping risk profiles in the future. These technologies will enable insurers to create more dynamic and personalized risk assessments, taking into account an array of factors, including an individual's behaviour, health data, and lifestyle choices. For example, by 2030, it is predicted that underwriting will be largely automated, with machine and deep learning models analysing internal and external data to make instant decisions on underwriting and pricing. This will result in a shift from the current "detect and repair" model to a predict and prevent" approach, transforming the insurance industry.
In conclusion, the development of more complex risk profiles is a significant change in the insurance industry, driven by technological advancements, shifting customer expectations, and external factors such as climate change and the pandemic. This evolution enables insurers to make more informed decisions, adapt their products and services, and ultimately, better manage risk.
The Intricacies of Insurance: Unraveling the Concept of Contribution
You may want to see also

Higher customer expectations
Over the years, customer expectations have evolved at the rate of digital innovation, and insurance providers are expected to keep up. Customers now expect a digital-first experience from their insurers, with 43% of customers stating they would leave their current provider if it became difficult to obtain support or service. This shift has been reflected in the insurance industry, with customers now expecting to be able to purchase policies online, make payments via mobile apps, and receive real-time updates about their policies.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the change in customer expectations, with customer and employee expectations changing more in 18 months than they did in the previous two decades. This put immense pressure on the industry, with insurers having to adjust practically overnight. As a result, the insurance business, which was once stable and predictable, is now facing a range of challenges.
Insurers are now expected to provide 24/7 support and digital-first experiences, as well as seamless, efficient, and positive interactions with their customers. Customers expect responses within minutes or seconds, and providers are now able to accomplish this using technology.
Insurers are also expected to provide a more personalized experience, with customers wanting tailored services and products. This has been made possible by the use of data analytics, which allows insurers to better understand customer needs and preferences and to identify new opportunities for growth.
The use of digital technology has also driven further transformations in the way insurers do business, with many now using data analytics to identify new revenue opportunities and develop more personalized products. For example, the use of the Internet of Things (IoT) is providing new opportunities for insurers to offer pay-as-you-go insurance products based on real-time data.
In addition, the rise of InsurTech companies has forced traditional insurers to re-think their business models and embrace digital transformation. InsurTech companies are using new technologies to challenge the traditional insurance business model and are starting to partner with insurers to offer their products and services to a wider audience.
Overall, the changing customer expectations have had a significant impact on the insurance industry, with insurers having to adapt their business models and strategies to meet the new demands. By leveraging data-driven decision-making and digital technologies, insurers can improve customer engagement, streamline operations, and drive growth.
Understanding Insurance Billing Cycles: When to Expect Your Next Premium Payment
You may want to see also

Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the insurance industry, with far-reaching consequences for both insurance providers and their customers.
Impact on Insurance Providers
The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital technologies in the insurance sector, with companies investing in new technologies to improve operational efficiency and customer experience. This has led to a greater focus on data analytics, automation, and online sales and services. The move towards digital transformation has helped insurers streamline operations, enhance customer engagement, and create new business opportunities.
The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of cybersecurity and regulation protocols to protect against cyber-attacks as more business is conducted online. Additionally, the insurance industry has had to adapt to changing customer expectations, with a growing demand for personalized digital experiences and 24/7 support.
Impact on Customers
The pandemic caused a substantial shift in policy sales and payouts for insurance providers. Initially, there was an expected surge in the purchase of life insurance policies due to rising infection rates and uncertainty. However, this trend took longer than anticipated, with applications rising by only 1% in the second quarter of 2020 compared to the previous year. Financial hardships and high unemployment rates during this period may have contributed to the delay in application growth.
As the pandemic progressed, life insurance applications picked up significantly, particularly among individuals under the age of 45. Online applications and purchases played a crucial role in driving this growth, with consumers embracing digital adoption due to lockdowns and health concerns.
The pandemic also led to an increase in payouts for insurance companies, especially in the life insurance sector. The high death toll from COVID-19, particularly among older adults, resulted in life insurance companies paying out over $90 billion in 2020, a 15.4% increase compared to 2019. This was the largest year-over-year rise since the 1918 influenza pandemic.
Long-Term Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic has had lasting effects on the insurance industry, even as vaccination rates rise and the economic recovery continues. Insurance companies are embracing new digital practices and trends to meet evolving customer expectations and remain competitive. There is an increased focus on offering personalized experiences, value-added services, and non-monetary benefits to customers.
The pandemic has also accelerated the consolidation and merger and acquisition (M&A) activity in the insurance industry. Companies that have embraced automated processes and digital transformation initiatives have become attractive acquisition targets. Additionally, supply chain disruptions due to the pandemic have created new challenges for underwriters, leading to delays in auto and homeowners' insurance claims and contributing to the rising cost of claims.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound and lasting impact on the insurance industry, changing the way insurance providers operate and interact with their customers. The acceleration of digital transformation, the shift in customer expectations, and the increase in claims and payouts are some of the key impacts that have shaped the industry in recent years.
The Fine Line Between Insurance and Utility Bills: Understanding the Difference
You may want to see also

Growth of Insurtech
The growth of Insurtech, or Insurance Technology, has been driven by the increasing adoption of technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and cloud computing. Insurtech helps insurers collect, analyse and streamline customer data, allowing them to target the right customers with affordable price quotations. It also aids in making better predictions of consumer needs and improving decision-making and insurance planning.
In 2021, the global Insurtech market size was valued at $9,415.28 million, and it is projected to reach $158,994.52 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 32.7% from 2021 to 2030. This growth is fuelled by the rapid digitalization of business models, with insurance companies leveraging innovative digital solutions to scale their businesses and develop more personalised customer experiences.
Insurtech platforms enable insurance companies to achieve proper data and risk management, improving underwriting accuracy and loss prediction. This results in increased operational efficiency and lower costs for insurance products, ultimately leading to higher profits for insurance providers.
The COVID-19 pandemic positively impacted the Insurtech market, as insurers increased their use of technology and digital solutions. The pandemic also accelerated the rate of digitalization across the insurance industry, with remote working and social distancing measures driving the adoption of advanced technologies.
The health insurance sector is expected to witness the most significant growth in the coming years due to the increasing awareness about healthy lifestyle habits and the need for insurance companies to invest in enhanced technologies within the healthcare domain.
The automotive insurance industry is also undergoing a transformation due to digitization, particularly telematics technology, which provides alternatives to traditional models in determining premiums.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the Insurtech market, driven by emerging economies such as China, India, Singapore, and South Korea, which are investing in innovative business models and cost-effective insurance premium plans.
Insurtech start-ups will play a critical role in the broader ecosystem, which includes venture capital investors, consultants, accelerators, and corporations. However, data security, privacy concerns, and changing regulatory frameworks are expected to be challenges that may hinder the growth of the Insurtech market.
The Unseen Hand: Understanding the Role of Insurance Producers
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The insurance industry has faced tremendous changes in the last few years, with the COVID-19 pandemic, the rise of new technologies, and shifting customer expectations. The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies as insurers had to adjust to remote workforces and expand their digital capabilities to support distribution. This has led to an increase in online applications and purchases of insurance policies, with customers increasingly expecting digital experiences and 24/7 support. The industry is also witnessing a shift from “detect and repair” to “predict and prevent”, with advanced technologies and data analytics being used to enhance decision-making, lower costs, and improve customer experiences.
The insurance industry has faced several challenges in recent years, including increased competition, regulatory changes, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic resulted in higher payouts for life insurance companies and changed customer behaviour, with a rise in online applications and purchases. Insurers also need to navigate the challenges posed by new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), which are disrupting traditional business models. Additionally, the heavy regulation of the industry means that digital transformation can be difficult to navigate without falling foul of existing regulations.
Digital transformation offers several benefits to the insurance industry, including improved customer engagement, increased efficiency, and new revenue opportunities. By leveraging data analytics, insurers can develop more personalised products, automate manual processes, and streamline claims processing, resulting in reduced costs and improved customer retention. Digital technologies also enable insurers to identify new revenue streams, such as pay-as-you-go insurance products based on real-time data. Furthermore, digital transformation enhances fraud detection, improves risk management, and enables better decision-making through predictive analytics.







