Life insurance is an important financial safety net for your loved ones, but how long does it last? The answer depends on the type of policy you choose. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10 to 30 years, while permanent life insurance offers lifelong protection with a cash value component. When selecting a term length, consider your financial responsibilities, such as mortgage payments, children's education, and income replacement needs. Additionally, factors like age, health, and eligibility can influence the term length you qualify for. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision about the duration of your life insurance coverage.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
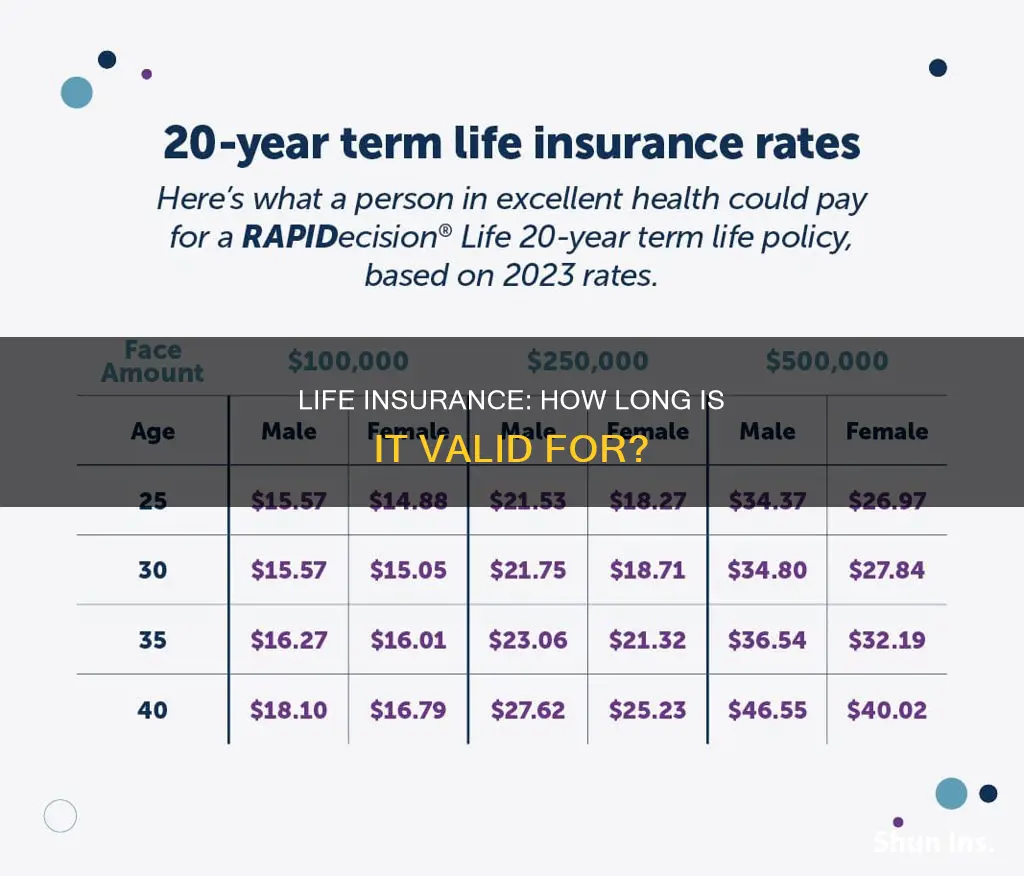
| Typical term lengths | 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40 years |
| Term length factors | Financial responsibilities, mortgage, children's education, retirement age |
| Permanent life insurance | Whole life, universal life |
| Permanent life insurance benefits | Death benefit, cash value account, tax advantages |
| Permanent life insurance drawbacks | Higher premiums, smaller payout if borrowing against policy |
| Term life insurance | Cheaper, set period of time |
| Annual renewable term life insurance | More costly in the long term, good for improving health to qualify for another policy |
| 5-year term life insurance | Covering temporary financial obligations |
| 10-year term life insurance | Older adults with shorter time periods |
| 20-year term life insurance | New parents, single-income families |
| 30-year term life insurance | Long-term financial obligations, e.g. mortgage, parents of young children |
| 40-year term life insurance | Less common, but available |
What You'll Learn

Term life insurance
When selecting a term life insurance policy, it is essential to consider factors such as financial obligations, family situation, long-term goals, and affordability. Financial obligations include outstanding debts like mortgages, student loans, or credit card balances, while family situation takes into account factors like a spouse's employment status and the expected cost of children's education. Long-term goals refer to significant expenses like a child's college education, and affordability relates to the level of insurance premiums that fit within an individual's budget.
However, there are also disadvantages to term life insurance. One notable drawback is the lack of cash value accumulation. Unlike permanent life insurance, term life insurance does not build cash value over time. Additionally, renewal or conversion of a term life insurance policy can result in sticker shock, with significantly higher premiums due to increased age and health risks.
In conclusion, term life insurance is a popular choice for individuals seeking affordable and flexible coverage for a specific period. By tailoring the term length to their financial situation and goals, individuals can ensure their loved ones are financially protected during the times they need it most.
AD&D Life Insurance: Scam or Legit?
You may want to see also

Permanent life insurance
Whole life insurance is one of the most common types of permanent life insurance. It covers you for your entire life, and the premiums remain the same even as your age and health change. You will also earn cash value on your policy, giving you another financial tool to help you achieve your goals.
Universal life insurance offers more flexibility than whole life insurance. It still provides a death benefit and allows your policy to accumulate cash value, but you have the option to adjust your premiums or raise/lower your death benefit amount within limits.
Variable universal life insurance works like universal life insurance but offers more flexibility in how the cash value is managed. You can invest your cash value in sub-accounts tied to the market, allowing it to grow more than it might with other permanent life insurance policies. However, because the sub-accounts are tied to the market, the value of your cash value could also decline.
The main benefit of permanent life insurance is that it lasts through the policyholder's entire life cycle. It also offers a cash value component and a handful of retirement planning benefits. However, permanent life insurance is more expensive than term life insurance for the same death benefit. As a result, some people may choose to buy a mix of term and permanent life insurance.
Life Insurance: Smart Investment or Money Pit?
You may want to see also

Whole life insurance
One of the key features of whole life insurance is its cash value component. A portion of the premiums paid goes into an investment account that grows over time, tax-free. This cash value can be accessed by the policyholder through loans or withdrawals. The cash value can be used for various purposes, such as supplementing retirement income or making large purchases. However, withdrawals and outstanding loans reduce the death benefit.
Group Life Insurance: Contestability and You
You may want to see also

Universal life insurance
The cash value of a universal life insurance policy earns interest at a rate set by the insurer, and this rate can change frequently. There is usually a minimum interest rate that the policy can earn. If interest rates drop, the cash value may not perform well. Unlike whole life insurance, universal life insurance does not guarantee a fixed rate of return.
Freeze Life Insurance Payments? Here's What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Life insurance for mortgage payments
Life insurance is often taken out following a major life milestone, such as getting married or becoming a parent. It is also common to take out life insurance when you take on a large financial obligation, like buying a home.
Life insurance for mortgage protection is a reliable way to establish financial stability and secure a home for your family. It ensures that the financial debt you owe toward your home can be paid off if something happens to you.
There are two main options for using life insurance to cover your home mortgage:
Option 1: Using one policy
You can purchase a term life insurance policy with a benefit amount that matches the outstanding balance of your mortgage. This policy lasts for the full term of your mortgage (usually 30 years). In the event of your passing, your family can use the death benefit to either pay off the mortgage or make continued mortgage payments.
Option 2: Using two policies
You can purchase a whole life insurance policy to provide long-term coverage that fits your financial situation. In addition, you can take out a term life insurance policy to cover the balance of your mortgage for the early period (10 to 15 years) when the amount owed is the highest. This will allow your family to pay off the mortgage or continue making payments if something happens to you.
It is important to remember that you have financial obligations beyond your mortgage, so you will probably want any coverage to cover additional expenses. Childcare, saving for retirement, and medical expenses also need to be considered when purchasing your life insurance policy. Your coverage should take the entire range of your financial needs into account.
California Prison Guards: Life Insurance Coverage Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Term life insurance policies typically last between 10 and 30 years, but you can also find shorter and longer terms ranging from one to 40 years.
The duration of your financial commitments will generally determine how long your life insurance policy should last. You should also consider factors such as your age, mortgage or debt, dependents, and income.
Yes, you can usually renew your policy on a year-to-year basis until you are 95 years old. However, the insurance company will typically increase your premium with each renewal.
If you need continued coverage, you can convert your term policy to a permanent policy or purchase a new term life insurance policy. Permanent policies provide coverage for life and include a cash value component, while term policies are pure life insurance products that only provide coverage for a specific term.







