Car insurance rates are determined by a multitude of factors, including age, driving history, location, and vehicle type. While some of these factors are beyond an individual's control, there are ways to obtain a lower rate. Comparing quotes from multiple companies, adjusting coverage options, and taking advantage of discounts are all strategies for reducing car insurance costs. It is also important to note that rates can vary significantly between companies, so shopping around is crucial for finding the best price.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Age | Younger and inexperienced drivers pay more than older and more experienced drivers. Rates start to decrease around age 25 and increase again around age 70. |
| Gender | Men tend to pay more than women as they are more likely to engage in riskier driving behaviours. |
| Driving Record | Drivers with a clean driving record pay less than those with speeding tickets, DUIs, or at-fault accidents on their records. |
| Credit Score | Drivers with poor credit pay more than those with good credit as they are seen as more likely to file claims. |
| Location | Urban areas tend to have higher rates than rural areas. Florida and Louisiana are among the most expensive states for car insurance. |
| Vehicle Type | The type of vehicle insured impacts the insurance rate. Certain safety and anti-theft features can help reduce rates. |
| Coverage Options | Collision and comprehensive insurance are optional but increase the rate. Higher coverage limits also increase the rate. |
| Discounts | Insurance companies offer various discounts, such as good student discounts and low-mileage discounts, which can reduce the rate. |
What You'll Learn

How much different are auto insurance rates by age?
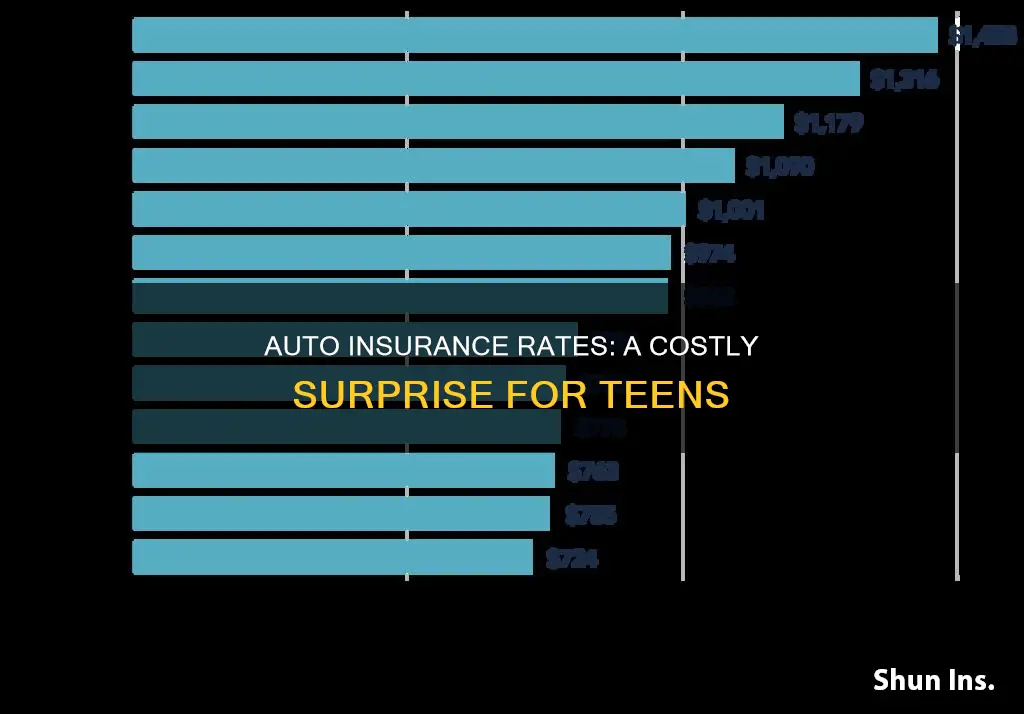
Age is a significant factor in determining car insurance rates. The cost of car insurance is highest for young and new drivers, particularly males, due to their lack of experience and the higher statistical risk of accidents. This risk is reflected in the insurance rates, with 16-year-olds paying an average of $3,192 per year for minimum coverage and $3,192 per year for full coverage. The gap between insurance premiums for males and females under 20 is around 14% and narrows to just 1% once drivers reach middle age.
As drivers mature and gain experience, premiums typically decrease. Drivers in their 20s can save around 9% on their car insurance, and rates continue to drop each year until the driver turns 25, when they can expect a discount of about 14%. Drivers over the age of 70 are considered riskier to insure again, as they have a higher car crash death rate than middle-aged drivers, and their insurance rates increase.
While age is a crucial factor, other factors also impact car insurance rates. These include location, driving history, vehicle type, credit score, and gender, which has a more considerable effect on young drivers under 25.
Insurance Risks: Driving Without a License
You may want to see also

How much different are auto insurance rates by gender?
The cost of auto insurance is influenced by a variety of factors, and gender is one of them. While the impact of gender on insurance rates is a controversial topic, with some states even banning the use of gender in rate calculations, it is evident that males generally pay more for auto insurance than females, especially during their teenage and young adult years. This difference in pricing is primarily due to the increased risk associated with male drivers, who are statistically more prone to accidents, speeding, and DUI convictions.
The gender gap in auto insurance rates is most prominent during the early years of driving. On average, female drivers between the ages of 16 and 24 pay around $500 less per year than their male counterparts. This disparity narrows down as drivers mature and gain experience, with rates becoming more comparable around the age of 25. However, it is worth noting that the gap doesn't completely disappear, and male drivers may still pay slightly higher rates in some cases.
The impact of gender on auto insurance rates is not consistent across all states. In California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Michigan, Montana, North Carolina, and Pennsylvania, gender is not a factor in determining insurance rates. These states have banned the use of gender as a pricing factor, ensuring that rates are unisex. On the other hand, in states that do consider gender, the difference in costs can vary. For example, in North Carolina, males pay about $3 more per year, while in Louisiana, they pay a staggering $404 more than females.
While the primary reason for the gender gap in auto insurance rates is the increased risk associated with male drivers, other factors also come into play. Male drivers tend to drive more miles, engage in riskier driving behaviors, and are less likely to wear seatbelts, all of which contribute to higher insurance rates. Additionally, the make and model of the vehicle, driving record, distance driven, location, marital status, and credit score (where applicable) are all factors that insurance companies take into account when determining rates.
It's worth noting that the debate around the use of gender in auto insurance rates is ongoing, with advocates arguing that it is discriminatory while insurance companies defend it as a fair practice based on actuarial research. As gender rights and equality issues gain prominence, it is likely that more states will move towards eliminating gender as a factor in insurance rate calculations.
Geico Auto Insurance: SSN-Free Coverage in Texas
You may want to see also

How much different are auto insurance rates by driving record?
A person's driving record is one of the biggest factors in determining their auto insurance rates. A clean driving record with no accidents or violations generally results in lower insurance premiums. Conversely, a history of accidents, traffic violations, or other infractions can lead to increased rates.
In the US, most states use a points system to codify the severity of various driving violations. Moving violations, such as speeding, are generally considered more severe as they are seen as having a higher potential to cause damage or harm. These violations are typically assigned a certain number of points, and accumulating a certain number of points within a given period (usually 18 months) can result in a suspended license. For example, in California, a driver's license will be suspended if they accumulate 4 points in a year, 6 points in two years, or 8 points within three years.
The impact of driving violations on insurance rates varies depending on the company and state regulations. Minor violations, such as speeding tickets, can increase insurance premiums by 10 to 15 percent. More serious violations, such as driving under the influence (DUI) or driving while intoxicated (DWI), can result in substantial increases in insurance rates or even refusal of coverage. For example, one accident can increase auto insurance rates by an average of $80 per month, while one speeding ticket can raise rates by $45 per month.
In addition to driving records, other factors that can affect auto insurance rates include age, gender, the type of car driven, location, and credit score. Younger and less experienced drivers are generally considered higher-risk and may pay higher insurance rates. Women tend to pay less for auto insurance than men, as they are statistically involved in fewer and less severe accidents. The cost and safety features of a car can also impact insurance rates, as can the location of the driver, with urban drivers often paying higher rates due to higher rates of vandalism, theft, and accidents.
To mitigate the impact of a less-than-perfect driving record on auto insurance rates, individuals can consider taking a defensive driving course, maintaining a clean record for an extended period, shopping around for quotes from multiple insurance providers, and improving their credit score.
Calculating Vehicle Repair Insurance Claims
You may want to see also

How much different are auto insurance rates by credit score?
Auto insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores to help them decide on the premium a customer will pay. While it's only one of many factors that go into determining the rate, having good credit can help save money.
Credit-based insurance scores are different from the credit scores that most people are familiar with. While credit scores try to predict the likelihood that a consumer will be late on a payment, credit-based insurance scores try to predict the likelihood that a consumer will file insurance claims that will cost the company more money than it collects in premiums.
Auto insurance companies can, and often do, consider credit history or use a credit-based insurance score before offering coverage. However, it's only one piece of the puzzle, as insurance companies are generally prohibited from making decisions solely based on credit history.
Drivers with poor credit pay $144 per month more for full coverage than those with good credit, on average. Poor credit raises rates by 88% compared to having good credit.
On average, drivers with poor credit pay 114% more for full coverage car insurance than those with excellent credit. Someone with an excellent credit score of 800 or above pays an average annual rate of $1,988 for full coverage car insurance. In contrast, someone with a poor credit score may pay an average of $4,262 or more.
Drivers with poor credit in New York pay one of the highest average rates for full-coverage car insurance at $7,506 per year.
Credit-based insurance scores generally put different weights on factors compared to other scores. Here's a breakdown of how FICO weighs insurance credit scores, according to the Department of Insurance, Securities and Banking:
- Payment history (40%)
- Outstanding debt (30%)
- Length of credit history (15%)
- Pursuit of new credit (10%)
- Credit mix (5%)
Some states—including California, Hawaii, Washington, Massachusetts, and Michigan—strictly limit or entirely prohibit insurance companies' use of credit information in determining auto insurance rates. In these states, credit scores don't affect insurance rates, no matter how good or bad they are.
Missouri Insurance Gap: What's the Deal?
You may want to see also

How much different are auto insurance rates by vehicle?
The make, model, and age of a vehicle are some of the most significant factors in determining the cost of auto insurance. The cost of insurance is influenced by the average cost of claims for various vehicle types. As a result, luxury vehicles with cutting-edge technology and advanced safety features are typically more expensive to insure because they are more expensive to repair or replace.
The brand of the vehicle also affects insurance premiums. According to Quadrant Information Services, Dodge has the highest car insurance costs on average, while Mazda has the lowest.
The age of a vehicle can also have a considerable impact on insurance premiums, especially for drivers under 25 or over 75. Insurance companies view younger and older drivers as riskier to insure due to their higher likelihood of accidents.
In addition to the type and age of the vehicle, other factors such as safety ratings, likelihood of theft, and sportiness can also influence insurance rates. Safer cars with better safety ratings tend to have lower insurance premiums. Certain vehicles, such as the Honda Accord and Chevy Impala, are frequently targeted by thieves, which drives up insurance prices. Sportier cars may also lead to higher insurance rates as they encourage speeding and increase the risk of collisions.
When determining insurance rates, insurers also consider the vehicle's features, such as upgraded trims or extra options. These additions can increase the vehicle's MSRP and, consequently, the insurance premium.
Overall, the cost of auto insurance varies depending on the make, model, age, and features of the vehicle, among other factors.
Auto Insurance and Death: Uncovering the Hidden Benefits
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Auto insurance rates differ by age because younger and inexperienced drivers are considered to be high-risk. Teenagers and young adults tend to pay more for auto insurance than drivers in their 40s, 50s, or 60s. Rates start to decrease around age 25 as drivers gain more experience and are less likely to be involved in accidents. Rates may increase again around age 70 as senior drivers may experience decreased reaction time and poorer eyesight.
In most states, auto insurance rates differ by gender, with men typically paying more than women. This is because men are generally considered to engage in riskier driving behaviors and have a higher rate of accident severity. However, the difference in rates between men and women tends to decrease after age 25. Additionally, some states, such as California, Hawaii, and Massachusetts, prohibit the use of gender as a factor in determining rates.
Auto insurance rates can differ significantly based on an individual's driving record. Drivers with a clean driving record will usually pay lower rates than those with speeding tickets, accidents, or DUI convictions. An at-fault accident or DUI conviction can result in a significant increase in insurance rates, with DUI convictions often having a more substantial impact.
Auto insurance rates can vary based on an individual's credit score. Drivers with poor credit scores are perceived as higher-risk and may pay significantly more for auto insurance than those with good credit scores. This is because insurance companies believe that individuals with poor credit scores are more likely to file claims. However, some states, such as California and Massachusetts, prohibit or limit the use of credit scores in determining insurance rates.
Auto insurance rates can differ based on the type of vehicle being insured. Factors such as the vehicle's make, model, age, safety features, repair costs, and safety ratings can all impact insurance rates. Generally, more expensive or luxury vehicles, as well as SUVs and sports cars, tend to have higher insurance rates due to higher repair costs and the potential for more severe accidents.







