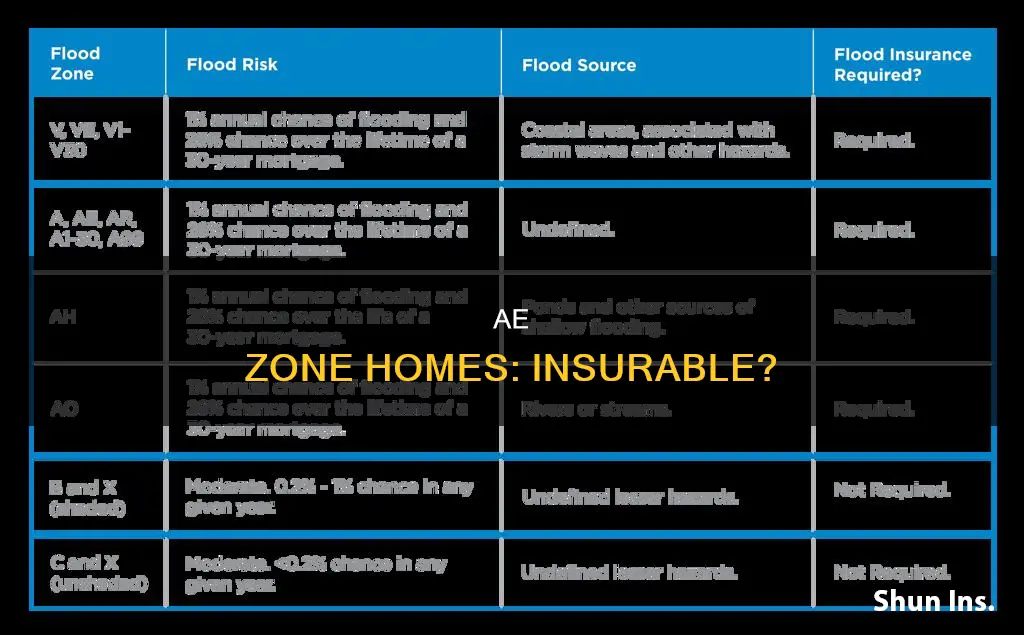
Flooding is one of the most destructive and costly hazards for homeowners. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), just one inch of water can cause up to $25,000 worth of damage to a home. Flood zones are geographic areas with a heightened risk of flooding, and they are classified according to their level of risk and the potential severity of flooding. Zone AE is one of the most common high-risk flood zones in the United States. It is also known as a Special Flood Hazard Area, with a 1% chance of flooding per year and a 26% chance over the life of a 30-year mortgage.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Risk of flooding | 1% chance of flooding per year; 26% chance of flooding during a 30-year mortgage |
| Proximity to bodies of water | Close to floodplains, rivers, and lakes; low-lying areas without bodies of water may also be included |
| Wave action | Expected to be less than 1.5 feet high |
| Building regulations | The elevation of the lowest floor must be at or above the zone's base flood elevation (BFE); enclosed areas below the BFE or lowest floor cannot be used as living spaces; electrical, plumbing, and HVAC equipment must be elevated to or above the BFE |
| Insurance requirements | Flood insurance is required for properties with federally-backed mortgages; the average cost of flood insurance in Zone AE is $852 per year |
What You'll Learn

What is an AE flood zone?
AE flood zones are areas that present a 1% annual chance of flooding and a 26% chance of flooding over the life of a 30-year mortgage. They are considered high-risk flood zones and are also known as Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHA). These zones are prone to flooding and are typically located near bodies of water, such as floodplains, rivers, and lakes. However, some AE flood zones may also include low-lying regions without large bodies of water.
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) regularly publishes detailed flood maps, known as Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs), to help homeowners, government officials, and insurance companies assess flood hazards. These maps are essential tools for determining flood risk and understanding the specific flood zone of a property. The maps outline various flood zones, including AE zones, and provide information about base flood elevations.
Properties located in AE flood zones are typically required to carry flood insurance due to the high risk of flooding. This requirement is typically mandated by mortgage lenders or FEMA itself. The flood insurance serves to protect the property's value, structure, and integrity in the event of a flood disaster.
It's important to note that flood zones, including AE zones, are now primarily used as a regulatory measurement to determine whether flood insurance is mandatory for a property. They are no longer directly used to calculate flood insurance premiums, as the NFIP's Risk Rating 2.0 program has shifted to considering other factors such as distance to water, the type of flood, and the elevation of the property.
AE flood zones are designated as high-risk areas due to the significant probability of flooding. These zones are carefully studied and monitored to ensure that homeowners, lenders, and insurance providers can make informed decisions regarding flood preparedness and mitigation.
House Insurance Payouts: Taxable?
You may want to see also

How do I know if my house is in an AE flood zone?
To know if your house is in an AE flood zone, you can refer to the flood maps published by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). FEMA regularly publishes detailed flood maps for over 20,000 communities across the U.S. to help homeowners, government officials, and insurance companies keep track of flood hazards. By entering your address at the FEMA Flood Map Service Center, you can view your city's flood map and identify your home's designated flood zone.
Flood zones are geographic areas with heightened risks of flooding, and most are located near bodies of water. Every zone is classified according to its level of risk and the potential severity of flood events. The most hazardous flood zones, including AE, begin with the letters A or V, according to the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP).
AE flood zones are considered high-risk areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding and a 26% chance of flooding over the life of a 30-year mortgage. These zones are typically located near floodplains, rivers, and lakes, but low-lying regions without large bodies of water may also fall under this designation.
By consulting FEMA's flood maps and understanding the associated terminology, you can determine if your house is located in an AE flood zone and take appropriate steps to protect your property and consider flood insurance options.
Farmers Insurance: Has the Harvest Begun?
You may want to see also

Do I need flood insurance for a house in an AE flood zone?
If your house is in an AE flood zone, it is in a high-risk flood zone. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), there is a 1% chance of flooding in this zone annually and a 26% chance during a 30-year mortgage.
If your property is in an AE flood zone and you have a federally-backed or government-backed mortgage, your mortgage loan requires you to have flood insurance. This is to ensure that the property's value, structure, and integrity are protected and preserved in the event of a flood.
Even if you don’t have a mortgage, it is still a good idea to consider purchasing flood insurance for your home in an AE flood zone. Homeowners insurance does not typically cover flood damage, and the cost of repairing or replacing items due to flood damage can be very high.
The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) is the main flood insurance provider in the United States. The average cost of NFIP flood insurance is $700 a year generally and $852 a year in zone AE. Insurance rates increase with risk, so flood zone AE rates are higher than those in lower-risk zones.
Farmers Insurance and Earthquake Loss Assessment: Understanding Your Coverage
You may want to see also

How much does flood insurance cost in an AE flood zone?
Flood insurance is generally required for homes in Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs), which are areas with a high-to-extreme risk of flooding. Zone AE is one such SFHA, with a 1% chance of flooding in any given year or a 26% chance during a 30-year mortgage period.
The average cost of flood insurance in Zone AE is $934 as of July 2023, according to FEMA. However, the cost of flood insurance can vary depending on several factors, including the age of the structure, the foundation type, flood loss history, and the elevation of the home. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) uses a unique combination of rating variables for each property to reflect its flood risk.
The NFIP offers federal flood insurance, but private flood insurers often sell cheaper policies with higher coverage limits. According to one study, homeowners can save 20-40% on their flood insurance premiums by purchasing from a private flood carrier.
Additionally, there are several ways to lower your flood insurance rates. These include:
- Elevating your house
- Moving water heaters and other systems to higher ground
- Filling in basements and crawl spaces
- Installing flood openings or barriers
- Increasing your policy deductible
- Community-wide discounts
- Using an elevation certificate to prove your home is above the Base Flood Elevation
Farmers Insurance Open Playoff: Where to Watch the Thrilling Conclusion
You may want to see also

What building regulations are there for houses in an AE flood zone?
Building in an AE flood zone comes with numerous regulations laid out by the American Society of Civil Engineers. Here are the key building regulations for houses in an AE flood zone:
- The elevation of the lowest floor: The lowest floor in a structure must be at or above the zone's base flood elevation (BFE). The BFE refers to the elevation that floodwaters are expected to rise to during a base flood event (a flood with a 1% chance of occurring in any given year).
- Enclosed areas below the BFE: Enclosed areas below the BFE or lowest floor cannot be used as living spaces, including basements. This means no sheetrock, bathrooms, or mechanical equipment can be located below the BFE. The space beneath the finished floor must contain flood vents to allow water to flow in and out, relieving the pressure of water pushing against the house.
- Electrical, plumbing, and HVAC equipment: All electrical, plumbing, and HVAC equipment must be elevated to or above the area's BFE to minimise the risk of water damage.
- Foundation requirements: The building foundation must be passive, allowing water to flow in and out easily. This can be achieved through flood vents placed within foundation walls.
- Renovation restrictions: The 50% rule applies to renovations in the flood zone. This means that if the cost of renovations exceeds 50% of the value of the existing structure, the entire building must be brought up to comply with FEMA regulations.
- Insurance requirements: Flood insurance is mandatory for properties in AE flood zones. This is to protect the property's value, structure, and integrity in the event of a flood disaster.
- Design and materials: When designing and constructing a home in a flood zone, it is important to select building materials that can withstand water damage and flowing water impacts. This includes choosing the appropriate foundation type for the specific flooding risks and state/city requirements.
It is essential to consult FEMA's flood maps and work with local professionals to ensure that any building or renovation project in an AE flood zone complies with all the necessary regulations.
Volcano-Proof Home Insurance: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Flood zones are geographic areas that face heightened risks of flooding, most of which are located near bodies of water. Every zone is classified according to its level of risk and the potential severity of flood events.
Zone AE is a high-risk flood zone that’s close to floodplains and bodies of water, like rivers and lakes. It has a 1% chance of flooding annually and a 26% chance during a 30-year mortgage.
The designation between AE and AE Coastal Zones is directly related to wave action. In an AE Zone, the wave action is expected to be less than 1.5 feet high. In an AE Coastal Zone, waves are expected to be larger, about 1.5–3 feet high.
The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) has strict requirements for buildings in high-risk flood zones. The three most noteworthy regulations for homes in flood zone AE are:
You can’t use enclosed areas below your lowest floor or the zone’s BFE as living spaces, including basements.
Is flood insurance required for houses in Zone AE?







