The average cost of car insurance varies depending on factors such as age, location, credit score, driving record, coverage level, and vehicle type. In the US, the national average cost of car insurance is $72 per month for minimum coverage and $223 per month for full coverage. However, these rates can differ significantly based on individual factors. For example, in Louisiana, the average annual cost of full coverage car insurance is $2,883, while in Maine, it is $1,175. Similarly, age plays a role, with younger drivers typically paying higher rates due to their lack of driving experience. Additionally, factors such as gender, vehicle type, and driving record can influence rates, with male drivers, sports car owners, and those with a history of accidents or speeding tickets often facing higher premiums.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average cost of car insurance in the U.S. | $72 per month for minimum coverage and $223 per month for full coverage |
| Average cost of car insurance by state | Louisiana, New York and Michigan are the most expensive states for full-coverage car insurance, while Maine, Vermont and Hawaii are the cheapest. |
| Average cost of car insurance by provider | USAA offers the lowest full-coverage insurance rates on average at $145 per month, but this coverage is only available for military members and their families. |
| Average cost of car insurance by age | Younger drivers with their own insurance policies tend to pay the most for car insurance. Seniors older than 75 also pay slightly higher rates overall than those between 25 and 55 years old. |
| Average cost of car insurance for high-risk drivers | Drivers with a history of speeding tickets, at-fault accidents or other violations in their driving history pay higher premiums than those with clean records. |
| Average cost of car insurance by vehicle type | The type of vehicle you drive plays a role in setting your car insurance rates. |
What You'll Learn

The impact of age and gender on insurance rates
Age and gender are two of the main factors that determine auto insurance rates.
Age
Age is an important indicator considered by insurance companies. Premiums tend to go down as you get older, with mature drivers experiencing more savings. The reasoning behind this is that younger drivers are more likely to get into an accident, resulting in higher claims costs. The same is true for seniors; once a person reaches a certain age, they may see insurance rates increase again due to a higher likelihood of being involved in accidents.
Gender
Gender is another factor used by insurers to determine premiums. Men are generally considered a greater threat to road safety than women. They tend to drive more, are more likely to be involved in accidents, and partake in riskier driving behaviours. As a result, males typically pay more for auto insurance than females.
However, the impact of gender on insurance rates varies by age. While men tend to pay more than women overall, the gender gap in rates narrows as drivers get older and gain more driving experience. In some age groups, women may even pay slightly more than men. Additionally, in certain states, insurers are prohibited from using gender as a factor in determining insurance rates.
In summary, age and gender can significantly influence auto insurance rates, with younger and male drivers often facing higher premiums due to perceived higher risk.
Auto Insurance: Canada's Requirement
You may want to see also

How location affects insurance rates
The location where one resides plays a significant role in determining auto insurance rates. Insurance companies use data to determine which areas have the highest likelihood of claims and use this information to set rates. The state, city, and ZIP code of the policyholder can increase or decrease their insurance rate.
Frequency of Claims in Your Area
Insurance companies designate areas with a high frequency of auto insurance claims as high-risk neighbourhoods. To offset their potential costs, insurance companies will quote higher premiums in those areas. A high-population area means a higher chance of car accidents. The chances of being in an accident are much higher in an urban area than in a rural one with less-populated roads.
Weather Conditions
Harsh weather conditions such as heavy rain, hail, or snow can lead to a higher chance of accidents. If you live in an area prone to flooding or harsh weather, the potential payout that a car insurance company would have to make with multiple policyholders can increase your premium to offset costs.
Crime Rates
If you live in a city or neighbourhood with frequent incidents of vandalism or theft, your insurance company will take that into account when calculating your rate. Areas with high unemployment rates may also result in higher insurance rates, as people may forego car insurance due to budget constraints.
Road Conditions
Roadways in poor repair or with dangerous intersections increase the odds of accidents, resulting in higher car insurance costs.
Population Density
Population density also affects insurance rates. Urban cities tend to have higher insurance rates than rural areas due to the increased threat of collisions, theft, or claims.
State Requirements
The minimum auto insurance limits required by your state can also increase your rates. For example, Michigan law promises unlimited protection for personal injuries, and its state law requires auto insurance companies to pay the victim of an accident up to three years of lost wages, resulting in some of the highest insurance rates in the country.
Auto Insurance for Caregivers: Michigan's Unique Requirements
You may want to see also

How driving history affects insurance rates
A driver's history is a key factor in determining their auto insurance rates. Insurance companies assess a driver's risk by looking at their driving record, which includes their history of moving traffic violations and at-fault accidents. A single accident can have a significant effect on insurance premiums, even if the driver was not at fault. Speeding tickets, distracted driving, and other moving violations can also increase insurance rates, with the increase depending on how much over the speed limit the driver was travelling.
Serious moving violations, such as speeding tickets and DUI offences, signal to insurance providers that a driver is more likely to be involved in a claim and raise the odds that premiums will rise. The more tickets accumulated, the higher the rates will be. For younger drivers, who pose a higher risk to insurers, a single speeding violation can even double or triple premiums. Most carriers will increase premiums for three years following a serious moving violation conviction and might also do so for an at-fault accident.
Insurance companies also take into account a driver's age, address, gender, credit score, and the type of car they drive when assessing risk. Teenage drivers, for example, will always pay high rates for auto insurance due to their minimal driving history and their young age, which places them in a high-risk class.
Insurers are in the business of assessing risk. If a driver's history is riddled with multiple examples of poor judgment and unsafe driving habits, insurance companies will view them as a high-risk customer and may refuse to provide coverage or do so at an extremely high rate. A clean driving record, on the other hand, will result in lower insurance rates.
Do You Have Auto Insurance? How to Verify Your Coverage
You may want to see also

How credit score affects insurance rates
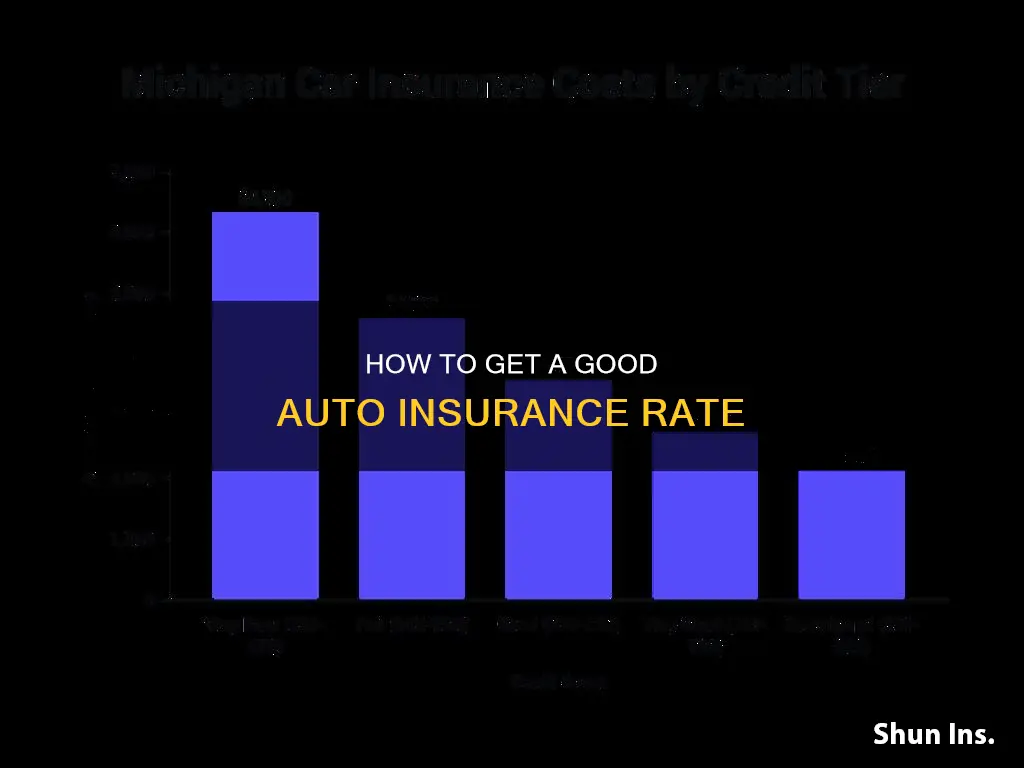
Credit scores have a significant impact on auto insurance rates, with drivers with poor credit often paying much higher premiums than those with good credit. This is because insurance companies believe that drivers with poor credit are more likely to file claims, and they compensate by charging more. In most states, an individual's credit score can influence their insurance rates, but there are exceptions. California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan prohibit or limit the use of credit scores in determining auto insurance rates.
When evaluating an individual's credit history, insurance companies use a credit-based insurance score. While each insurer has its own proprietary formula for calculating this score, common factors that are typically considered include:
- Outstanding debt or amount of current debt
- Length of credit history
- Credit mix, such as credit cards, auto loans, and mortgage loans
- Payment history, including any late payments or delinquencies
- Pursuit of new credit, including recent attempts to open new lines of credit
It's important to note that insurance companies do not use the same credit scores as lenders or credit card issuers. The credit-based insurance score is designed to predict the statistical likelihood of an individual filing insurance claims that cost the company more than it collects in premiums. Improving one's credit score can take time but is worth considering the potential savings on insurance premiums.
Additionally, getting an insurance quote or having insurance coverage does not typically affect an individual's credit score. Insurance companies usually perform a "soft pull" or soft inquiry when checking an individual's credit, which does not impact their credit score. However, missing payments on insurance premiums may be reported to credit agencies and could negatively affect one's credit score.
Auto Insurance Lapse: Is It Worth the Risk?
You may want to see also

How vehicle type affects insurance rates
The vehicle type can affect insurance rates in several ways. Firstly, the make and model of the car influence the insurance rates. The brand of the car, or the manufacturer, is an important factor, as certain brands are associated with different safety systems and features. For example, a Ferrari and a Jeep will have different airbag systems. The model refers to the specific product line offered by the manufacturer, and even similar models are considered separate. Each model has different characteristics, affecting the insurance cost.
The age of the car also plays a role, with newer cars generally having higher insurance costs. However, older collectible cars or classic cars may be an exception, as they can attain greater value over time. The size and weight of the vehicle matter too, with larger and heavier vehicles often having higher premiums since they have a higher potential for damage and pose a greater risk to other road users.
The safety features installed in the vehicle can also impact insurance rates. Cars with features like anti-lock brakes, electronic stability control, and theft prevention systems often have lower premiums because they reduce the likelihood of accidents and protect drivers from costly damages.
Additionally, the cost of repairs and replacement parts for different vehicle types varies. Foreign cars and luxury cars tend to have more expensive parts, resulting in higher insurance costs. Electric vehicles (EVs) are also usually more expensive to insure due to their higher risk of being totalled and the higher cost of repairs.
The likelihood of theft also influences insurance rates, with certain cars being targeted more frequently by thieves. Sporty cars and convertibles are also associated with higher insurance rates, as they are linked to riskier driving behaviour and have higher theft rates.
In summary, insurance companies consider various aspects of the vehicle type when determining insurance rates, including the make, model, age, size, weight, safety features, repair costs, replacement value, and theft risk. These factors collectively contribute to the overall risk assessment and subsequent insurance rates for different vehicle types.
Auto Insurance: Choosing the Right Coverage Limits
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The average cost of car insurance varies depending on the type of coverage you choose. The national average for full coverage car insurance is $2,681 per year or $223 per month, while minimum coverage costs an average of $869 per year or $72 per month.
Many factors influence the cost of car insurance, including your age, gender, location, driving record, credit score, vehicle type, and coverage level.
To get a good auto insurance rate, it is recommended to shop around and compare quotes from multiple insurance providers. You can also consider bundling your home and auto insurance policies, paying your premium in full upfront, taking a defensive driving course, and utilizing discounts offered by insurance companies.