Life insurance is a policy that provides a death benefit payout to beneficiaries if the policyholder passes away while it's active. There are several types of life insurance, each with its own unique features and benefits. Here is an introduction to the seven types of life insurance:
1. Whole Life Insurance: This is a permanent coverage type that lasts the entire life of the policyholder. It is often more expensive upfront but offers guaranteed support for loved ones.
2. Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance is a temporary policy with coverage for a specific term or set amount of time. It is generally more affordable than whole life insurance.
3. Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance is a permanent policy with an investment portion known as the cash value, which grows tax-deferred. It offers flexibility in adjusting premium payments and benefit values.
4. Final Expense Insurance: This type of permanent life insurance offers a smaller death benefit payout to cover funeral costs, burial expenses, and other end-of-life expenses.
5. Group Life Insurance: Group life insurance is offered by employers or organizations to provide benefits for employees or members. It can include term or whole life insurance options.
6. Variable Life Insurance: Variable life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance where the cash value is tied to investment accounts. The cash value can fluctuate based on the performance of those investments.
7. Credit Life Insurance: Credit life insurance helps loved ones pay off large debts, such as mortgages or car loans, in the event of the policyholder's death. The payout is made directly to the lender.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of types | 5 or 8 |
| Examples | Term life insurance, Whole life insurance, Universal life insurance, Variable life insurance, Final expense life insurance, Group life insurance, Mortgage life insurance, Credit life insurance, Supplemental life insurance |
| Main types | Term life insurance, Permanent life insurance |
| Permanent life subtypes | Whole life insurance, Universal life insurance, Variable life insurance, Final expense insurance, Survivorship life insurance/joint life insurance |
| Coverage length | Temporary or permanent |
| Complexity | Simple or complex |
| Coverage amount | Small or large |
| Cash value | Yes or no |
| Flexibility | Flexible or inflexible |
What You'll Learn

Whole life insurance
Withdrawals and outstanding loan balances reduce death benefits. Whole life insurance guarantees payment of a death benefit to beneficiaries in exchange for level, regularly-due premium payments. The policy includes a savings portion, called the “cash value”, alongside the death benefit. In the savings component, interest may accumulate on a tax-deferred basis. Growing cash value is an essential component of whole life insurance.
There are several main types of whole life insurance, categorized based on how premiums are paid. Level Payment policies feature premiums that remain unchanged throughout the duration of the policy. This is the most common type of payment plan. Single Premium policies are those in which the insured pays a one-time large premium, which funds the policy for life. Limited Payment policies allow the insured to pay a limited number of payments. Modified Whole Life Insurance offers lower premiums than a standard policy in the first two or three years, and higher-than-standard premiums in the later years. It is more expensive in the long run.
Life Insurance: Geico's Accelerated Rider Option Explained
You may want to see also

Universal life insurance
- The interest rate for a universal life policy's cash value is not fixed and can change over time based on market conditions.
- A universal life policy's cash value can eventually grow and result in a zero-cost policy, where all premiums are paid from the built-up value.
Policyholders can adjust their premiums and death benefits within certain limits. They can increase the death benefit, although this may require a medical exam, or decrease it to lower their premiums. The cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn partially, usually without tax implications. However, unpaid loans will reduce the death benefit, and if the cash value falls too low, the policy may lapse.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Universal Life Insurance
Advantages:
- Flexible death benefit and premium payments
- Potential for cash value growth
- Ability to borrow against the cash value without tax implications
Disadvantages:
- Risk of large payment requirements or policy lapse if cash value is not monitored
- Returns and interest rates are not guaranteed
- Some withdrawals may be taxed
- Cash value is lost at the policyholder's death
Life Insurance Risk Factors: What Determines Your Premiums?
You may want to see also

Variable life insurance
Variable universal life insurance (VUL) is a type of variable life insurance that offers flexibility. In addition to death benefit protection, VUL allows policyholders to allocate their cash value among a wide range of variable investment options, including purely market-driven and fixed options with guaranteed minimum interest crediting.
DFAS: Life Insurance and Annuities for Survivors
You may want to see also

Final expense insurance
The main drawback of final expense insurance is that its face amount is typically much lower than other types of life insurance. Additionally, while the policy is intended to cover funeral costs, the beneficiary can use the death benefit for any purpose.
VGLI Whole Life Insurance: Is It Worth the Cost?
You may want to see also

Term life insurance
One of the key features of term life insurance is the ability to choose a term length that suits your unique needs and circumstances. For example, you may opt for a shorter term if you anticipate having fewer financial obligations as you age, or a longer term if you want to ensure coverage for a longer period. Additionally, term life insurance offers the flexibility to scale your death benefit up or down with increasing and decreasing term policies.
During the term, your premiums will remain the same, providing stability and predictability. However, if you outlive the term, your policy will lapse, and the insurance company will retain the premium payments. In contrast, if the policyholder passes away during the term, the beneficiary will receive a tax-free death benefit.
There are several types of term life insurance policies available, including fixed term, increasing term, decreasing term, and annual renewable. Fixed term is the most basic and popular option, with static premiums for the duration of the term. Increasing term allows you to increase the value of your death benefit over time, while decreasing term reduces premium payments over time, potentially resulting in a smaller death benefit. Annual renewable term life insurance provides coverage on a yearly basis and must be renewed by the policy end date, with premiums typically increasing each time.
THC Use and Amica Life Insurance: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
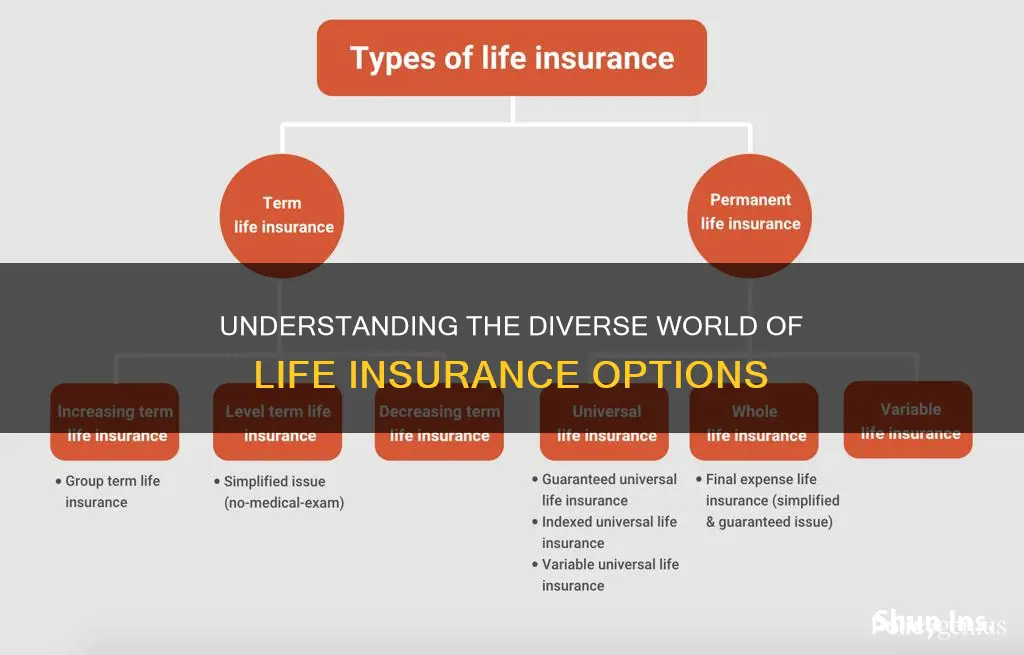
There are two main types of life insurance: term life and permanent life. Term life insurance covers a specified period, such as 1, 5, 10, or 30 years, while permanent life insurance covers the insured person's lifetime. Within these two main types, there are several subtypes of life insurance:
There are two subtypes of term life insurance: level term and decreasing term. Level term life insurance offers a fixed death benefit throughout the policy, while decreasing term life insurance reduces the potential death benefit over the policy's term, typically in one-year increments.
There are several subtypes of permanent life insurance, including whole life insurance, universal life insurance, variable life insurance, and final expense insurance. Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage with fixed premiums and death benefits, while universal life insurance offers more flexibility with adjustable premiums and death benefits. Variable life insurance is a riskier option as the death benefit and cash value fluctuate based on investment performance. Final expense insurance, also known as burial or funeral insurance, is a small policy designed to cover end-of-life expenses such as funeral costs and medical bills.
When choosing a type of life insurance, it's important to consider your budget, coverage needs, and financial goals. Term life insurance is typically more affordable and suitable for specific situations, such as covering a mortgage or providing income replacement for a set period. On the other hand, permanent life insurance offers lifelong coverage and can build cash value over time, making it a good option for long-term financial planning.







