Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company. In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. There are several fundamental principles of life insurance, including the requirement for both the insurer and insured to disclose all material facts relevant to the insurance contract. The insured party must also have a financial stake in the life being insured.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Honesty | Both parties must disclose all material facts relevant to the insurance contract |
| Financial stake | The insured party must have a financial stake in the property or life being insured |
| Peace of mind | Life insurance brings peace of mind knowing there will be financial support for your loved ones |
What You'll Learn
- The insured party must have a financial stake in the life being insured
- The insurer must disclose all features of the policy
- The insured must disclose all information related to the risk
- The insurer must have a clear understanding of the risks involved
- The policy can be voided if information is misrepresented or concealed

The insured party must have a financial stake in the life being insured
One of the fundamental principles of life insurance is that the insured party must have a financial stake in the life being insured. This means that the insured party will suffer financially if the insured person dies. This is also known as having an 'insurable interest' in the life insured.
Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company. In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured's death. This brings peace of mind, knowing there will be financial support for loved ones.
The principle of insurable interest ensures that the insured party has a legitimate reason for purchasing life insurance. It also helps to prevent fraud or abuse of the insurance system. For example, it prevents people from taking out life insurance policies on strangers or people they do not know well, with the intention of profiting from their deaths.
In addition, the principle of insurable interest protects the insurance company from paying out large sums of money to beneficiaries who may not have a genuine need for the financial support. By requiring the insured party to have a financial stake in the life being insured, the insurance company can be confident that the death benefit will be used to cover financial losses or expenses incurred as a result of the insured's death.
Overall, the principle of insurable interest is essential to maintaining the integrity and fairness of the life insurance system. It ensures that life insurance is used for its intended purpose of providing financial protection and support to those who need it.
Employee Life Insurance: Worth the Cost?
You may want to see also

The insurer must disclose all features of the policy
Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company. In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured's death. The insurer must disclose all features of the policy. This is a primary principle of insurance. According to this principle, you have to disclose all the information that is related to the risk, to the insurance company truthfully. You must not hide any facts that can have an effect on the policy from the insurer. If some fact is disclosed later on, then your policy can be cancelled. On the other hand, the insurer must also disclose all the features of a life insurance policy. According to this principle, you must have an insurable interest in the life that is insured. That is, you will suffer financially if the insured dies. The insured party must have a financial stake in the property or life being insured. This principle ensures that the insurer has a clear understanding of the risks involved and can accurately assess the appropriate premium.
Whole Life Insurance at 60: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

The insured must disclose all information related to the risk
Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company. In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. The insured must disclose all information related to the risk. This is a primary principle of insurance. According to this principle, you have to disclose all the information that is related to the risk, to the insurance company truthfully. You must not hide any facts that can have an effect on the policy from the insurer. If some fact is disclosed later on, then your policy can be cancelled. On the other hand, the insurer must also disclose all the features of a life insurance policy. This principle ensures that the insurer has a clear understanding of the risks involved and can accurately assess the appropriate premium.
The principle of full disclosure is based on the concept of utmost good faith, which is a fundamental principle of insurance. It requires both parties to act with honesty and fairness in their dealings with each other. By disclosing all relevant information, the insured can ensure that the insurer has a complete understanding of the risk and can make an informed decision about whether to accept the risk and what terms and conditions to apply.
The insured's duty of disclosure extends beyond the initial application process. It is a continuing duty, which means that the insured must disclose any changes or developments that may affect the risk during the term of the policy. For example, if the insured develops a new medical condition or starts a new high-risk hobby, they must inform the insurer. This allows the insurer to reassess the risk and make any necessary adjustments to the policy.
The insured's failure to disclose all information related to the risk can have serious consequences. It may result in the insurer refusing to pay a claim, cancelling the policy, or voiding the contract. The insurer may also seek to recover any payments made under the policy if it is found that the insured withheld or misrepresented material information. Therefore, it is crucial for the insured to understand their duty of disclosure and provide complete and accurate information to the insurer.
Income Provider Option: Life Insurance's Financial Safety Net
You may want to see also

The insurer must have a clear understanding of the risks involved
Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company. In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. This is a primary principle of insurance. According to this principle, you have to disclose all the information that is related to the risk, to the insurance company truthfully. You must not hide any facts that can have an effect on the policy from the insurer. If some fact is disclosed later on, then your policy can be cancelled. On the other hand, the insurer must also disclose all the features of a life insurance policy. This principle ensures that the insurer has a clear understanding of the risks involved and can accurately assess the appropriate premium.
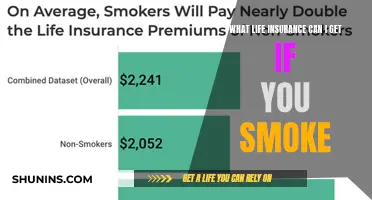
The insurer must be able to accurately assess the appropriate premium for the policy. To do this, they must have a clear understanding of the risks involved. This includes understanding the likelihood of a claim being made and the potential cost of that claim. The insurer will use a range of factors to assess the risk, including the age, health, and lifestyle of the insured. For example, a young, healthy non-smoker is likely to be considered a lower risk than an older person with a serious health condition who smokes.
The insurer must also consider the potential impact of the insured's death on the beneficiaries. Life insurance is intended to provide financial support for loved ones in the event of a death. The insurer must understand the financial needs of the beneficiaries and assess whether the policy will be sufficient to meet those needs. This includes considering the potential loss of income, educational costs, and other expenses.
By having a clear understanding of the risks involved, the insurer can ensure that the policy is appropriately priced and that the insurance company has the financial capacity to pay out claims. This helps to protect both the insurer and the insured, ensuring that the policy is fair and sustainable.
Term vs Life Insurance: Is It Worth the Switch?
You may want to see also

The policy can be voided if information is misrepresented or concealed
Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company. In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured's death. The policy can be voided if information is misrepresented or concealed. This is because the insurance company must have a clear understanding of the risks involved to accurately assess the appropriate premium. Both parties are expected to disclose all material facts relevant to the insurance contract. The insured party must have a financial stake in the property or life being insured. This means that they will suffer financially if the insured dies.
The principle of utmost good faith is a primary principle of insurance. This principle dictates that both the insurer and the insured must disclose all information related to the risk. The insured must not hide any facts that can have an effect on the policy from the insurer. If some fact is disclosed later on, then the policy can be cancelled. On the other hand, the insurer must also disclose all the features of a life insurance policy. This principle ensures that both parties are dealing with each other with the highest degree of honesty and fair dealing.
The principle of insurable interest is also important in life insurance. This principle states that the insured party must have an insurable interest in the life that is insured. This means that they will suffer financially if the insured dies. This principle ensures that the insured party has a financial stake in the life being insured.
The principle of indemnity is another important concept in life insurance. This principle states that the insured party should be compensated for any loss or damage that they suffer. This principle ensures that the insured party is made whole again after a loss or damage. It is important to note that the insurance company's primary duty is to indemnify the insured, not to enrich them.
Whole Life Insurance: A Viable Retirement Option?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance is a contract with an insurance company.
In exchange for premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death.
You must disclose all material facts relevant to the insurance contract.
Any misrepresentation or concealment of information can lead to the voiding of the policy.
The insured party must have a financial stake in the property or life being insured.