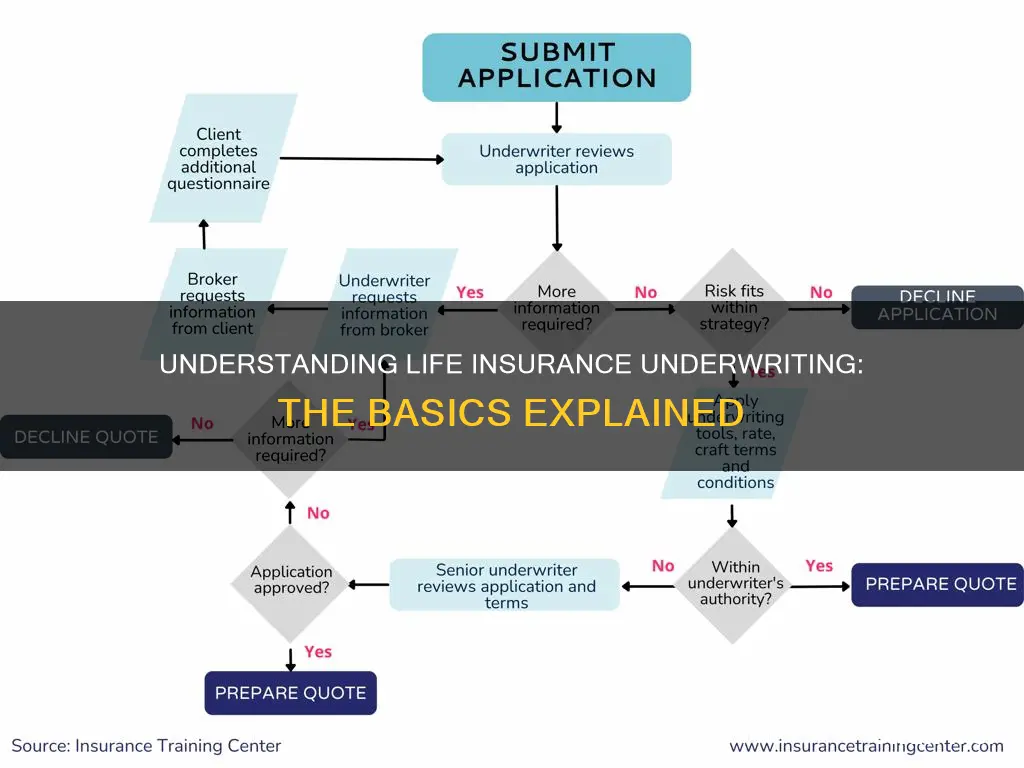
Life insurance underwriting is the process of evaluating an individual's application for life insurance to determine their eligibility and the terms of their coverage, including the premium they will pay. Underwriting involves a detailed analysis of personal and health information, including age, medical history, and lifestyle choices, as well as financial factors. The underwriter's goal is to assess the applicant's risk profile and offer a policy that reflects their true risk and financial context. This process can vary in duration, ranging from a few days to several weeks, depending on the complexity of the application and the insurer's specific procedures.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A detailed process that life insurance companies use to assess an applicant's eligibility for coverage and determine the appropriate premium |
| Types | Traditional (or "full"), accelerated, simplified, automated, guaranteed issue |
| Time taken | 24 hours to 6-8 weeks |
| Factors considered | Age, gender, health status and medical history, occupation, lifestyle, policy type, coverage amount, credit standing, family medical history, criminal history, tobacco use, financials, foreign travel, citizenship status, existing policies, military service, driving record |
| Purpose | To assess the level of risk an applicant poses to the insurer and determine the terms of coverage, including the premium |
| Process | Application, medical exam, information analysis, insurance classification, underwriting decisions and policy terms |
What You'll Learn

Medical underwriting: Evaluating health and lifestyle factors
Medical underwriting is a crucial aspect of life insurance underwriting, where an applicant's health and lifestyle factors are scrutinised to evaluate the risk they present to the insurer. This process involves a detailed analysis of various elements, including age, medical history, habits, and occupation. Here's an in-depth look at the key considerations in medical underwriting:
Age
An individual's age is a significant factor in determining their life insurance premiums. Younger applicants are generally considered lower-risk as they have a longer life expectancy, which provides a more extended period for paying into their policies. Consequently, insurers often offer lower premium costs for younger policyholders.
Medical History and Health Status
An applicant's medical history and current health status play a pivotal role in medical underwriting. Insurers will assess any underlying health conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, or heart disease, as well as a family history of severe or hereditary illnesses. The presence of such conditions typically leads to higher coverage costs. In some cases, a medical examination, including blood tests and urine samples, may be required to confirm an individual's health status.
Occupation
The nature of one's occupation can also impact their life insurance premiums. Individuals in high-risk careers, such as firefighting, piloting, police work, or certain construction trades, are likely to incur higher premiums due to the increased chances of premature death associated with these professions.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices and habits are carefully evaluated during medical underwriting. Engaging in dangerous hobbies like mountain climbing or skydiving, or partaking in risky behaviours such as heavy drinking or smoking, can result in elevated premiums. Insurers consider these factors as they increase the likelihood of claims being made against the policy.
Height and Weight
An applicant's height and weight are also taken into account during the medical underwriting process. Being significantly overweight or underweight can impact an individual's overall health and, consequently, their life expectancy. This, in turn, can influence the cost of their life insurance coverage.
Prescription History
Insurers will often scrutinise an applicant's prescription history as part of the medical underwriting process. This helps them understand any existing health conditions and the medications being used to manage them. Certain prescriptions may indicate a higher risk profile, potentially leading to higher premiums.
Motor Vehicle Records
Motor vehicle records may also be reviewed to identify any risky behaviours or concerns. For example, multiple traffic violations or accidents could indicate a higher risk factor, potentially impacting an individual's life insurance premiums.
Credit History
In some cases, an applicant's credit history may be considered during medical underwriting. While not directly related to health, credit history can provide insights into financial responsibility and overall stability, which could influence an insurer's assessment of risk.
Criminal Record
A background check for any criminal record may also be conducted during the medical underwriting process. Certain criminal offences could indicate a higher risk profile, potentially impacting an individual's eligibility for coverage or resulting in higher premiums.
The information gathered during medical underwriting allows insurers to assess the overall risk presented by each applicant. This evaluation helps determine their eligibility for coverage, the specific terms of the policy, and the premium rates they will pay. It is important to note that the process can vary between insurers, and each company has its own underwriting guidelines and risk classifications.
End-of-Life Insurance: Understanding Cash Value and Benefits
You may want to see also

Financial underwriting: Ensuring coverage aligns with finances
Financial underwriting is a crucial aspect of the life insurance application process, aiming to ensure that the coverage amount aligns with the applicant's financial circumstances and needs. This process involves a detailed analysis of the applicant's financial situation, including their income, assets, liabilities, and other financial indicators. Here's a more detailed overview:
Financial Information:
Insurers will request comprehensive financial information from applicants, such as income, net worth, assets, debts, and expenses. This enables them to gauge the applicant's financial stability and capacity to afford the policy premiums. The income factor is particularly significant, as it helps prevent or reduce speculation. While it is often based on earned income, adjustments can be made on a case-by-case basis, considering factors like total net worth, estate tax consequences, and age.
Credit History:
The applicant's credit history, including their credit score and report, is another essential aspect of financial underwriting. Insurers assess this information to evaluate the applicant's financial responsibility and payment behaviour. A good credit history can indicate lower financial risk and influence the underwriting decision.
Occupation and Industry:
Underwriters also consider the applicant's job and industry, as these factors can provide insights into job stability and income potential. Certain occupations may be deemed riskier than others, which can impact the premium rates.
Policy Face Amount:
The face amount or death benefit of the policy applied for also plays a role in financial underwriting. Higher coverage amounts typically trigger a more comprehensive financial evaluation. Insurers want to ensure that the applicant isn't applying for more coverage than they can justify or afford.
Existing Policies:
Insurers will also want to know about any existing life insurance policies held by the applicant. This information helps assess the applicant's overall insurance needs and potential financial strain.
Financial Ratios:
Financial ratios, such as debt-to-income ratios and liquidity ratios, may be used by insurers to assess the applicant's financial health and ability to manage their finances.
Medical History:
While primarily a factor in medical underwriting, certain financial aspects of the applicant's medical history may also be considered. For instance, a history of serious medical conditions could impact the applicant's economic well-being.
The information gathered during financial underwriting enables insurers to make informed decisions about the applicant's eligibility for coverage and the premium rates they will be offered. Applicants with higher financial risk profiles may face increased premium rates or be deemed ineligible for specific policies. Therefore, it is crucial to provide accurate and honest financial information during the underwriting process.
Life Insurance Payments: Can You Press Pause?
You may want to see also

Insurance classification: Assigning risk categories
The insurance classification is the penultimate step in the life insurance underwriting process. It is when the underwriter assesses all the gathered information and assigns the applicant an insurance classification rating. This rating is an indicator of the applicant's insurability based on their health and lifestyle factors.
The "standard" classification is the baseline, representing the average risk profile for males and females. Applicants can be moved up or down from this baseline depending on their health and lifestyle risks.
The insurance classification categories include:
- Preferred Plus/Elite: Applicants in this category are in excellent health, have a great height-to-weight ratio, and have minimal or no bad habits that would impact their health.
- Preferred: Applicants in this category are in good health but not good enough to qualify for Preferred Plus/Elite. They may have a minor health issue, such as high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- Standard Plus: Applicants in this category are still eligible for coverage, but there may be some concerns about their medical record or a family history of disease. Their life insurance costs will likely be higher than those in the Preferred Plus/Elite or Preferred categories.
- Standard: This is the category that most people fall into and is the baseline for policy rates.
- Substandard: Applicants with significant health conditions or a short track record of managing a health condition are given a substandard rating. This category involves a further classification system called "table rating." Depending on how the applicant scores in that system, they will be required to pay a certain percentage on top of the standard price for coverage.
It is important to note that these insurance classification categories exist for both smokers and non-smokers, with smokers typically paying higher premiums. Additionally, insurance companies may have different rules to qualify for each rate class, and an applicant's rating is not set in stone. It is possible to improve one's risk profile and potentially reduce their premium costs by making healthy lifestyle changes.
Northwestern Mutual: Drug Testing for Life Insurance Policies
You may want to see also

Risk assessment: Determining premium costs
Risk assessment is a crucial aspect of life insurance underwriting, influencing the premium costs that an individual will need to bear. This process involves evaluating various factors to determine the likelihood of the insured person passing away during the policy period. Premium costs are directly linked to the assessed level of risk, with higher-risk individuals facing higher premiums.
Several factors are considered in the risk assessment process, including age, health status, medical history, occupation, gender, lifestyle choices, and credit standing. Younger individuals, statistically having a longer life expectancy, pose less risk to insurers and are therefore offered lower premium costs. On the other hand, older individuals or those with pre-existing health conditions are deemed higher-risk and are likely to pay more for coverage.
Health status and medical history play a significant role in risk assessment. A medical examination is often conducted to identify any underlying health issues, such as high cholesterol or glucose levels, or the presence of drugs in the system. The results of these examinations are instrumental in determining the risk factor associated with insuring an individual.
Occupational hazards are also taken into account. Individuals in high-risk careers, such as firefighters, pilots, or police officers, are usually required to pay more for their policies. Lifestyle choices, including dangerous hobbies like skydiving or mountain climbing, or habits such as smoking or excessive drinking, can also lead to higher premium costs.
In addition, gender is a factor, as life expectancy differs between males and females, and this is reflected in the premium costs. Credit standing, in states where it is permitted, can also influence the premium, with insurers factoring in credit-based insurance scores.
The risk assessment process culminates in assigning the insured person to a specific risk class, such as preferred plus, preferred, standard plus, standard, or substandard. These classifications are based on health, lifestyle, and other factors, and they directly impact the premium costs, with higher-risk individuals paying more for their life insurance coverage.
Life Insurance Agents: Generating Leads for Success
You may want to see also

Underwriting tools: Using technology for accurate ratings
Underwriting tools are an important part of the life insurance application process, helping to streamline the work of insurance companies and their employees. These tools are designed to improve efficiency, allowing employees to focus on serving customers.
Underwriting software enables users to write rules and policies that are then automatically used in the underwriting process. Applications can perform actions such as executing insurance policies, performing pricing and rate analyses, calculating standard and premium quotes, and creating auditable paper trails.
One of the main purposes of underwriting tools is to maintain the conversion of prospects into customers by balancing corporate and regulatory requirements. These tools also help manage submissions of tasks and claims and include a rating engine that calculates premiums by coverage, validating variants from standard rates.
Benefits of underwriting software include attracting new customers with a quick application process, developing innovative insurance policies, and boosting productivity for underwriters through overall automation.
When it comes to life insurance underwriting, underwriters use tools and technology to determine accurate ratings for applicants. This involves analysing various risk factors, such as cigarette and alcohol consumption, workplace dangers, medical test results, and body mass index (BMI). Each variable is related to the probability of cost to the insurance company, and advanced computations are used to predict losses by analysing historical data.
The use of technology and models helps underwriters assess the life expectancy of applicants, determine their risk class and classification, and ultimately set the amount of coverage and monthly premium.
- AIM, which centralises underwriting, accounting, and claims operations to increase efficiency and accuracy.
- Applied Epic, a cloud-based agency management system offering powerful automation capabilities and visibility across the business.
- AURA (Automated Underwriting and Risk Analysis), an e-underwriting platform and rules engine.
- Cirrus, a cloud-based rating solution that is ready to generate quotes on Day 1.
- Earnix, a provider of mission-critical systems for global insurers and banks, enabling customers to provide smart and personalised products.
- Intellect Xponent, an AI and Analytics-based underwriting workstation that transforms the way commercial lines are underwritten.
- IVANS Rating Services, a cloud-based, end-to-end integrated data exchange solution for exchanging quote information with distribution channels.
- LexisNexis, which offers solutions for automating the coverage verification process, providing faster and more accurate quotes, and accessing public records for evaluating life insurance risks.
- Oracle Insurance Insbridge Enterprise Rating, which provides an adaptive solution for product management, premium calculation, and underwriting rules management.
Gerber Life Insurance: Does It Have an Expiry Date?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance underwriting is the process of evaluating an individual's application for life insurance by assessing their personal and health details, financial situation, and other relevant factors to determine their eligibility for coverage, the terms of their policy, and the premium amount.
Factors such as age, gender, medical history, occupation, lifestyle choices, income, credit history, and existing insurance coverage are considered during the underwriting process.
The duration of the underwriting process can vary from 24 hours to several weeks, depending on the complexity of the application and the insurer's specific procedures.
Traditional underwriting involves a detailed health questionnaire, a medical exam, and lab tests, resulting in more affordable premiums but longer processing times. Accelerated underwriting uses algorithms and data sources to make rapid decisions, often on the same day, but may result in higher premiums and lower coverage amounts.







