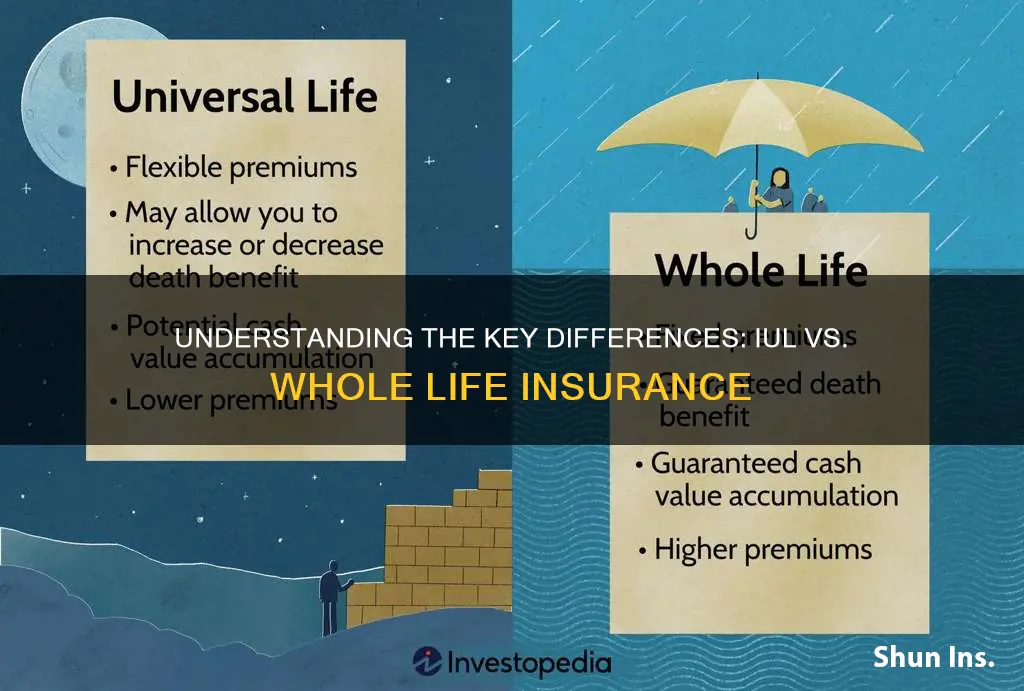
When it comes to insurance, understanding the differences between various types can be crucial for making informed decisions. Two common types of life insurance are IUL (Indexed Universal Life) and Whole Life. IUL insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a flexible premium and potential for investment growth, while Whole Life provides lifelong coverage with a fixed premium and a guaranteed death benefit. The key distinction lies in their structure: IUL allows for potential investment gains, which can be used to pay premiums, while Whole Life offers a consistent, predictable policy that builds cash value over time. This comparison highlights the unique features and benefits of each, helping individuals choose the insurance plan that best suits their financial goals and needs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of Policy | - Indexed Universal Life (IUL) is a type of permanent life insurance with an investment component. - Whole Life Insurance is a permanent life insurance policy with a fixed death benefit and premiums. |
| Investment Component | - IUL policies offer a variable investment account where a portion of the premium is invested in a separate account, allowing for potential growth. - Whole Life has no investment component; the entire premium goes towards the death benefit and policy accumulation. |
| Death Benefit | - IUL: The death benefit is typically equal to the cash value plus any accumulated interest or gains. - Whole Life: The death benefit is guaranteed and remains constant throughout the life of the policyholder. |
| Premiums | - IUL: Premiums can vary based on market performance and the policy's investment strategy. - Whole Life: Premiums are fixed and remain the same over the life of the policy. |
| Flexibility | - IUL: Offers more flexibility in premium payments and policy customization. - Whole Life: Less flexible in terms of premium adjustments and policy modifications. |
| Tax Advantages | - Both IUL and Whole Life provide tax-deferred growth of cash value. - IUL: Potential for tax-deductible premiums (subject to regulations). - Whole Life: Tax-deductible premiums in certain circumstances. |
| Lapse Risk | - IUL: Risk of policy lapse if the cash value falls below a certain threshold. - Whole Life: Less risk of lapse as the policy builds cash value over time. |
| Surrender Value | - IUL: Surrender value increases with market performance and investment gains. - Whole Life: Surrender value is fixed and increases with policy accumulation. |
| Longevity Benefits | - IUL: Can provide a guaranteed minimum death benefit and potential for higher returns. - Whole Life: Offers guaranteed death benefit and long-term financial security. |
| Cost | - IUL: Generally more expensive due to the investment component and potential for higher returns. - Whole Life: Typically more affordable, especially for younger policyholders. |
What You'll Learn
- Cost: IUL is generally more expensive upfront, while whole life is a fixed cost
- Flexibility: IUL offers investment options, allowing policyholders to control growth
- Death Benefit: Whole life guarantees a fixed death benefit, whereas IUL varies based on investment performance
- Liquidity: IUL provides more liquidity through policy loans and withdrawals
- Long-Term Value: Whole life builds cash value steadily, while IUL may fluctuate

Cost: IUL is generally more expensive upfront, while whole life is a fixed cost
When considering insurance options, understanding the cost implications of different policies is crucial. One of the key differences between Indexed Universal Life (IUL) and whole life insurance lies in their cost structures. IUL policies often come with higher upfront costs compared to whole life insurance. This is primarily due to the investment component of IUL, which allows policyholders to participate in market gains, potentially offering higher returns but at a higher initial price.
In contrast, whole life insurance provides a fixed cost structure. This means that once the initial premium is paid, the cost of the policy remains consistent throughout its term. Whole life insurance offers a guaranteed death benefit and a permanent policy, providing long-term financial security. The fixed nature of these policies ensures that policyholders know exactly what they will pay over the life of the contract, making it easier to budget and plan for the future.
The higher upfront cost of IUL can be attributed to the potential for higher returns and the flexibility it offers. Policyholders can allocate a portion of their premium to an investment account, which can grow tax-deferred. While this feature provides an opportunity for increased returns, it also means that the initial outlay is more significant. Over time, as the investment account grows, the policy's cash value increases, potentially offsetting some of the higher initial costs.
On the other hand, whole life insurance offers a more straightforward and predictable cost model. The fixed premiums ensure that policyholders are not exposed to market volatility, and the policy's value is guaranteed. This predictability can be advantageous for those seeking long-term financial planning, as it allows for better budgeting and a clearer understanding of future expenses.
In summary, the cost difference between IUL and whole life insurance is a significant factor for prospective buyers. IUL's higher upfront costs reflect its investment potential, while whole life insurance's fixed premiums provide stability and predictability. Understanding these cost structures is essential for individuals to make informed decisions when choosing between these two insurance options.
Understanding Allocation Percent: Life Insurance Explained
You may want to see also

Flexibility: IUL offers investment options, allowing policyholders to control growth
When it comes to insurance, understanding the various types and their unique features is crucial for making informed decisions. One such comparison is between Indexed Universal Life (IUL) and Whole Life insurance, two popular permanent life insurance policies. One of the key differences that sets IUL apart is its flexibility, particularly in terms of investment options.
IUL policies offer policyholders a unique advantage by providing a combination of insurance protection and investment opportunities. Unlike traditional whole life insurance, which has a fixed premium and death benefit, IUL allows for a degree of customization. Policyholders can choose how they want to allocate their money between the insurance component and the investment portion. This investment aspect is a significant factor that contributes to the flexibility of IUL.
The investment options within IUL policies are designed to provide growth potential while also ensuring a level of safety. Policyholders can select from various investment accounts, often referred to as "investment options" or "investment accounts." These options typically include a mix of stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. By allowing policyholders to make these choices, IUL empowers individuals to take control of their insurance policy's growth and performance. This level of control is a significant advantage, especially for those who prefer a more active role in managing their financial assets.
With IUL, individuals can adjust their investment strategy over time, adapting to changing market conditions and personal financial goals. This flexibility enables policyholders to potentially maximize their returns while also ensuring that their insurance coverage remains in place. For those who want to optimize their financial resources, IUL provides a way to do so while maintaining the essential safety net of life insurance.
In summary, the flexibility offered by IUL, through its investment options, is a notable feature that sets it apart from whole life insurance. This aspect allows policyholders to actively manage their financial growth and make informed decisions about their insurance policy's performance, providing a level of control that is not typically found in traditional whole life insurance products.
Whole Life vs Universal Life Insurance: Which is Better?
You may want to see also

Death Benefit: Whole life guarantees a fixed death benefit, whereas IUL varies based on investment performance
When it comes to insurance, understanding the nuances between different types of policies is crucial, especially when considering the death benefit, which is the amount paid to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon the insured individual's death. Two common types of life insurance are Whole Life and Indexed Universal Life (IUL). While both offer financial protection for loved ones, they differ significantly in how the death benefit is determined.
Whole Life Insurance is a permanent life insurance policy that provides a guaranteed death benefit for the entire life of the insured individual. This means that, regardless of market fluctuations or changes in the insured's health, the death benefit remains fixed. For example, if you purchase a $500,000 Whole Life policy and pass away at any point during your lifetime, the insurance company will pay out exactly $500,000 to your designated beneficiaries. This predictability and guarantee make Whole Life an attractive option for those seeking long-term financial security.
On the other hand, IUL offers a unique blend of insurance and investment opportunities. The death benefit in IUL policies is not fixed but rather linked to the performance of an investment account. When you purchase an IUL policy, a portion of your premium is invested in an investment account, typically an index fund or a similar asset allocation. The performance of this investment account directly impacts the death benefit. If the investment grows, the death benefit can increase, potentially providing a higher payout than the initial premium amount. Conversely, if the investment underperforms, the death benefit may be lower than the premium paid. This variable aspect of IUL makes it appealing to those who want to potentially maximize their death benefit through investment growth.
The key difference lies in the certainty of the death benefit. With Whole Life, you have a guaranteed payout, which can provide peace of mind, especially for those with long-term financial planning goals. In contrast, IUL offers the potential for a higher death benefit but with more variability, as it is directly tied to investment performance. This variability can be a double-edged sword, as it may lead to higher returns but also carries the risk of lower payouts if the investments underperform.
In summary, when considering Whole Life and IUL, the choice between the two depends on your specific needs and risk tolerance. Whole Life provides a fixed, guaranteed death benefit, making it a stable and predictable option. IUL, on the other hand, offers the potential for higher death benefits through investment growth but with the risk of lower payouts if the investments do not perform as expected. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision about your life insurance needs.
Life Insurance: Are You Prepared for the Future?
You may want to see also

Liquidity: IUL provides more liquidity through policy loans and withdrawals
When comparing IUL (Indexed Universal Life) and whole life insurance, one of the key differences lies in the liquidity and flexibility offered by IUL policies. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an individual can access the cash value of their insurance policy without incurring significant penalties or fees.
IUL policies offer policyholders a higher level of liquidity compared to traditional whole life insurance. This is primarily due to the ability to take out loans against the cash value of the policy. Policyholders can borrow money from their insurance company using the accumulated cash value as collateral. These policy loans are typically interest-free and can be used for various purposes, such as funding education, starting a business, or covering unexpected expenses. The loan amount is usually returned to the policy with interest, ensuring that the policy's value remains intact.
Additionally, IUL policies often allow for policy withdrawals, which enable policyholders to access a portion of the cash value without taking out a loan. Withdrawals provide immediate access to funds, offering policyholders the freedom to use their money when needed. This feature is particularly beneficial for those who require quick access to funds for financial obligations or opportunities.
The liquidity provided by IUL policies is a significant advantage, especially for individuals who value financial flexibility and the ability to respond to changing financial needs. It allows policyholders to utilize their insurance policy as a financial tool, providing a safety net while also offering the potential for growth and access to funds when required.
In contrast, whole life insurance typically has lower liquidity. While it provides guaranteed death benefit and cash value accumulation, accessing the cash value often requires a surrender charge, and loans may be limited or not available at all. This difference in liquidity highlights the flexibility and adaptability that IUL offers to policyholders.
Whole Life Insurance: Your Alternative Banking Option
You may want to see also

Long-Term Value: Whole life builds cash value steadily, while IUL may fluctuate
When considering long-term financial planning, understanding the differences between various insurance products is crucial. Two popular options in the insurance market are Indexed Universal Life (IUL) and Whole Life insurance. While both offer permanent coverage, they differ significantly in how they accumulate value over time.
Whole Life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides coverage for the entire life of the insured individual. One of its key advantages is the steady accumulation of cash value. With Whole Life, a portion of the premium paid goes towards building a cash reserve, which grows tax-deferred. This cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing a financial safety net for the policyholder. Over time, the policy's cash value increases, ensuring a guaranteed death benefit and a fixed premium, providing long-term financial security.
On the other hand, IUL offers a unique approach to permanent life insurance. It combines the benefits of life coverage with an investment component. IUL policies also accumulate cash value, but this value is linked to an investment account that tracks a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. The cash value in IUL policies can fluctuate based on the performance of the underlying index. This means that while IUL can provide a death benefit, the cash value may increase or decrease over time, depending on market conditions.
The difference in long-term value accumulation is significant. Whole Life insurance offers a consistent and predictable growth rate, ensuring that the cash value builds steadily over the policy's lifetime. This predictability is valuable for those seeking a reliable financial plan. In contrast, IUL provides an opportunity for potentially higher returns but with more volatility. Policyholders can benefit from market growth while also having the security of a guaranteed death benefit.
In summary, when evaluating long-term value, Whole Life insurance excels in providing a steady and guaranteed cash value accumulation, making it an attractive choice for those seeking financial stability. IUL, on the other hand, offers the potential for higher returns but with the risk of market fluctuations, making it a more volatile investment option. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals to make informed decisions regarding their insurance and financial planning needs.
Whole Life Insurance: Guaranteed Issue, Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The main distinction lies in their coverage period and flexibility. IUL, or Index Universal Life, is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a flexible premium and the potential for investment growth. It provides coverage for a specific term, often with the option to increase or decrease the death benefit based on market performance. On the other hand, Whole Life Insurance offers lifelong coverage with a fixed premium and a guaranteed death benefit. This means the policy will pay out a specified amount upon the insured's death, regardless of when it occurs.
IUL policies typically include an investment component, allowing policyholders to allocate a portion of their premium to various investment options. These investments can be linked to market performance, such as stock market indices, and may offer higher potential returns compared to traditional whole life insurance. In contrast, Whole Life Insurance does not have an investment component; instead, it focuses solely on providing death benefit coverage. The premiums are invested internally by the insurance company, and any growth is used to fund the policy's death benefit and other expenses.
Yes, both IUL and Whole Life Insurance offer tax advantages. With IUL, the cash value accumulation may be tax-deferred, allowing it to grow tax-free until it is withdrawn. Additionally, policyholders can make tax-deductible premium payments, providing a potential tax benefit. Whole Life Insurance also offers tax advantages, as the cash value grows tax-free, and withdrawals or loans against the policy's cash value may be tax-free if used for qualified expenses. However, it's important to note that tax laws can vary, and consulting a financial advisor is recommended to understand the specific tax implications for your situation.







