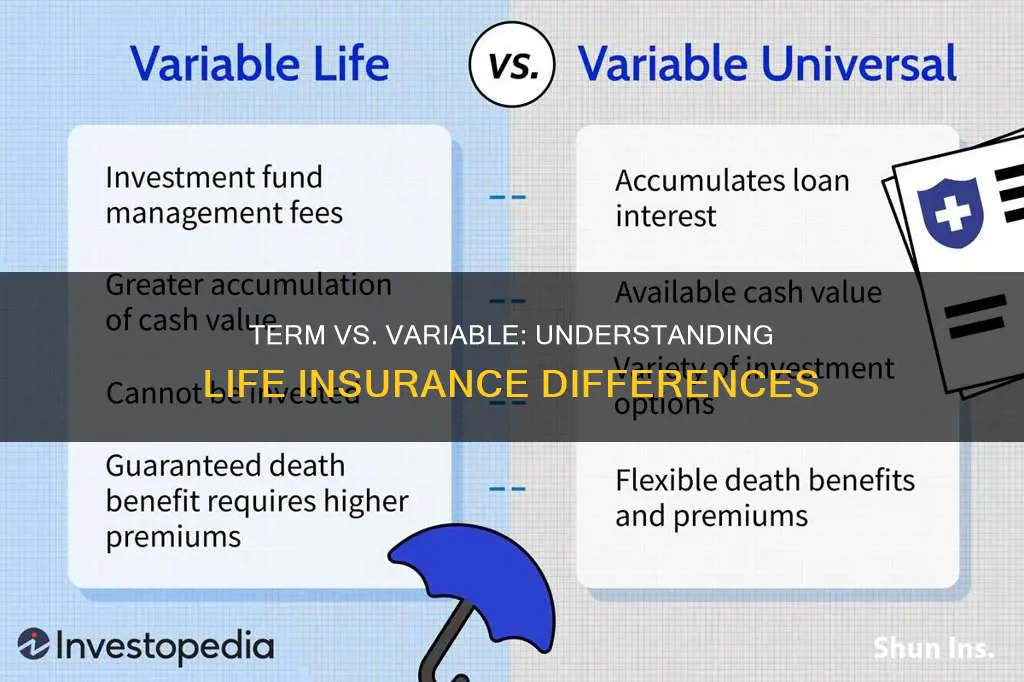
Term life insurance and variable life insurance are two distinct types of life insurance policies, each with its own unique features and benefits. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years, and offers a fixed death benefit if the insured dies during that term. It is a straightforward and cost-effective option, ideal for those seeking temporary coverage for a defined period. On the other hand, variable life insurance combines life coverage with an investment component. It allows policyholders to invest a portion of their premium in various investment options, offering the potential for higher returns but also carrying more risk. This type of insurance provides permanent coverage and allows for policy customization, making it suitable for those who want both insurance protection and investment opportunities. Understanding the differences between these two types of policies is essential for individuals to choose the best fit for their financial goals and risk tolerance.
What You'll Learn
- Term Duration: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, unlike variable life, which offers permanent protection
- Cost Structure: Term policies typically have lower premiums, while variable life insurance charges higher fees for investment components
- Lapse Risk: Term insurance does not have investment risks, whereas variable life insurance may lose value due to market fluctuations
- Flexibility: Variable life offers investment options, allowing policyholders to adjust their death benefit and cash value
- Liquidity: Term life insurance is more liquid, allowing easy conversion to a permanent policy, unlike variable life's complex process

Term Duration: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, unlike variable life, which offers permanent protection
Term life insurance is a type of coverage that provides a specific period of protection, offering a straightforward and cost-effective solution for individuals seeking insurance. Unlike variable life insurance, which provides permanent coverage, term life insurance is designed to meet the needs of a particular time frame. This type of policy is often chosen for its simplicity and affordability, making it an attractive option for those who require insurance for a defined period, such as covering mortgage payments or providing financial security for a family during a specific stage of life.
The duration of term life insurance is a critical aspect that sets it apart from other forms of insurance. It is typically available in various terms, such as 10, 20, or 30 years, and the insured individual pays a fixed premium for the entire term. Once the term ends, the policy expires, and further coverage may need to be obtained if desired. This structured approach ensures that the insurance is tailored to the specific needs of the individual during that particular period.
In contrast, variable life insurance offers a different approach to permanent coverage. With variable life, the policyholder can adjust the death benefit and premium payments over time, providing flexibility. However, this flexibility often comes with higher costs and more complex investment options, making it less straightforward than term life insurance. Variable life insurance is more suitable for those who want to build a cash value component within their policy and are willing to manage the investment aspects.
The key advantage of term life insurance is its predictability and affordability. Since the coverage is limited to a specific period, the insurance company can offer competitive rates, making it an excellent choice for those who need insurance for a particular goal, such as protecting a business partner's share in a partnership or providing financial security for a child's education. After the term ends, the individual can decide whether to renew the policy or obtain a new one to continue the coverage.
Understanding the difference between term and variable life insurance is essential for making informed financial decisions. Term life insurance provides a simple, term-specific solution, while variable life insurance offers more customization but with additional complexity. By considering the duration and flexibility of each type of policy, individuals can choose the insurance that best aligns with their financial goals and needs.
Life Insurance: Part of Your Inheritance?
You may want to see also

Cost Structure: Term policies typically have lower premiums, while variable life insurance charges higher fees for investment components
When considering life insurance, understanding the cost structure is crucial as it directly impacts the overall value and affordability of the policy. One of the primary differences between term and variable life insurance lies in their cost structures, particularly in terms of premiums and fees.
Term life insurance is a straightforward and cost-effective option. It provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. During this term, the policyholder pays a fixed premium, which remains consistent throughout the duration. The simplicity of term insurance is one of its greatest strengths. With no investment components or variable features, the cost is primarily for the death benefit, ensuring that the premiums are generally lower compared to other types of life insurance. This makes term life insurance an attractive choice for those seeking affordable coverage without the complexity of additional fees.
On the other hand, variable life insurance offers a different cost structure. This type of policy combines insurance with an investment component, allowing policyholders to invest a portion of their premiums in various investment options. While this provides the potential for higher returns, it also results in higher costs. Variable life insurance charges fees for the investment management and administration of these investment components. These fees can vary depending on the investment choices made and the performance of the underlying funds. As a result, the premiums for variable life insurance are often higher than those for term policies, reflecting the added complexity and the potential for higher returns.
The higher fees associated with variable life insurance are a significant consideration for consumers. These fees can impact the overall cost-effectiveness of the policy, especially over the long term. It is essential for individuals to carefully evaluate their financial goals and risk tolerance before choosing between term and variable life insurance. Understanding the cost structure and the potential benefits of each type of policy will enable them to make an informed decision that aligns with their needs and preferences.
In summary, the cost structure is a critical aspect of differentiating between term and variable life insurance. Term policies offer lower premiums due to their simplicity and focus on providing pure insurance coverage. In contrast, variable life insurance, with its investment components, charges higher fees, resulting in more expensive premiums. This difference in cost structure highlights the trade-offs between simplicity and added features when selecting the most suitable life insurance policy.
Whole Life vs Universal Life Insurance: Key Differences Explained
You may want to see also

Lapse Risk: Term insurance does not have investment risks, whereas variable life insurance may lose value due to market fluctuations
When considering life insurance, it's important to understand the key differences between term and variable life insurance, especially regarding lapse risk and investment aspects. Term insurance is a straightforward and traditional form of life coverage, providing protection for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. One of its primary advantages is its simplicity and predictability. During the term, the policyholder pays regular premiums, and in return, the insurer provides a death benefit if the insured passes away within the agreed-upon period. The beauty of term insurance lies in its lack of investment risks. The premiums are used solely to fund the death benefit and administrative costs, ensuring that the policy remains affordable and predictable throughout its duration. This simplicity makes term insurance an attractive choice for those seeking pure life coverage without the complexities of investment components.
On the other hand, variable life insurance offers a different approach. It combines life coverage with an investment component, providing policyholders with the opportunity to grow their money through various investment options. With variable life insurance, a portion of the premium goes into an investment account, where it can potentially earn interest, dividends, or capital gains. This feature may appeal to those who want their insurance policy to serve as a long-term investment strategy. However, this investment aspect also introduces a level of risk. The value of the investment account can fluctuate based on market conditions, and if the investments underperform, the policyholder may experience a loss. This risk is a significant consideration when comparing term and variable life insurance.
The key difference in lapse risk is that term insurance is not subject to investment risks. Since term policies do not have an investment component, they are less susceptible to market volatility. If the insured individual passes away during the term, the death benefit is guaranteed, and the policy remains in force. In contrast, variable life insurance policies may face lapse risks due to the investment nature of the policy. If the investment account value drops significantly, the policyholder may struggle to keep up with the required minimum premium payments, leading to a potential lapse in coverage. This risk highlights the importance of understanding the investment performance of variable life insurance policies to ensure long-term financial security.
In summary, when evaluating life insurance options, it is crucial to recognize that term insurance provides pure life coverage without investment risks, making it a stable and predictable choice. In contrast, variable life insurance offers investment opportunities but also introduces the possibility of market-related losses and lapse risks. Understanding these differences can help individuals make informed decisions about their insurance needs and financial goals.
Exchange IRA Money for Life Insurance: A Smart Move?
You may want to see also

Flexibility: Variable life offers investment options, allowing policyholders to adjust their death benefit and cash value
Variable life insurance offers a unique level of flexibility compared to traditional term or whole life insurance. One of its key advantages is the ability to customize the policy to fit the policyholder's specific needs and financial goals. This is achieved through the investment options available within the variable life policy.
When you purchase a variable life insurance policy, you are essentially combining insurance coverage with an investment account. The policyholder can choose from a variety of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, which are managed by the insurance company. This investment component allows the policyholder to potentially grow their cash value, which is the portion of the policy that accumulates over time. The cash value can be used for various purposes, providing flexibility in how the policy is structured.
One of the primary benefits of this flexibility is the ability to adjust the death benefit. The death benefit is the amount paid out to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon their passing. With variable life insurance, you can increase or decrease the death benefit based on your financial situation and goals. For example, if you have a growing family and want to ensure a substantial financial safety net, you can allocate more funds to the death benefit. Conversely, if you have already established a financial foundation, you might choose to adjust the death benefit downward, potentially increasing the overall return on your investment.
Additionally, the investment options within variable life insurance provide the opportunity to customize the cash value accumulation. Policyholders can make strategic decisions about how to allocate their investments, aiming for growth or more conservative returns. This level of control allows individuals to adapt their insurance policy as their financial circumstances change over time. For instance, if you experience a significant financial windfall, you could allocate more funds to the investment portion, potentially increasing the overall value of the policy.
In summary, variable life insurance stands out for its flexibility, primarily through the investment options it offers. This feature enables policyholders to actively manage their death benefit and cash value, ensuring that their insurance policy aligns with their evolving financial needs and objectives. This level of customization is a significant advantage for those seeking a more tailored and adaptable insurance solution.
Paramedical Exams: Life Insurance's Vital Step
You may want to see also

Liquidity: Term life insurance is more liquid, allowing easy conversion to a permanent policy, unlike variable life's complex process
Term life insurance is known for its straightforward nature and offers a simple way to ensure financial security for a specific period. One of its key advantages is liquidity, which refers to the ease with which the policy can be converted into a permanent life insurance plan. This process is relatively simple and allows policyholders to transition from a temporary coverage to a more permanent solution without much hassle. In contrast, variable life insurance, which is more complex, often requires a more intricate and lengthy process to convert it into a permanent policy. This complexity can be a significant drawback for those seeking a seamless transition to a more comprehensive insurance plan.
When considering liquidity, term life insurance provides policyholders with the flexibility to make changes as their needs evolve. For instance, if an individual's financial situation improves, they can opt to convert their term policy into a permanent one, ensuring long-term coverage without the need for a new application process. This ease of conversion is particularly beneficial for those who want to adapt their insurance strategy over time without facing a complicated and potentially lengthy process.
The simplicity of converting term life insurance into a permanent policy is a significant advantage, especially for those who prefer a more straightforward approach to insurance management. It allows individuals to make informed decisions about their long-term financial security without the added complexity of variable life insurance. Moreover, this liquidity aspect ensures that policyholders have the freedom to choose the best insurance plan for their evolving needs.
In contrast, variable life insurance often involves a more intricate process for conversion, which can be a deterrent for many. The complexity arises from the variable nature of the policy, which includes investment components that can affect the overall structure and conversion process. This added layer of complexity may not be desirable for those seeking a simple and direct approach to life insurance.
In summary, term life insurance excels in liquidity, offering a straightforward conversion process to permanent coverage. This simplicity is a significant advantage over variable life insurance, which often requires a more intricate and time-consuming conversion process. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions about their insurance needs and ensure they have the right coverage for their specific circumstances.
Retired Military: Free Life Insurance Benefits Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years, and is designed to offer financial protection during that time. It is a straightforward policy with a fixed premium and a death benefit. On the other hand, variable life insurance offers both death benefit coverage and an investment component. The premiums are flexible and can vary based on market performance, allowing policyholders to potentially earn higher returns but also carrying more risk.
Term life insurance is generally more affordable and offers pure insurance coverage without the investment aspect. The premiums are typically lower because the policy only provides coverage for a defined term. Variable life insurance, due to its investment features, often comes with higher costs and fees. These additional charges can vary and may include investment management fees, policy management fees, and other associated costs.
Variable life insurance allows policyholders to allocate a portion of their premium payments into various investment options. These investments can include mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and other securities. The performance of these investments directly impacts the cash value of the policy. Policyholders can choose to increase or decrease their investment allocation over time. This feature provides flexibility but also means that the policy's value can fluctuate, and there is a risk of losing some or all of the investment gains if the market performs poorly.







