Auto insurance is a contract between you and your insurance company. By applying for coverage, you agree to pay an auto insurance premium to the insurance company. In return, the company agrees to pay covered costs associated with an auto accident once the deductible has been met under the policy terms. Auto insurance terms can be confusing, and it's important to understand them to ensure you have the right coverage for your needs. This introduction will explain some of the key terms related to auto insurance and help you navigate the world of car insurance with confidence.
What You'll Learn

Deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses
When it comes to auto insurance, it's important to understand the concept of deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses. These are essential components of your insurance policy that can significantly impact your financial obligations in the event of a claim.
Deductibles:
A deductible refers to the amount of money you, the policyholder, are responsible for paying upfront before your insurance company covers the remaining costs as per your policy terms. In simple terms, it is the portion of a claim that you pay yourself. For instance, if you have a $500 deductible and your car repairs cost $5,000, you will pay the deductible of $500, and your insurance company will cover the remaining $4,500.
The deductible amount can vary depending on your insurance policy and the type of coverage you have selected. Typically, deductibles apply to comprehensive or collision coverage in auto insurance. Choosing a higher deductible often results in lower insurance rates, but it's important to remember that you will have to bear a larger portion of the cost yourself in the event of a claim.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses:
Out-of-pocket expenses refer to the total amount you pay for covered services before your insurance company starts covering all costs. This includes your deductible, copays, and coinsurance.
- Copay (or Copayment): This is a fixed amount you pay each time you use a covered service, such as a doctor's visit or filling a prescription. For example, you may have a $20 copay each time you visit a specialist doctor.
- Coinsurance: This is the portion of the insurance bill you are responsible for paying after meeting your deductible. It is typically expressed as a percentage. For instance, with 20% coinsurance, you pay 20% of the total bill, while your insurer covers the remaining 80%.
It's important to note that your monthly insurance premium payments do not count towards your out-of-pocket expenses. Additionally, out-of-pocket expenses reset at the start of each new policy year.
Understanding your deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses is crucial when selecting an auto insurance policy. It allows you to make informed decisions about the level of coverage you require and helps you prepare financially in case of an accident or claim.
Texas Auto Insurance: Understanding Windshield Replacement Coverage
You may want to see also

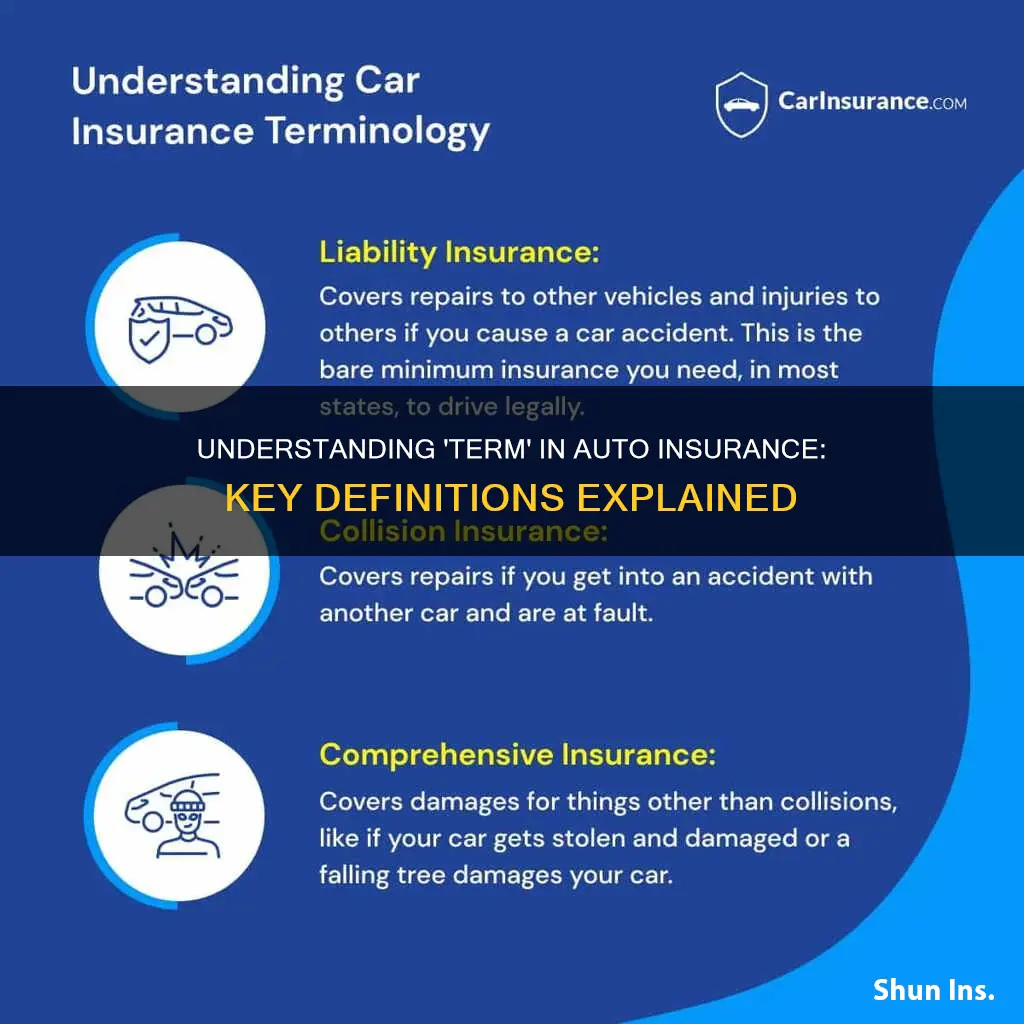
Types of coverage: collision, comprehensive, liability, etc
Auto insurance is a contract between you and your insurance company. By applying for coverage, you agree to pay an auto insurance premium to the insurance company. In return, the company agrees to pay covered costs associated with an auto accident once the deductible has been met under the policy terms.
There are various types of coverage, including collision, comprehensive, and liability insurance.
Collision Insurance
Collision insurance covers damage to your vehicle caused by an accident with another vehicle or object. For example, if you rear-end another car and need to replace your bumper, collision insurance will cover the cost of repairs. It also covers accidents involving stationary objects like road signs and guardrails, as well as single-car rollovers. Collision insurance is not required by state law, but it is typically required for a car loan or lease.
Comprehensive Insurance
Comprehensive insurance covers damage to your vehicle from unexpected non-collision incidents. This includes theft, animal damage, falling trees, and weather damage such as hail or floods. For example, if a tree branch falls on your parked car during a storm and causes damage, comprehensive insurance will cover the repairs. Like collision insurance, comprehensive insurance is not required by state law but is usually required for a car loan or lease.
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance covers your legal liability if you are at fault in an accident. It pays for the other party's injury treatment and property damage, as well as your legal defence costs if you are sued. Liability insurance is the most common way to satisfy financial responsibility laws that require vehicle owners and drivers to have enough money to compensate anyone they might injure in an accident.
Other Types of Coverage
In addition to collision, comprehensive, and liability insurance, there are other types of coverage that you can add to your auto insurance policy:
- Medical payments coverage (MedPay): Pays for your own injury treatment and that of your passengers, regardless of who caused the accident, up to your policy limit.
- Personal injury protection (PIP): Similar to MedPay, PIP covers your injury treatment and that of your passengers, as well as lost wages and other expenses related to the accident, regardless of fault.
- Uninsured motorist coverage: Covers your injuries and property damage if you are hit by a driver who does not have insurance or has insufficient insurance.
- Underinsured motorist endorsement: Covers you if you are involved in an accident with a driver who does not have enough liability insurance to pay for the damages.
- Rental reimbursement coverage: Pays for your rental car expenses if you need a temporary vehicle while your car is being repaired due to a covered loss under comprehensive or collision benefits.
Auto Insurance: Can You Hit Pause?
You may want to see also

Claims and how to file them
Auto insurance is a contract between you and your insurance company. By applying for coverage, you agree to pay an auto insurance premium to the insurance company. In return, the company agrees to pay covered costs associated with an auto accident once the deductible has been met under the policy terms.
An auto insurance claim is a request for payment from your car insurer to cover vehicle repairs, injury treatment, or other costs. If your claim is approved, you will receive payment based on your policy's terms for the loss suffered.
- Collect information: Write down the details of the incident, including the location, time, a basic description of the event, and how severe the damage is. If another driver is involved, document their name, contact information, insurance company, policy number, vehicle information, and the names of any passengers. Also, get the contact information of any witnesses. Take photos of the property damage, including the surrounding area and the entire scene.
- Talk to the police: If you're dealing with damage resulting from a car accident, call the police to the scene. An official police report will likely be required to file a claim. Do not admit or accuse any other driver of fault—the police and your insurance company will ultimately decide who is to blame.
- Keep track of paperwork: Hold on to all paperwork related to the accident, especially receipts. Depending on your policy, you may be able to get reimbursed for towing or immediate services.
- File a claim with your car insurance company: Contact your insurer as soon as possible. Give as much detail as you can and be prepared to share all the information you have written down. Make a note of the claim number your insurer provides.
- Schedule an inspection of your vehicle: An insurance adjuster will usually request that you schedule an inspection of your vehicle at a certified repair shop to determine if your vehicle can be repaired or if it is a total loss.
- Check if a rental car will be provided: If you will be without a vehicle for an extended period, check if you have rental reimbursement coverage in your policy to help cover the cost of a rental car.
- Know your deductible: Your deductible is the amount you need to reach before your insurance will start providing payment. If the cost of repairs is less than your deductible, you will have to pay for everything yourself. Collision coverage applies when you are involved in an accident with another vehicle or object, while comprehensive coverage offers protection for damage that doesn't stem from a collision, such as weather-related events or vandalism.
- Understand the process for a total loss vehicle: If your vehicle is a total loss, you or the company you are financing or leasing the car through may be eligible for compensation for the market value of your vehicle. If your car is stolen, you may receive compensation for its replacement cost value, which is the cost of a new car of the same make and model.
It is important to note that insurance laws and requirements may vary by state or country, so be sure to review the specific regulations in your region.
Auto Insurance Costs in Long Beach, CA: What to Expect
You may want to see also

Insurance industry jargon and definitions
The world of auto insurance can be confusing, with its own unique and quirky jargon. Here's a guide to help you understand some of the key terms related to auto insurance policies, claims, and coverage.
Policy and Coverage
- Policy: This is the contract between you and your insurance company. It outlines the rights and duties of both parties and details the coverage provided.
- Coverage: This refers to the specific risks or incidents that your insurance policy will cover. Different types of coverage include collision, liability, comprehensive, medical, and uninsured motorist coverage.
- Declarations Page ("Dec Page"): This is usually the first page of your insurance policy. It includes basic information such as your name, address, the insured property, policy period, amount of coverage, and premiums.
- Limits: The maximum amount your policy will pay for a given accident or incident. Each type of coverage has its own limits.
- Deductible: The amount you (the policyholder) are responsible for paying out-of-pocket before the insurance company pays a claim. Choosing a higher deductible can lower your insurance premiums.
- Premium: The cost of your insurance coverage, which can be paid monthly, yearly, or per six-month period.
Claims and Incidents
- Claim: A request for payment from your insurance company to cover vehicle repairs, injury treatment, or other costs associated with a covered incident.
- Covered Incident: Something that your policy will pay for. This could include accidents, collisions, or specific non-collision issues like theft or fire, depending on your coverage.
- Loss: The term used in the insurance world to refer to the amount of damage to a vehicle or property, or the injury suffered by a person.
- Total Loss: When the damage to a vehicle or property is so extensive that repair costs would surpass its value.
- Actual Cash Value (ACV): The fair market value or dollar value of an item, vehicle, or property at the time it was damaged, stolen, or destroyed.
Insurance Providers and Regulations
- Insurance Company/Insurer: The company that issues the insurance policy and agrees to pay for losses and provide covered benefits.
- Agent: A licensed individual or organization authorized to sell and service insurance policies for an insurance company.
- Broker: A licensed individual or organization who sells and services insurance policies on your behalf.
- Financial Responsibility Law: A law requiring vehicle owners and drivers to have sufficient funds or insurance to compensate anyone they might injure in an accident.
- Liability Insurance: Coverage for a policyholder's legal liability, resulting from injuries to other persons or damage to their property.
Additional Terms
- Uninsured Motorist Coverage: Provides coverage for injuries and property damage when you're involved in an accident with an uninsured driver or a driver with insufficient insurance.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Pays for damage to your car caused by reasons other than collision, such as fire, theft, vandalism, or natural disasters.
- Collision Coverage: Pays for damage to your car caused by physical contact with another vehicle or object, such as a tree or guardrail.
- Medical Payments Coverage (MedPay): Covers the medical costs resulting from an auto accident for you, your family, your passengers, and pedestrians, regardless of who is at fault.
- Personal Injury Protection (PIP): Similar to MedPay, it covers medical treatment, lost wages, and other expenses related to an accident, regardless of who is at fault.
These definitions should help you better understand the key terms related to auto insurance and make more informed decisions about your coverage options.
Auto Insurance vs Medical Bills: Who Pays the Price?
You may want to see also

How to customise your policy
Auto insurance is a contract between you and your insurance company. By applying for coverage, you agree to pay a premium to the insurance company, and they agree to pay for covered costs associated with an auto accident. The cost of your auto insurance, or premium, can be paid monthly, yearly, or every six months.
There are several types of auto insurance coverage, and you can customise your policy by making coverage selections to cover different types of accidents and related issues. Here are some of the main types of auto insurance:
- Collision coverage: This helps pay the cost of repairing or replacing your car if it is damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. After making a claim, you usually pay a deductible before your insurance kicks in.
- Comprehensive coverage: This covers damage to your vehicle caused by things other than a collision or rollover, such as hail damage or a tree falling on your car. You usually pay a deductible before your insurance steps in. Comprehensive car insurance can also offer additional coverage if your vehicle is stolen, extending to custom equipment and certain electronic devices.
- Liability coverage: In most states, you are required to have liability coverage. There are two types: bodily injury liability and property damage liability. Bodily injury liability covers injuries to your passengers and, in some cases, the driver and passengers of the other vehicle when you are at fault in a car accident. Property damage liability covers damage to someone else's property if you are at fault in an accident, usually meaning damage to their car but also covering other types of property.
- Medical coverage: There are two types of medical coverage: medical expense and personal injury protection. Medical expense coverage pays for medical care provided to you and your passengers in a car accident, regardless of who is at fault. Personal injury protection helps reimburse you and your passengers for lost income, childcare expenses, medical expenses, and other costs if you are hurt in an accident, again regardless of who is at fault.
- Uninsured motorist coverage: This provides protection when you are in an accident with a driver who does not have insurance.
- Underinsured motorist coverage: This protects you financially if you are in an accident with a driver whose insurance limits are not high enough to cover your full expenses after a claim. It also provides coverage for insured members of your household and passengers in your vehicle.
- Emergency roadside assistance: This helps pay for service and support when your car can't make it to a repair shop. Services include towing, battery jumps, tire servicing, gas and oil delivery, locksmith services, and roadside repairs.
- Rental car reimbursement: This helps pay for a rental car while your car is in the shop after a covered accident.
- Auto lease/loan protection: This helps pay the difference between what your car is worth and what you owe if your car is totalled in a covered event.
- Accidental death and dismemberment: This coverage provides financial benefits in the worst-case scenario, regardless of who is at fault.
- Road trip accident accommodations: Eligible customers can use this coverage to help pay for emergency expenses like lodging, meals, and alternate transportation when they are involved in an accident more than 100 miles from home.
- New car replacement: This coverage, available only for brand-new vehicles, helps replace your car if it is totalled.
- Pet coverage: This can help pay for your pet's medical expenses if they are in your vehicle when you are involved in an accident or your car is stolen.
In addition to these standard coverage options, you can also get add-on coverage for customisations or modifications made to your car. This includes custom paint jobs, murals, graphics, decals, electronic equipment, custom tires, custom spoilers, speed enhancements, and more. While some insurers regard a vehicle as "customised/modified" only when its chassis, body, or frame are structurally modified or its performance is considerably augmented, others do not provide any coverage for enhancements beyond tires and rims. Therefore, it is important to read your existing policy thoroughly to understand coverage exclusions and exceptions and consult with your insurer before making any changes to your vehicle.
Auto Insurance for Your Child: What's the Cost?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Actual Cash Value (ACV) is the value of a car considering its age, mileage, make, model, and overall condition. It also refers to the fair market value of an item, which is the dollar amount a buyer is willing to pay and a seller is willing to accept.
A binder is a temporary agreement that provides short-term insurance coverage until a formal policy can be issued or delivered.
Comprehensive coverage pays for damage to your car caused by something other than a collision, such as fire, theft, vandalism, windstorm, flood, etc. It also covers a list of non-collision issues like animal collisions, falling objects, and fire.
A deductible is the amount of money the policyholder must pay out-of-pocket for covered losses before the insurance company pays a claim. Choosing a higher deductible typically lowers your insurance premiums.
Liability insurance covers the policyholder's legal liability resulting from injuries to other persons or damage to their property. It pays for the legal defense costs if the policyholder is sued as a result of an accident.







