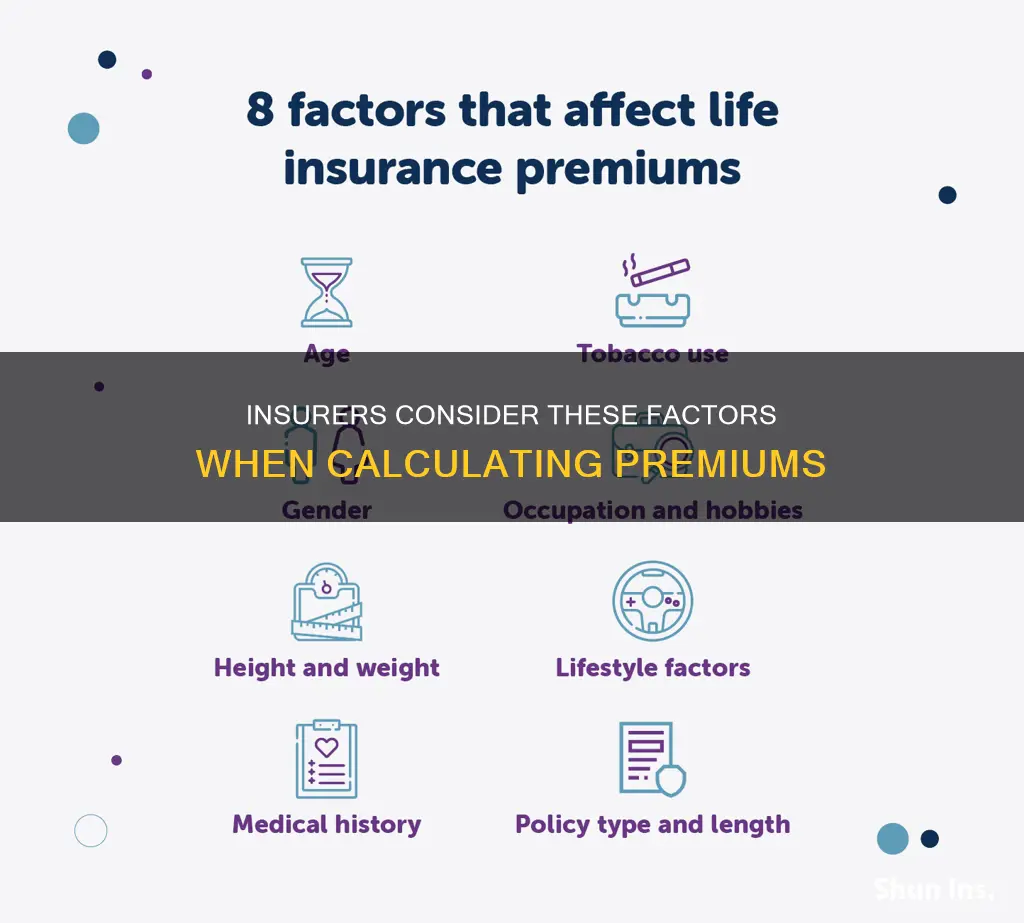
When determining whether to accept a group life plan, insurers consider several factors, including the average age of the group, the number of dependents, and the incontestable period. Additionally, they may look at the adverse selection tendency, which is minimised when all eligible employees are covered under a non-contributory health insurance plan. Insurers also consider various factors when calculating life insurance premiums, such as age, gender, health, family medical history, lifestyle, and occupation.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average age | |
| Number of dependents | |
| Incontestable period | |
| Grace period | |
| Family medical history | |
| Gender | |
| Health | |
| Lifestyle | |
| Driving record | |
| Smoking status | |
| Occupation |
What You'll Learn

Average age
When determining whether to accept a group life plan, insurers will consider the average age of the group. This is because age is a primary factor influencing insurance premium rates, whether for term or permanent policies. The younger you are, the lower your insurance payments will be, as insurers are taking on less risk when insuring a young person in good health.
In the case of term life insurance, the premium is established when you buy the policy and remains the same every year. However, once the term expires, you will likely face very steep rates based on your age. With some permanent life insurance policies, the premium rises annually.
Age also affects whether a person will qualify for life insurance coverage at all, with qualifying medical exams becoming more stringent as you get older. Most carriers only offer 20-year term policies to those aged 18 to 70. After that, you cannot get a term that lengthy.
The reason is simple: the older you are, the more likely you are to become ill or die while under coverage. Insurers use actuarial tables to help set life insurance rates and estimate life expectancy and mortality.
In the context of car insurance, age is also one of the biggest factors influencing rates. Younger drivers are considered riskier to insure than older drivers, and so pay more for coverage.
Updating Your Insurance Details: Navigating the DEERS System
You may want to see also

Number of dependents
The number of dependents is a crucial factor that insurers consider when determining coverage and premiums. Dependents are individuals who are eligible for inclusion in a policyholder's insurance plan, typically comprising the spouse, domestic partner, and children. Here's a detailed overview of how the number of dependents impacts insurance considerations:
Spouse as a Dependent:
In most cases, a policyholder's spouse can be added as a dependent on their health insurance plan. This is applicable for legally married couples, and usually doesn't extend to ex-spouses or domestic partners unless specific criteria are met. The inclusion of a spouse as a dependent can impact the overall cost of the insurance plan and the benefits available.
Children as Dependents:
Biological children, adopted children, stepchildren, and foster children are typically considered dependents. The age limit for dependent children is usually up to 26 years old, and their coverage may continue even if they have a baby, go to school, or become employed. Insurers may also offer coverage for children with disabilities or special needs, extending beyond the standard age limit. The number of dependent children directly influences the cost and scope of the insurance plan.
Other Dependents:
In certain circumstances, individuals beyond the immediate family can be considered dependents. For example, grandchildren, siblings, or parents may qualify as dependents if they have special needs, disabilities, or legal guardianship arrangements. Additionally, domestic partners or same-sex partners may be recognised as dependents under specific insurance policies or in certain states. The inclusion of these additional dependents can further impact the cost and coverage options offered by insurers.
Impact on Insurance Costs and Benefits:
The number of dependents directly influences the cost of insurance premiums. Generally, adding dependents results in higher overall premiums. However, having a larger number of dependents may also increase the likelihood of qualifying for financial assistance or tax benefits associated with health insurance plans. Insurers may offer family plans or customised packages to accommodate multiple dependents, ensuring that each dependent has access to essential healthcare services.
Open Enrollment and Special Circumstances:
Insurers typically allow the addition or removal of dependents during open enrollment periods, which are usually held annually. Additionally, special enrollment periods may be available following significant life events, such as the birth of a child, marriage, divorce, or the adoption of a child. These periods provide flexibility for policyholders to update their dependent information and ensure continuous coverage for their loved ones.
Flight Flexibility: Utilizing Purchase Insurance to Alter Travel Plans
You may want to see also

Health and family medical history
When it comes to health insurance, health and family medical history are significant factors that insurers consider when determining premium costs and coverage. This is because an individual's health and family medical history can indicate their potential health risks and likelihood of developing certain medical conditions.
A family health history provides valuable insights into the genetic background, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices that may increase the risk of specific health issues. For example, a family history of heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, certain cancers, or type 2 diabetes can indicate a higher-than-average chance of an individual developing these conditions. Insurers use this information to assess the potential future health risks of the insured person.
In addition to family history, insurers also consider an individual's personal health profile, including their current health status and any pre-existing medical conditions. This information helps insurers determine the likelihood of future health issues and the associated costs of treatment. While family history plays a role, an individual's personal health profile is typically a more significant factor in calculating insurance premiums.
It is important to note that having a family history of medical issues does not guarantee that an individual will develop those issues themselves. However, it can still impact the cost of insurance and the likelihood of certain health problems developing. As such, it is crucial for individuals to be honest about their family medical history when applying for insurance to ensure they receive appropriate coverage and avoid issues with their insurer in the future.
Furthermore, understanding one's family medical history can empower individuals to make informed lifestyle choices and take preventative measures to reduce their risk of developing certain health conditions. For example, individuals with a family history of cancer may opt for regular screenings to detect any potential issues early on. Similarly, those with a family history of heart disease may be advised to adopt healthier diets and increase their physical activity to lower their chances of developing cardiovascular problems.
In summary, health and family medical history are crucial factors that insurers consider when determining insurance premiums and coverage. By assessing an individual's health status and family history, insurers can identify potential future health risks and calculate the associated costs. While family history is important, an individual's personal health profile typically carries more weight in the overall calculation of insurance premiums.
Unraveling the Complexities of Retroactive Insurance Billing
You may want to see also

Lifestyle and occupation
When it comes to lifestyle and occupation, insurers consider a range of factors to assess the risk associated with providing an individual with insurance coverage.
Lifestyle
Engaging in risky activities or hobbies such as racing cars, scuba diving, rock climbing, bungee jumping, or extreme sports can significantly impact insurance eligibility and rates. Insurers view these activities as potential threats to an individual's health and safety, leading to higher premiums or even exclusion from coverage. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as smoking, heavy drinking, drug use, and lack of self-care can also result in higher insurance rates or difficulties in obtaining coverage.
Occupation
Certain occupations are considered high-risk due to their hazardous nature, increased possibility of injury or death, or adverse effects on health and safety. These include jobs such as:
- First responders (law enforcement, firefighters)
- Active military personnel
- Media, medical, or government workers in conflict zones or emerging countries
- Aviation jobs (pilots)
- Construction workers
- Natural resources workers (mining, fishing, logging, etc.)
- Bartenders
- Marijuana industry workers
- Railway workers
- Soldiers
- Policemen
Individuals in these occupations often face higher insurance premiums or challenges in obtaining coverage. The risk associated with specific duties and the likelihood of premature death are key factors in determining insurance rates and eligibility.
COBRA Coverage: Understanding Your Insurance Continuation Rights
You may want to see also

Driving record
A driver's record is one of the most important factors that insurers consider when assessing insurance applications. It gives them a good indication of how an applicant drives and how responsible they are behind the wheel. Insurers will check an applicant's driving record when they apply for auto insurance and when they renew their policy.
Insurers will look for accidents, traffic violations, and claims when reviewing a person's driving record. They will also check for speeding tickets, at-fault accidents, and DUIs. These driving behaviours increase an applicant's risk as a driver, which leads to higher insurance rates.
In the US, insurers typically look back at the previous three to five years of an applicant's driving record, although some states may look back as far as ten years. In Canada, insurers tend to request a three- or five-year driver's record.
In the US, each state has a points system to codify the severity of driving violations. If a driver accumulates a set number of points within a given period, their licence will be suspended. For example, in New York, a driver's licence will be suspended if they accumulate 11 points or more within 18 months. In California, a driver will be suspended for four points in a year, six points in two years, or eight points within three years.
In Canada, a driver's abstract (or motor vehicle record) is used to check a person's driving history. This record includes driver's licence suspensions, demerit points, active fine suspensions, driving convictions, and suspensions and reinstatements over the past three years.
A person's driving record can lower or increase their insurance premiums. A clean driving record can help a person benefit from lower premiums or even discounts for staying accident or violation-free. Conversely, a poor driving record can lead to higher insurance rates or even result in an insurer dropping or refusing to insure a driver if they are deemed too high-risk.
Understanding Insurance Billing Procedures Post-Sale: A Guide for Psychotherapy Corporations
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Insurers would consider the average age of the group.
Age is the most important factor. The younger you are, the lower your payments.
Insurers will consider your health, lifestyle, family medical history, driving record, and whether or not you smoke.
Adverse selection is the tendency of less favourable insurance risks to seek or continue insurance to a greater extent than others.
A non-contributory health insurance plan helps the insurer to avoid adverse selection.







