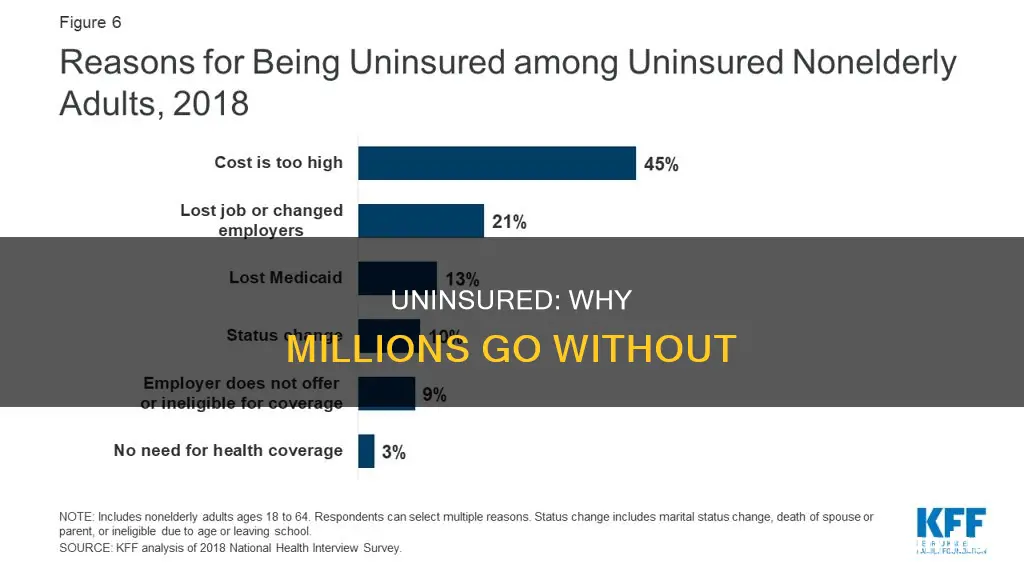
There are many reasons why some people are uninsured. In 2022, 25.6 million non-elderly individuals were uninsured in the US, with 64% of uninsured non-elderly adults citing the high cost of insurance as the main reason for lacking coverage. Many uninsured people do not have access to coverage through their job, and some people, particularly poor adults in states that did not expand Medicaid, remain ineligible for financial assistance. Additionally, undocumented immigrants are ineligible for federally funded coverage.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| High cost of insurance | 64% of uninsured nonelderly adults in 2022 |
| Lack of access to coverage through a job | Many |
| Ineligibility for financial assistance | Some |
| Undocumented immigrant status | Undocumented immigrants are ineligible for federally funded coverage |
| Lack of awareness of coverage options | Some |
| Difficulty of signing up for coverage | 22.2% of uninsured nonelderly adults in 2022 |
What You'll Learn

Cost of insurance
The cost of insurance is a significant factor in why some people are uninsured. Insurance premiums can be expensive, and for those on low incomes, it may be challenging to afford coverage. The premium rate for a life insurance policy, for example, is determined by mortality and interest rates, as well as the expense factor, which includes operating costs. Similarly, health insurance premiums can be high, and individuals must also consider additional costs such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
In the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has made it possible for millions to access subsidised healthcare plans. However, many consumers are ineligible for these subsidies, and the high costs of insurance remain a barrier for some. As of the first quarter of 2023, 7.7% of US adults, or 25.3 million people, were uninsured. This is a decrease from the previous quarter, but the number remains significant.
The consequences of being uninsured can be dire. In the case of car insurance, for instance, being uninsured can result in penalties and legal consequences if one is found at fault in an accident. Additionally, uninsured individuals may face challenges in receiving compensation for their injuries and losses.
The impact of being uninsured extends beyond financial penalties. Lack of health insurance can lead to reduced access to medical services and poorer health outcomes. Uninsured individuals may forgo preventive care, resulting in more severe health issues that require emergency treatment. This, in turn, can lead to substantial medical debt, which is a significant contributor to bankruptcies in the US.
Furthermore, insurance fraud also affects the cost of insurance for policyholders. In Australia, for example, fraudulent or exaggerated claims have resulted in millions of dollars in additional costs for car insurance policyholders.
Overall, the cost of insurance is a critical factor in the decision to remain uninsured for many individuals. The high premiums, additional costs, and potential consequences of being uninsured create a challenging situation for those who are unable to afford coverage.
American Family Insurance Policy Changes: Understanding Fee Structures
You may want to see also

Lack of access to coverage through work
The rising costs of medical care are putting it out of reach for many, and the growing number of high-deductible plans requires people to pay a lot out of pocket before insurance kicks in. This results in many turning away from necessary healthcare.
Government initiatives like the expansion of Medicaid have helped lessen the impact of uninsured status as a barrier to healthcare coverage. However, as the cost of insurance continues to rise, many companies are no longer able to offer it as a benefit to their employees. Shopping for insurance in the private market often leaves people with expensive policies and high-deductible plans.
**Understanding Short-Term Recovery Insurance: A Safety Net for the Unexpected**
You may want to see also

Ineligibility for financial assistance
In the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) allows millions to choose a government-subsidized healthcare plan. However, many consumers are ineligible for subsidies, and many of those who qualify have chosen not to participate. As a result, in the first quarter of 2023, 7.7% of adults, or 25.3 million people, were without health insurance.
There are several reasons why people may be ineligible for financial assistance with healthcare costs. Firstly, individuals must meet certain criteria to be eligible for government-subsidized healthcare plans. For example, to be eligible for FEMA's Individuals and Households Program (IHP), which provides financial assistance and direct services to those affected by disasters, applicants must be a U.S. citizen, non-citizen national, or qualified non-citizen. FEMA must also be able to verify the applicant's identity.
Secondly, an individual's income may disqualify them from receiving financial assistance. In the U.S., Delaware State offers Medicaid and Healthcare Connections Programs to assist uninsured patients. However, patients must first be screened for these programs to be eligible for financial assistance. Similarly, the Affordable Care Act requires individuals to apply for insurance and provide proof of eligibility before applying for financial assistance.
Thirdly, an individual's insurance status can affect their eligibility for financial assistance. For example, individuals who already have insurance or other forms of disaster assistance may not be eligible for further financial aid. Additionally, those with private insurance may not be eligible for certain charity assistance programs.
Finally, an individual's ability to provide the necessary documentation can impact their eligibility for financial assistance. Applicants for financial assistance may need to provide various forms of documentation, such as proof of occupancy, ownership, income loss, or information concerning their housing situation prior to the disaster.
Earthquake Insurance: Who's Covered?
You may want to see also

Immigration status
Undocumented immigrants face barriers to accessing care due to their high uninsured rates. They often delay or go without the care they need. While they can obtain low-cost care through community health centres, this care is often limited to preventive and primary care, leaving them with challenges in accessing specialty services.
Some states have taken steps to expand coverage to immigrants, including adult immigrants, in recent years. As of June 2024, 12 states and Washington D.C. provide fully state-funded coverage for income-eligible children regardless of immigration status. Six states and Washington D.C. also provide fully state-funded coverage to some income-eligible adults regardless of status. Most states have taken up options in Medicaid and CHIP to expand coverage to lawfully present immigrant children and pregnant women.
Undocumented immigrants are not considered lawfully present and are therefore ineligible to enrol in health coverage through the ACA Marketplaces. However, individuals with Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) status will be considered lawfully present and eligible for Marketplace health coverage with income-based subsidies starting November 1, 2024.
In summary, immigration status plays a significant role in determining an individual's access to health insurance coverage. Undocumented immigrants face barriers to coverage and care, while lawfully present immigrants may have more options but still face some restrictions. States have implemented various programs to expand coverage for immigrants, but these efforts are limited by funding constraints.
Understanding Insurance Coverage: Navigating Lab Bill Payments
You may want to see also

Lack of awareness of coverage options
In the United States, the illiteracy rate in 2020-21 was 77.7%, and this lack of education is a significant barrier to understanding insurance options. This issue is not limited to rural areas but is also present in urban sections.
Misconceptions about health insurance are deep-rooted, and many believe that healthy people don't need it. However, this perception changes when facing a medical contingency, and people then realise the importance of having insurance.
Additionally, a significant portion of the population in the US falls below the poverty line, and for them, spending money on health insurance is not a priority.
The state of public hospitals also plays a role in insurance awareness. Many people rely on private hospitals due to the lack of basic facilities in public hospitals, and public hospitals are often dependent on insufficient government funds.
Lack of healthcare professionals is another issue, as they play a vital role in spreading awareness about proper healthcare and insurance. India, for example, has a doctor-to-patient ratio of 1:1456, far below the recommended 1:1000 by the WHO.
Lastly, free coverage under group plans offered by employers can also lead to a lack of awareness about other insurance options and the importance of having comprehensive coverage.
Naming Additional Insureds: A Quick Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The high cost of insurance is a key reason why many are uninsured. In 2022, 64% of uninsured non-elderly adults cited the cost of coverage as the main reason they lacked insurance.
People without insurance coverage have lower access to care than people who are insured. Uninsured people are more likely to delay or forgo care due to costs. They are also less likely to receive preventive care and services for major health conditions and chronic diseases.
Uninsured individuals often face unaffordable medical bills when they do seek care. These costs can quickly translate into medical debt since most uninsured people have low or moderate incomes and little to no savings.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded health insurance to millions of Americans, and pandemic-era policies have further protected people with low incomes. However, some people remain ineligible for financial assistance, including undocumented immigrants.







