Auto insurance companies ask about the number of miles driven because it helps them determine the risk of insuring a driver. The more miles driven, the higher the chance of an accident, and the higher the insurance premium will be. Conversely, drivers who cover fewer miles are considered lower risk and are often rewarded with lower premiums or discounts. Annual mileage is just one of many factors that insurance companies use to calculate premiums, including age, gender, location, and driving record.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Reason for asking | To assess the risk of the driver getting into an accident and filing a claim |
| Mileage and insurance rates | Higher mileage generally leads to higher insurance rates |
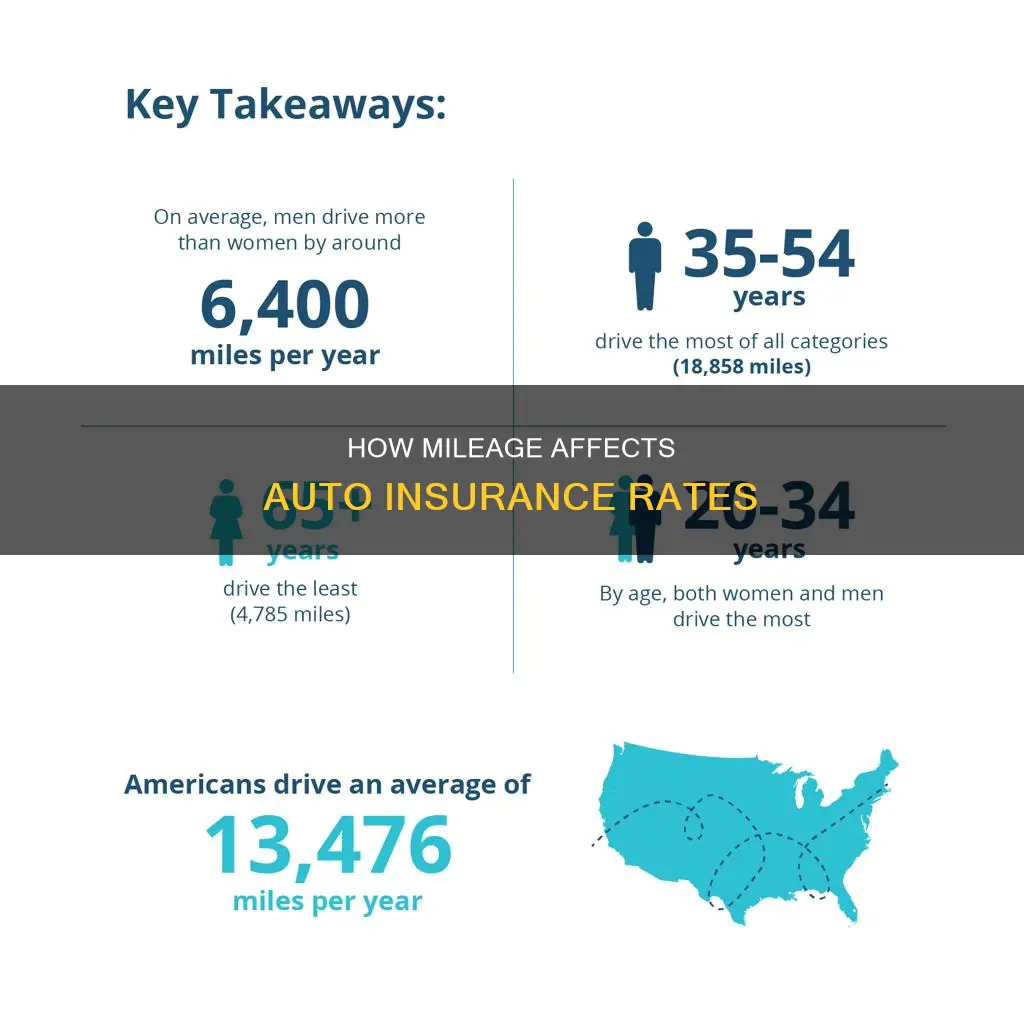
| Average annual mileage | 13,000-13,500 miles |
| Low mileage | Less than 7,500-12,000 miles per year |
| High mileage | More than 15,000 miles per year |
| Impact on insurance policy | Going over the annual mileage could invalidate the insurance policy |
| Mileage tracking methods | Telematics, manual checks, third-party data |
What You'll Learn

Higher mileage = higher risk of accidents
Auto insurance companies ask about the number of miles driven because it helps them determine the risk of accidents. The more miles driven, the higher the chances of getting into an accident. This is why car insurance companies consider higher mileage to indicate a higher risk of accidents and, consequently, higher insurance rates.
The annual mileage driven is a significant factor in calculating insurance rates. Insurance companies use this information to assess the likelihood of the driver filing a claim. The higher the mileage, the higher the risk of a collision, and thus, the higher the insurance rate. For instance, someone who drives 15,000 miles or more annually is generally considered a high-mileage driver and may face higher insurance costs.
Insurance companies employ various methods to calculate a driver's annual mileage. They may rely on the honour system, where the driver provides an estimated annual mileage. Some companies conduct random mileage checks to verify the accuracy of the provided information. Additionally, insurance companies may utilise telematics devices installed in the car, or they may obtain odometer readings from third-party sources, such as auto repair shops.
The impact of annual mileage on insurance rates can vary. While some companies may have specific mileage brackets that directly influence the rates, others may use a more nuanced approach. For example, a driver with an annual mileage of 10,000–15,000 miles may fall into a certain insurance rate category, while a driver with a mileage of 15,000–20,000 miles may be placed in a higher rate category.
It is important to note that insurance companies consider other factors beyond annual mileage when determining insurance rates. These factors include the type of vehicle, the amount of coverage, the driver's age, gender, driving record, and location. However, annual mileage remains a crucial aspect of the calculation, and higher mileage is generally associated with higher insurance rates due to the increased risk of accidents.
Farmers and Mechanics Insurance: Exploring Commercial Auto Coverage
You may want to see also

Annual mileage affects insurance premiums
The number of miles driven annually is a key factor in determining insurance premiums. Insurance companies use annual mileage to assess the risk of a driver making a claim, with higher mileage indicating a greater chance of accidents and subsequent claims. This data is used to calculate insurance rates, with higher mileage resulting in more expensive premiums.
Insurance companies employ various methods to calculate annual mileage, including telematics devices installed in vehicles, manual checks by agents, and third-party sources such as auto repair shops. They may also rely on the driver's honesty when providing an estimated annual mileage.
The Impact of Commuting
Commuting is a significant factor in annual mileage calculations. Driving to work, even if it involves parking outside a train station, increases annual mileage and can lead to higher insurance rates. Insurance companies consider commuting in densely populated areas or cities to carry a higher risk of accidents.
Low Mileage and Savings
Drivers who cover less than the average annual mileage may be eligible for low-mileage insurance, which can result in significant savings. This type of insurance is ideal for those who work from home, use public transportation, or drive infrequently. Low-mileage insurance is typically offered as a standalone policy or a program within standard auto insurance. It calculates premiums based on a flat monthly rate plus a small per-mile fee.
Adjusting Annual Mileage
It is crucial to inform your insurance provider if your annual mileage changes. Updating your estimated mileage can lead to a lower premium, especially if it falls within the insurer's low-mileage bracket. However, exceeding your annual mileage estimate may invalidate your policy, as insurers only cover the mileage you initially declared.
Other Factors Influencing Premiums
While annual mileage is a significant factor, insurance companies also consider other variables when setting premiums, such as the type and model of the vehicle, the level of coverage, the driver's age, gender, driving record, and place of residence.
Navigating Auto Insurance Abroad: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Insurers may invalidate policies if annual mileage exceeded
Insurers may invalidate your policy if you exceed your annual mileage, meaning they won't pay out if you need to make a claim. This is because car insurance policies only cover the annual mileage estimate you provided. Any journeys outside of this are technically not insured.
If you go over your annual mileage, you may not get a payout at all if you claim. In other cases, you won't be able to claim as much as you thought. Some insurers will also charge a lump sum to cover the difference between your current policy price and what you would have been charged if your mileage was correct.
Insurers often use annual mileage to calculate your car insurance price, so it's important to be as accurate as possible. Generally, the higher your estimated mileage, the higher your car insurance premium will be. This is because the more you drive, the more likely you are to get into an accident and make a claim.
If you think you might exceed your annual mileage before your policy ends, it's important to inform your insurer. They may charge an "adjustment fee" to update your details, which could cost between £15 and £30. Your policy cost may also increase to reflect the additional miles you need insurance for.
If your premium becomes too expensive, you may want to consider cancelling your policy and purchasing one with higher mileage coverage. Keep in mind that insurers often charge a cancellation fee, and if you pay your policy by direct debit, you'll typically end up with additional cancellation fees.
Understanding Stacked Auto Insurance Policies: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Telematics devices can track mileage
Telematics devices are small electronic devices installed in vehicles to monitor and record data related to the vehicle's performance and location. They are commonly used in fleet management, insurance programs, and personal vehicle tracking systems. These devices use GPS technology and cellular communication to transmit data to a remote server, which can then be analysed and used for various purposes.
One of the key pieces of data that telematics devices capture is mileage or the number of miles driven. By tracking mileage, telematics devices can help insurance companies assess risk and set premiums accordingly. The more miles driven, the higher the chance of an accident, and thus the higher the insurance rate. Conversely, drivers who travel fewer miles are considered lower risk and may be eligible for low-mileage discounts.
Telematics devices can also assist in improving driving behaviour and promoting safe driving habits. For example, by tracking harsh acceleration, braking, and speeding, these devices can provide drivers with real-time alerts about potential hazards and help them develop safer driving practices. This not only improves safety but can also lead to lower insurance costs as telematics devices can help reduce the risk of accidents.
In addition to mileage tracking, telematics devices offer several other benefits. They can aid in vehicle maintenance by tracking faults and notifying users of necessary repairs, reducing the risk of breakdowns. They can also help optimise routes, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce fuel costs by monitoring driving behaviour. Moreover, telematics devices can simplify compliance reporting, automate mileage tracking, and even assist in theft prevention by enabling the tracking of stolen vehicles.
Overall, telematics devices that track mileage play a crucial role in the insurance industry, helping insurance providers set accurate rates based on driving behaviour and mileage. They also offer numerous advantages to drivers, including improved safety, reduced costs, and enhanced vehicle maintenance.
Safeco Auto Insurance: Understanding Medical Expense Coverage
You may want to see also

Low-mileage drivers may be eligible for discounts
Driving fewer miles per year means you pose less of a risk to your insurer and will therefore pay less. This is because the more you're behind the wheel, the greater the odds of being in a car accident.
Insurance companies consider under 12,000 miles a year to be lower than average. However, some insurers require that you drive less than 10,000 miles to qualify for low mileage, and they wait to hand out bigger discounts until you are under that number of annual miles.
Some insurers might offer even bigger low-mileage discounts if you drive less than 7,000 or 5,000 miles annually.
If you drive less than 26 miles per week, you may be eligible for "pay per mile" insurance. With this type of coverage, you pay for each mile you drive.
Some of the major companies that offer low-mileage car insurance and mileage-based savings programs include:
- Nationwide SmartRide
- Progressive Snapshot
- Allstate (Milewise program)
- State Farm Drive Safe and Save
- Farmers (Signal program)
If you're a low-mileage driver, you may be able to save money on your car insurance premiums by contacting your insurance agent or company and letting them know about the change.
Best Auto Insurance Leads: Effective Strategies for Agents
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Insurance companies want to know how many miles you drive because it helps them determine how big a risk you pose as a driver.
The more miles you drive, the more likely you are to get into an accident, and the higher your insurance rate will be. Conversely, driving fewer miles will generally result in a lower insurance rate.
Insurance companies typically ask for an estimated annual mileage when you buy a policy. Some companies may also track your mileage through telematics devices installed in your car, or by getting odometer readings from a third party, such as auto repair shops.
On average, Americans drive around 13,000 miles per year, so any number lower than this is usually considered low mileage. However, insurance companies may have different definitions of low mileage, with some considering under 10,000 miles or even 7,000 miles as low mileage.
Going over your annual mileage could invalidate your insurance policy, meaning your insurer may not pay out if you need to make a claim. It is important to inform your insurer if you think you will exceed your estimated mileage to avoid any issues.







