Protecting your credit score can have a significant impact on your auto insurance rates. In most states, car insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores, which means your credit score can influence your premium. While a higher credit score generally leads to lower insurance rates, a poor credit score can result in substantially higher premiums. This is because insurance companies often associate lower credit scores with a higher likelihood of filing insurance claims, and they compensate by charging higher rates. However, it's important to note that not all states allow the use of credit scores in determining insurance rates, and there are other factors beyond credit scores that insurance companies consider when setting premiums.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Credit score impact on auto insurance rates | In most states, a higher credit score decreases auto insurance rates |
| Poor credit impact on auto insurance rates | Poor credit raises rates by 86-88% compared to good credit |
| Poor credit auto insurance rates by state | Poor credit drivers in Washington, D.C. experience a 250% rate increase compared to the average |
| Poor credit auto insurance rates by company | State Farm charges $471 per month for full coverage for poor credit drivers, while Geico charges $258 per month |
| Credit-based insurance score | Insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores to determine how risky a customer is in terms of filing auto insurance claims |
| Credit-based insurance score factors | Outstanding debt, credit history length, credit mix, payment history, pursuit of new credit |
| States prohibiting credit-based insurance scores | California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Michigan |
| Improving credit score | Pay bills on time, minimize hard credit inquiries, monitor credit score, maintain old lines of credit, lower credit utilization ratio |
What You'll Learn

How credit scores affect insurance rates
Credit scores can have a significant impact on insurance rates, with those with poor credit often facing much higher premiums than those with good credit. This is because insurance companies tend to correlate lower credit scores with a higher likelihood of making an insurance claim.
In most states, car insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores, which means your credit score can impact your premium. Drivers with excellent credit generally pay the lowest rates, while those with poor credit pay the highest. This is because insurance companies view drivers with poor credit as more likely to make a claim, and so charge them more.
However, this isn't the case in all states. Four states—California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan—ban the use of credit scores to determine insurance rates. In these states, insurance companies base rates on factors like driving records and location.
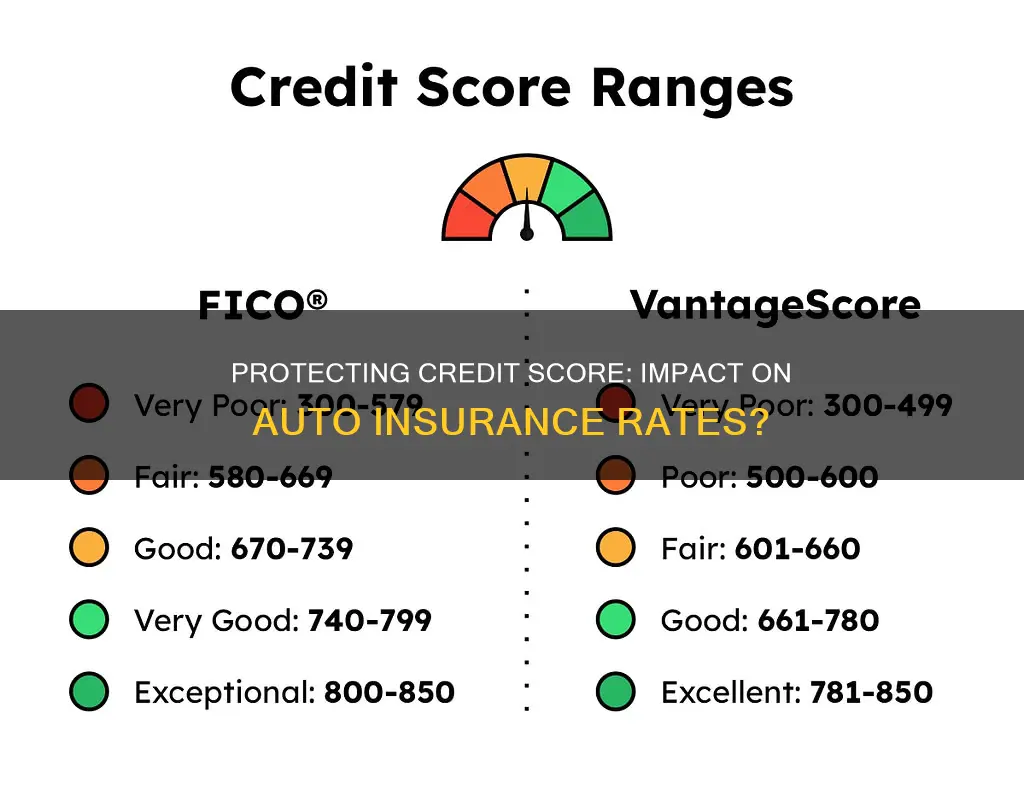
Credit-based insurance scores are different from the typical credit scores calculated by FICO and VantageScore. While these credit scores predict the likelihood of a consumer being late on a payment, credit-based insurance scores predict the likelihood of a consumer filing insurance claims.
Insurance companies use a range of factors to determine credit-based insurance scores, including outstanding debt, credit history length, credit mix, and payment history.
Improving your credit score can help lower your insurance premium. This can be done by paying bills on time, keeping hard credit inquiries to a minimum, monitoring your score, maintaining old lines of credit, and keeping credit utilization low.
The Great Insurance Divide: Iowa vs. Michigan Auto Policies Explored
You may want to see also

States where credit scores don't affect insurance rates
In the United States, credit scores can have a significant impact on car insurance rates, with those with poor credit often facing much higher premiums. This is because insurers believe that drivers with poor credit are more likely to file insurance claims. However, some states have restricted or banned the use of credit scores in determining insurance rates. Here is a list of states where credit scores do not affect insurance rates:
- California: In California, insurance companies are not allowed to use credit scores or credit history when underwriting or rating auto policies or setting rates for homeowners insurance.
- Hawaii: Hawaii bans the use of credit ratings in determining auto insurance policy prices. However, credit can impact homeowners insurance rates.
- Maryland: While credit history can be considered when determining rates for a new auto insurance policy, it cannot be used to deny an application, cancel a policy, refuse to renew, or increase renewal premiums. For homeowners insurance, credit history cannot be used to refuse coverage, cancel a policy, refuse to renew, or base insurance rates.
- Massachusetts: Massachusetts law forbids the use of credit information or credit-based insurance scores when setting rates, underwriting new policies, or renewing auto policies. Credit also cannot be used to determine homeowners insurance rates.
- Michigan: In Michigan, credit information or credit-based insurance scores cannot be used to deny, cancel, or refuse to renew auto or homeowners insurance policies. Credit scores also cannot be used to determine auto insurance rates.
- Nevada: Nevada has temporarily restricted the use of credit-based insurance scores during the COVID-19 pandemic until May 20, 2024. Insurance companies cannot consider negative credit information from events after March 1, 2020, for certain decisions.
- Oregon: Insurers in Oregon cannot cancel or refuse to renew a policy due to credit history. Credit can be considered when initially offering a policy, but only certain information from the credit report can be used.
- Utah: Credit information can be used when initially underwriting an auto policy, but it cannot be the sole factor. After 60 days, credit information cannot be used to cancel, refuse to renew, or decline coverage for a new vehicle. Credit information can only be used to offer discounts on premiums.
It is important to note that the impact of credit scores on insurance rates can vary across states, and some states may have different regulations regarding the use of credit scores. Additionally, other factors such as age, driving record, location, and vehicle type also influence insurance rates.
Tornado Damage and Auto Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Improving your credit score
- Pay your bills on time: Late and missed payments are the biggest factors that affect your credit score. Set up autopay for at least the minimum amount due and create calendar reminders to ensure timely payments.
- Lower your credit utilisation: Aim to keep your credit utilisation below 30%. This is calculated as the percentage of your available credit limit that you're using. For example, if you have a credit limit of $10,000 and a debt of $7,500, your credit utilisation is 75%. Aim for 30% or less by paying off some of your debt.
- Maintain old credit accounts: The length of your credit history can contribute significantly to your score. Instead of closing old credit accounts, consider using them sparingly and making timely payments. This will help fortify your credit history and lower your credit utilisation ratio.
- Diversify your credit mix: Having different types of credit, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages, can improve your credit score. However, avoid taking on more debt than necessary just for the sake of building credit.
- Limit new credit applications: Each new credit application results in a hard inquiry, which can negatively impact your score. Only apply for new credit when necessary, and consider prequalification options that use soft credit checks instead.
- Dispute inaccurate information: Inaccurate information on your credit report can significantly harm your score. Review your credit reports from Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion for any discrepancies and dispute them promptly.
- Become an authorised user: If you're new to credit, consider asking a loved one to add you as an authorised user on their credit card. Ensure the account has a positive payment history and a low credit utilisation rate.
- Monitor your score regularly: Keeping a close eye on your credit score allows you to take proactive measures to improve it. Additionally, routine checks can help identify errors or signs of identity theft early on.
Auto Shops and the Insurance of Auto Parts: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

How insurance providers use credit scores
Credit scores are a significant factor in determining insurance rates. While the specific criteria may vary across providers, insurers generally use credit scores to assess the risk of insuring an individual and their vehicle. A low credit score indicates a higher risk of filing insurance claims, which is unfavourable for insurance providers.
Insurance providers use a credit-based insurance score, which is distinct from the typical FICO credit score used for credit cards and loans. This score reflects the likelihood of filing insurance claims that will cost the company more money than they collect in premiums. While credit-based insurance scores are not used in all states, they are a prevalent factor in determining insurance rates.
Insurers consider various factors when calculating credit-based insurance scores, including outstanding debt, credit history length, credit mix, and payment history. These factors contribute to assessing an individual's financial management and the potential impact on insurance claims.
It's important to note that insurance providers do not rely solely on credit scores when determining rates. Other factors, such as demographics, vehicle type, insurance coverage, and driving history, also play a role in calculating insurance premiums.
By understanding how credit scores influence insurance rates, individuals can take steps to improve their creditworthiness and potentially lower their insurance costs. Maintaining a good credit score involves timely bill payments, minimising hard credit inquiries, regularly monitoring their score, and effectively managing credit utilisation.
Comps Unavailable: Auto Insurance's Next Steps Explained
You may want to see also

Additional factors that affect insurance rates
Several factors other than credit scores can affect insurance rates. Here are some of the additional factors:
Driving Record
Your driving record is a significant factor in determining insurance rates. A history of traffic violations, accidents, or a DUI/DWI conviction will result in higher insurance premiums. Conversely, maintaining a clean driving record can lead to lower rates and even safe-driver discounts.
Age and Driving Experience
Young and inexperienced drivers generally face higher insurance rates due to their higher risk of accidents. Insurance rates typically decrease after the age of 25 as driving experience increases. Senior drivers may also see an increase in insurance rates after a certain age due to increased accident risks and injury susceptibility.
Location
The location where the car is driven and parked impacts insurance rates. Urban areas with higher population density, theft rates, and accident frequency tend to have higher insurance premiums. Rural areas, on the other hand, often have lower rates due to less congested roads and lower crime rates.
Vehicle Type
The type of vehicle being insured also affects insurance rates. Certain vehicles are statistically more likely to be stolen or involved in accidents, leading to higher insurance costs. Additionally, expensive or high-performance vehicles with high repair costs will also result in higher insurance premiums.
Insurance History
A gap in insurance coverage or a lack of continuous coverage can lead to higher insurance rates. Insurance companies perceive this as a higher risk, assuming that the driver may have been driving without insurance during that period.
Marital Status
Marital status can also influence insurance rates, with married drivers often receiving lower premiums. This is because married individuals are statistically less likely to be involved in accidents, resulting in fewer claims.
Annual Mileage
The number of miles driven annually can impact insurance rates. Those with longer daily commutes or higher annual mileage will likely pay more for insurance as the chances of being involved in an accident increase.
These factors, along with others such as gender, vehicle ownership status, insurance company, and selected coverage options, collectively contribute to determining insurance rates.
Auto Insurance and Rental Cars: Understanding the Damage Waiver
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
In most states, insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores, which means your credit score can impact your car insurance premium. Drivers with excellent credit pay the lowest rates, while drivers with poor credit pay the highest rates.
You can check your credit score by purchasing it from one of the major credit bureaus or directly through FICO. You can also access it for free through certain banks and credit card companies, as well as third-party services.
While there is no universal definition of a "good" credit score, scores in the higher ranges are generally viewed more favourably and could lead to more advantageous insurance rates. FICO defines a good credit score as anywhere from 670 to 739, with above 800 being excellent and below 579 being poor.
You can improve your credit score by paying your bills on time, lowering your credit utilization rate, and maintaining old lines of credit. Monitoring your score regularly and keeping hard credit inquiries to a minimum can also help.







