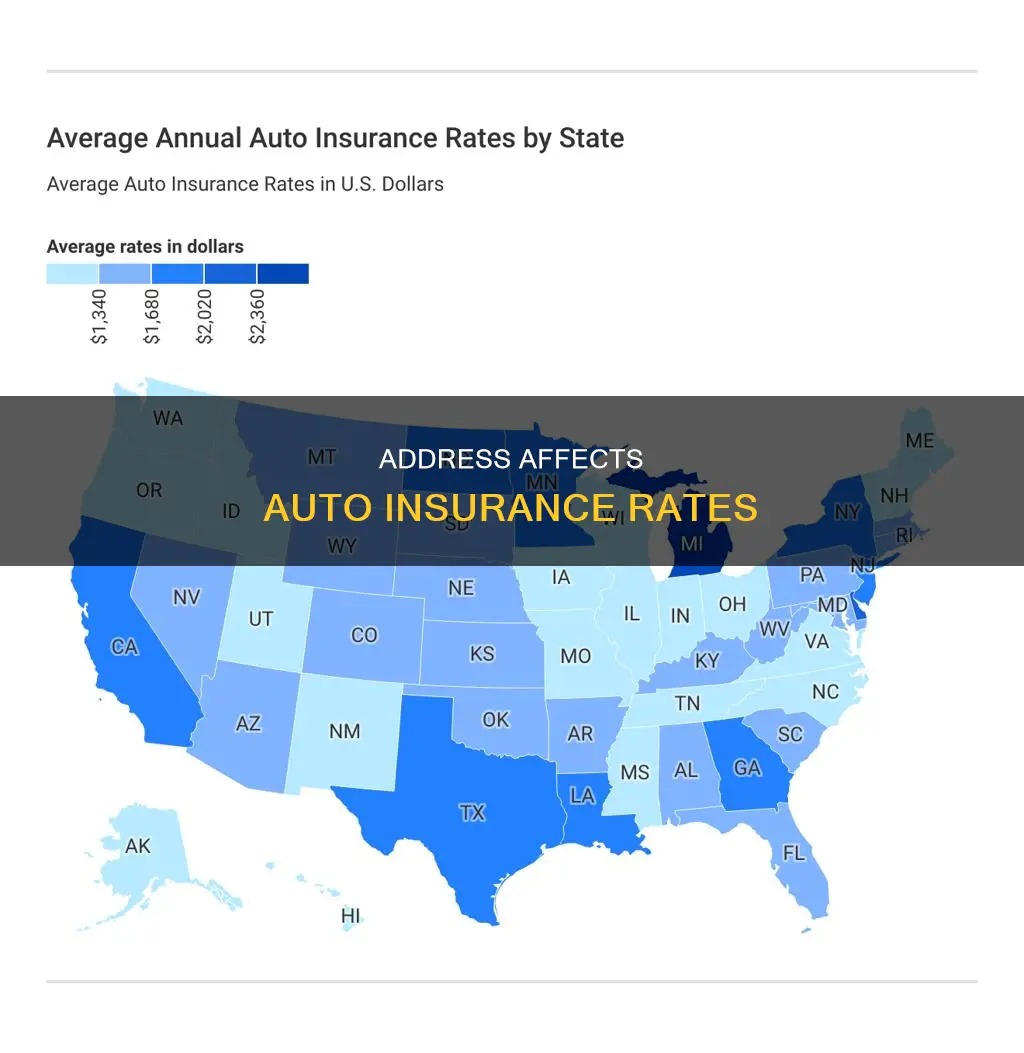
Auto insurance rates are based on several factors, and one of the most important is your address. Your address is used by insurance companies to assess your risk level and set rates. This includes crime rates, population density, weather, state laws, and road conditions, all of which can vary significantly depending on where you live. For example, urban areas tend to have higher insurance rates due to increased accident and car theft probabilities. On the other hand, rural areas may have higher rates because of longer travel distances and higher uninsured driver percentages.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Crime rates | Higher crime rates lead to higher insurance premiums |
| Population density | More people means more cars and a higher chance of accidents, so insurance premiums are higher |
| Claims volume and frequency | Areas with more claims will have higher insurance premiums |
| Road conditions | Poor road conditions increase the risk of accidents, so insurers charge higher premiums |
| Weather | Areas with severe weather conditions will have higher insurance premiums |
| State laws | Each state has different laws on coverage types and minimum limits, which affects insurance premiums |
| Natural disasters | Areas prone to natural disasters will have higher insurance premiums due to increased claims |
| Traffic | Heavy traffic increases the risk of accidents, leading to higher insurance premiums |
| Parking location | Parking on the street is considered riskier than parking in a secure garage or driveway, impacting insurance rates |
| Homeownership | Renters pay more for insurance than homeowners |
| Job location | A longer commute increases insurance premiums |
What You'll Learn

Population density
Living in a densely populated area typically leads to higher car insurance premiums. This is because accidents are more likely to occur in these areas due to a higher number of vehicles on the road. A greater number of people in a small area increases the chances of traffic congestion and car accidents. As a result, insurance companies charge higher premiums in metropolitan areas.
For instance, states like Louisiana, Florida, and Michigan have higher insurance costs due to their large population, high accident fatality rates, and poor highway infrastructure. In contrast, states with lower population density, such as Idaho, Iowa, and Maine, tend to have cheaper insurance rates.
However, population density is not the only factor influencing insurance rates. Other factors include the cost of living, weather conditions, local claims history, state minimum insurance requirements, and the percentage of uninsured drivers.
Lo Jac: Auto Insurance Rates Adjusted?
You may want to see also

Crime rates
According to the National Insurance Crime Bureau, there were over one million thefts across the US in 2023. California, Texas, Florida, and Washington had the highest car theft rates. As a result, residents in these states can expect to pay higher insurance premiums.
Insurers also consider the type and frequency of claims filed in an area when calculating rates. If you live in an area with a high frequency of claims and average expenses, you will likely pay higher insurance costs.
Additionally, areas with higher population densities tend to have higher crime rates. Big cities often have higher crime rates and more crowded roads, which increase the likelihood of accidents and vehicle crimes. This data is used by insurers to charge higher premiums in metropolitan areas.
On the other hand, rural areas typically have lower crime rates and fewer people, resulting in lower insurance rates. Moving to a low-crime area or garaging your vehicle in a secure location can help lower your insurance premium.
Permit Holders: Auto Insurance Options
You may want to see also

Natural disasters
In the United States, natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, wildfires, tornadoes, and earthquakes are becoming increasingly common and costly. These events can cause widespread damage to vehicles, including car flooding, fire damage, and mechanical and electrical issues. As a result, insurance companies are facing higher claims payouts, which they pass on to policyholders in the form of higher premiums.
Comprehensive car insurance is the type of coverage that typically pays for vehicle repairs or replacements due to natural disasters. This coverage is optional but highly recommended, as it provides financial protection against these unpredictable events. The cost of comprehensive insurance varies by state, with Idaho and California being the cheapest and Tennessee and Wyoming the most expensive.
It is important to note that insurance companies may place restrictions on policy changes or new purchases during an impending major storm, so it is crucial to have comprehensive coverage in place beforehand. Additionally, comprehensive coverage only applies if it was in place before the natural disaster occurred.
The impact of natural disasters on auto insurance rates is particularly notable in coastal states like Florida and Louisiana, where hurricanes and floods are common. The frequency and severity of these events drive up claims frequencies and insurance costs.
In summary, natural disasters are a significant factor in determining auto insurance rates. The increasing occurrence of such events will likely lead to higher premiums, especially in areas prone to hurricanes, floods, wildfires, and other natural disasters. Comprehensive coverage is essential for financial protection, but policyholders should be mindful of potential restrictions during active storms and the need to have coverage in place before a disaster strikes.
Auto Insurance Rates: What's a Good Deal?
You may want to see also

Road conditions
Traffic congestion, caused by multiple lanes merging into fewer lanes, can also impact insurance rates. The higher the volume of traffic, the greater the chances of accidents and subsequent insurance claims. Insurers consider the type and frequency of claims when calculating rates, taking into account the costs of parts and labour for vehicle repairs.
In addition, the absence of safety features and inadequate security measures in parking areas can influence insurance rates. Drivers who park their vehicles on the street or in unsecured locations may face higher insurance rates compared to those who have access to secure garages or parking lots with safety features like alarm systems and security cameras.
Furthermore, road conditions related to weather events and natural disasters can also impact insurance premiums. Areas prone to extreme weather conditions, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, often experience a higher number of property damage claims. Insurers may raise rates in these areas to compensate for their increased costs. On the other hand, areas with milder weather conditions may see less impact on their insurance rates.
It is worth noting that seasonal weather conditions, such as snowy and icy roads during winter, can also affect insurance rates. Comprehensive auto insurance, which covers a range of perils, including natural disasters, theft, and accidents involving animals, is particularly relevant in areas with challenging weather conditions.
While road rage itself may not directly impact insurance rates, it can lead to traffic violations and accidents, which can result in higher premiums. Driving behaviours, including erratic driving, hard braking, and rapid acceleration, can be monitored by insurers through apps or devices, potentially affecting insurance costs.
Gap Insurance: Credit Score Impact
You may want to see also

Number of uninsured drivers
The number of uninsured drivers in the United States is a significant issue, with approximately 28-29 million uninsured drivers on the road. This equates to about 1 in 7 or 1 in 8 drivers, or 14% to 13% of all motorists, depending on the source. The rate of uninsured drivers has not changed much over the past decade, fluctuating between 12.3% and 12.6% from 2010 to 2019.
The percentage of uninsured drivers varies by state, with Mississippi having the highest rate at 29.4% or 29%, and New Jersey the lowest at 3.1% or 3%. Other states with high rates of uninsured drivers include Michigan, New Mexico, Tennessee, Washington, and Florida, where more than 20% of drivers are uninsured.
The high rate of uninsured drivers in Mississippi may be due to the state's low household income, as insurance can be costly. On the other hand, New Jersey's low rate of uninsured drivers can be attributed to low insurance prices caused by increased competition and major insurance reforms enacted in 2003.
The presence of uninsured drivers on the road can have financial implications for insured drivers. Even with uninsured motorist coverage, insurance companies in many states can increase rates after an uninsured motorist claim is filed. Additionally, insured drivers may bear the cost of damages and injuries caused by uninsured drivers, which amounts to an estimated $13 billion per year.
To address the issue of uninsured motorists, some states have implemented "no pay, no play" laws, insurance verification systems, and random selection programs. "No pay, no play" laws limit the amount that uninsured drivers can collect if they are in an accident with an insured driver, but these laws have not been effective in reducing the number of uninsured drivers. Insurance verification systems help law enforcement identify uninsured motorists, and random selection programs select a certain percentage of registered vehicles each month for insurance verification.
Gap Insurance: Refinancing Risks
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A garaging address or ZIP code is where you typically park your vehicle when you're not using it.
Your auto premiums can increase when you change your address because factors like your ZIP code, city, and state play a role in how insurers determine rates.
It depends. Living in a bigger city can be more expensive, but many other factors, including population density, road conditions, weather, crime, and accident rates, affect car insurance costs.
You should insure the car at the address where you park it the most often when not in use.
It depends. You can usually keep your car insurance with the same company when you move, even if you move to a new state unless the insurer doesn’t cover that state.







