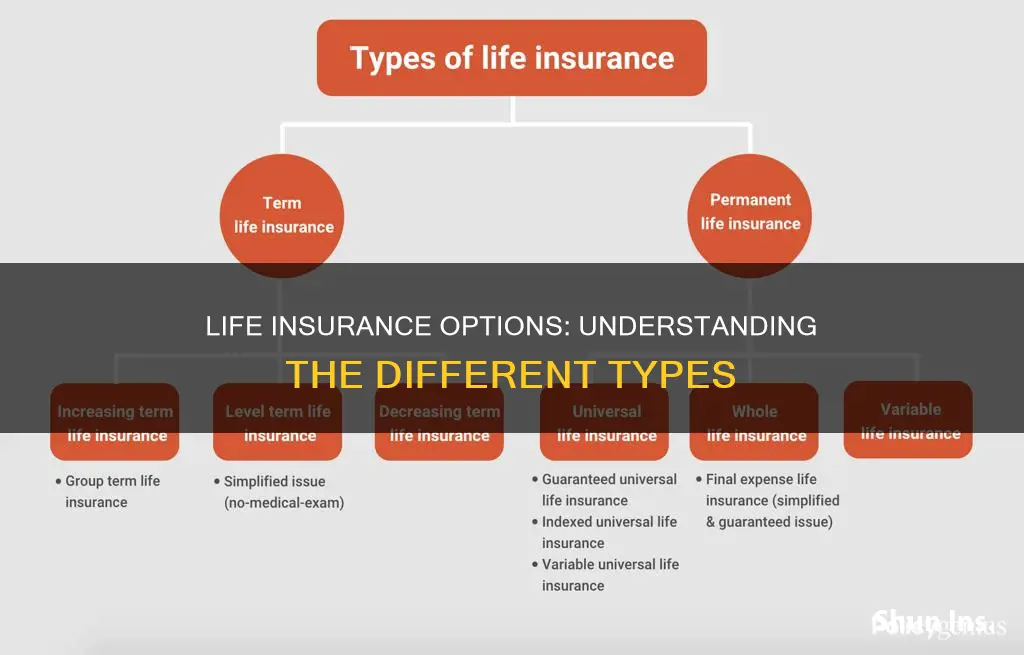
Life insurance is a way to ensure that your family is looked after if you are no longer around to help them. There are many different types of life insurance policies to match different needs. The main types of life insurance include term life insurance, whole-of-life insurance, joint life insurance, critical illness cover, terminal illness cover, and family income benefit. Term life insurance covers you for an agreed period, for example, 30 years, and is often taken out to cover a loan or ongoing financial obligation. Whole-of-life insurance covers you for your entire life and pays out whenever you die, as long as you've maintained your premiums. Joint life insurance covers two people at the same time and pays out if one of them passes away. Critical illness cover pays out a lump sum if you fall seriously ill, helping to cover medical expenses and other costs. Terminal illness cover pays a lump sum to your family if you are diagnosed with a terminal illness and have less than a year to live. Family income benefit pays a regular monthly income to your beneficiaries until the policy's expiry date if you die.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To provide financial support to loved ones after death |
| Payment type | Lump sum or monthly income |
| Payment recipients | Chosen people, beneficiaries, family members, spouse, children |
| Payment uses | Funeral expenses, mortgage, debts, inheritance tax, medical expenses, everyday costs |
| Policy type | Term life insurance, whole-of-life insurance, joint life insurance, critical illness cover, terminal illness cover, family income benefit, mortgage life insurance, over-50s life insurance |
| Policy length | Whole life or set period (e.g. 20-40 years) |
| Payout amount | Fixed or decreasing over time |
| Payout conditions | Death, terminal illness, critical illness |
What You'll Learn

Level term life insurance
At the end of the term, you have a few options:
- Renewal: You may have the option to renew your coverage for another term or, more likely, renew it year to year. If your contract has a guaranteed renewability clause, you may not need to have a new medical exam to keep your coverage going. However, your premiums are likely to increase because they'll be based on your age at renewal time.
- Conversion: With this option, you can convert your term contract to a permanent one that will last the rest of your life. In this case, again, you may not need to have any new medical exams, but premiums are likely to rise due to your age and new coverage. Different companies offer various options for conversion, so be sure to understand your choices before taking this step.
- Expiration: If you don't renew or convert your coverage at the end of the contract, it expires. That means you won't have life insurance coverage, including a death benefit, anymore. It's possible to apply for a new insurance contract, but you will need to take a medical exam, and your premiums are likely to rise.
Pros
- Predictable premiums: Level term premiums always remain the same, making budgeting easier.
- Clear coverage period: You can pick the term that best fits your needs, allowing you to align your coverage with financial responsibilities, such as paying a mortgage or covering education costs.
- Simplicity: This type of insurance contract is very straightforward, making it easy to understand and manage.
- Affordability: Typically, term life insurance is more affordable than permanent coverage, so it's a cost-effective way to secure financial protection.
- Flexibility: At the end of your contract's term, you have multiple options to continue or move on from coverage, often without needing a medical exam. If your budget or coverage needs change, death benefits can be reduced over time and result in a lower premium.
Cons
- Coverage expiration: Unlike permanent life insurance, level term contracts have an end date, so you won't have coverage or death benefits once the policy has run out.
- No cash value: Level term insurance contracts don't accumulate cash value. The premiums pay for the death benefit, but there isn't an investment component to potentially grow the contract's worth.
- Renewal costs: As with other kinds of term life insurance, once the contract ends, you'll likely pay higher premiums for coverage because it will recalculate at your current age and health.
- Fixed coverage: Level term offers predictability. However, if your financial situation changes, you may not have the necessary coverage and might have to purchase additional insurance.
Merrill Lynch: Life Insurance Options and Opportunities
You may want to see also

Decreasing term life insurance
The cost of decreasing term life insurance gets lower throughout the term. The price you pay depends on several factors, such as the amount of coverage, the length of the term, your age, health, lifestyle, and occupation.
When purchasing a decreasing term life insurance policy, you will need to choose the number of years it will be active (usually between five and 30 years) and your starting death benefit. The payout that your beneficiaries will receive will then decrease by a certain percentage each month or year, depending on the policy. If you pass away during the policy term, your beneficiaries can file a claim for the death benefit amount available at that time.
Index Life Insurance: How Does It Work?
You may want to see also

Whole-of-life insurance
A portion of the premiums paid into a whole-of-life insurance policy is usually put into an investment account to grow throughout the life of the plan. This cash value grows in a tax-deferred account at an established rate, and the policyholder can access this cash value if needed. When the plan ends, the accrued cash value of the plan is paid out to the beneficiary. If the beneficiary is named as an irrevocable life insurance trust, the tax liability may be lower.
Whole Life Insurance Dividends: What, Why, and How?
You may want to see also

Family income benefit
Here's how it works:
Policy Term
You choose the term of the policy, usually aligning with the years when your dependents would need financial support the most, such as until your children reach adulthood or finish their education.
Premiums
You pay regular monthly premiums for the policy. The premium amount depends on various factors, including your age, health, smoking status, the level of cover you choose, and the term of the policy.
Benefit Payments
Regular monthly payments are made from the time of your death until the end of the policy. For example, if you choose £20,000 annual cover and a term of 25 years, and you pass away 10 years into the policy term, the policy will pay out £20,000 every year for the remaining 15 years. The income is normally paid monthly and is tax-free.
Critical illness cover can be added to the policy, providing an income in the event of certain serious illnesses being diagnosed. This means that a claim can be made even if the insured person does not pass away.
However, family income benefit may not be suitable for those who want to use life insurance to pay off their mortgage in one go, as the monthly payments may not be sufficient to do this. Additionally, the payout that loved ones would receive decreases significantly over time. For instance, if you chose a policy with a term of 30 years and passed away in the last year, your loved ones would only receive a total of £24,000.
Life Insurance: A Retirement Plan?
You may want to see also

Critical illness cover
The payout amount will differ depending on the insurer, but it is typically a percentage of the overall payout or a defined lump sum. It's important to carefully review the policy to understand what critical illnesses are covered and for how long. Additionally, critical illness cover is usually purchased at the outset and cannot be added to an existing policy.
In summary, critical illness cover is a crucial consideration when planning your financial future. It ensures that you are prepared for the unexpected and can maintain financial stability during challenging times.
Haven Life Insurance: Is It Worth the Hype?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The main types of life insurance are term life insurance and whole-of-life insurance. Term life insurance covers you for an agreed period, for example, 30 years. Whole-of-life insurance covers you for your whole life, rather than a fixed period.
The different types of term life insurance are decreasing term life cover, level term life cover, and increasing term life cover. Decreasing term life cover is usually used to cover a large debt such as a mortgage, with the payout shrinking over time. Level term life cover provides a fixed payout if you die at any point during the term. Increasing term life cover provides a payout that rises over time, usually to keep up with inflation.
Critical illness cover is an add-on to your life insurance policy. It pays out a tax-free lump sum if you are diagnosed with a critical illness.







