Life insurance rates can fluctuate based on a variety of factors, including age, gender, health, and lifestyle choices. Age is one of the most significant factors influencing premiums, with rates typically increasing by about 8% to 10% for each year of age. The likelihood of a payout increases as individuals journey through life, elevating the risk to insurers. This means that older applicants are generally deemed to be at a higher risk of illness or death and are therefore charged higher premiums.
In addition to age, other factors such as overall health, gender, lifestyle choices, and the type of life insurance policy can also impact rates. For example, individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or risky hobbies may be subject to higher premiums. On the other hand, term life insurance policies, which offer coverage for a specific term, tend to have lower premium rates compared to permanent life insurance policies.
While life insurance rates can fluctuate, it is important to note that certain factors such as ethnicity, race, sexual orientation, and marital status do not impact the rates offered.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Main factors determining life insurance rates | Age, health history, tobacco use, profitability of the insurance company, mortality rates, company expenses, interest rate environment, gender, lifestyle, occupation, type of life insurance policy, family medical history, driving record, height, weight, credit history |
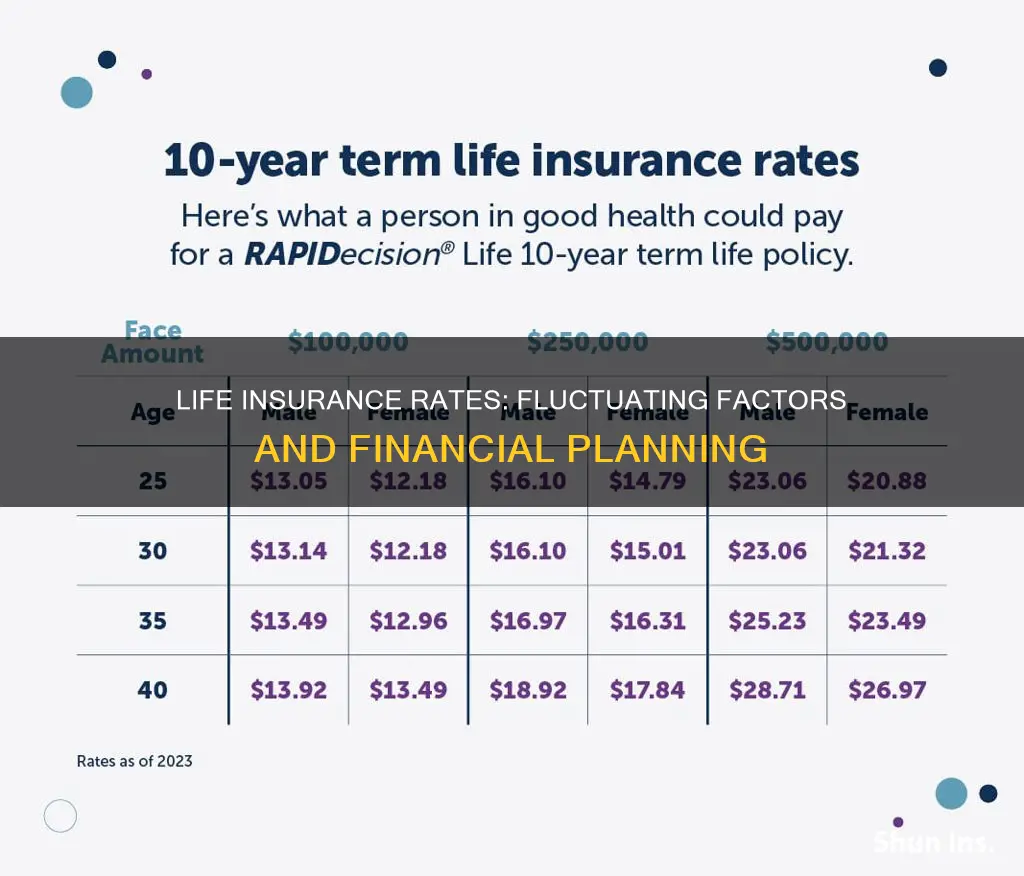
| Average cost of life insurance per month | $26 |
| Average cost of life insurance per year | $312 |
| Average cost of life insurance for a 20-year, $250,000 term life insurance policy for a healthy 30-year-old buyer | $144 per year |
| Average cost of life insurance for a 20-year, $250,000 term life insurance policy for a healthy 40-year-old buyer | $197 per year |
| Average cost of life insurance for a 20-year, $250,000 term life insurance policy for a healthy 50-year-old buyer | $485 per year |
What You'll Learn

Life insurance rates and age
Life insurance rates are determined by a number of factors, with age being a primary consideration. The older you are, the more expensive your premiums will typically be. This is because the cost of life insurance is based on actuarial life tables that assign a likelihood of dying while the policy is in force. The older you are, the more likely it is that day will come.
The premium amount increases, on average, about 8% to 10% for every year of age. This can be as low as 5% annually if you're in your 40s, and as high as 12% annually if you're over 50. The older you get, the more likely you are to suffer from health complications, and the shorter your life expectancy becomes. This elevated risk of a claim being made means insurers will charge a higher premium to offset that risk.
The type of life insurance policy you choose will also affect the cost. Term life insurance is typically the most affordable option because it only offers coverage for a limited number of years. Permanent life insurance policies are generally more expensive because they are intended to provide coverage for your entire lifetime and include a cash value component.
Your health is another major factor that contributes to the cost of life insurance. People who suffer from pre-existing medical conditions may not live as long as healthy people and are therefore considered a higher risk. As a result, insurance companies may charge higher rates for people with health issues.
Your gender also plays a role in determining your premium. Men typically pay more for life insurance than women. This is because, on average, women have a longer life expectancy than men.
Life insurance rates can also be influenced by your job and lifestyle choices. Applicants who engage in low-risk activities often pay less than those who participate in high-risk roles or hobbies.
In summary, age is a critical factor in determining life insurance rates, with older individuals typically paying higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of a claim being made. Other factors, such as health, gender, and lifestyle, also play a role in determining the cost of life insurance.
Cigna Life Insurance: Drug Testing Requirements Explained
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and health
Life insurance rates are largely determined by an individual's health and age. The healthier and younger a person is, the lower their premiums tend to be.
Insurers typically classify applicants using terms like "super preferred", "preferred", and "standard", with "super preferred" being the healthiest category. The younger an applicant is, the more likely they are to be placed in a healthier category.
In addition to age and current health, insurers also take into account an applicant's family medical history, gender, smoking status, driving record, occupation, and lifestyle.
Health
Health is a major factor that contributes to the cost of life insurance. People with pre-existing medical conditions may not live as long as healthy people and are therefore considered higher risk. As a result, insurance companies may charge higher rates for people with health issues or a family history of disease.
Most insurance companies use rating tiers to determine an applicant's health risks. Each company has its own specific rating system, but the categories are generally defined as follows:
- Preferred Plus: Individuals with no family history of disease or pre-existing conditions who are in excellent health.
- Preferred: Individuals in great health but with a family history of one or two illnesses.
- Standard Plus: Individuals who are mostly healthy but may be slightly overweight or have minor conditions without a long family history of disease.
- Standard: Individuals who suffer from moderate health issues and have a strong family history of disease.
- Substandard: Applicants with moderate to severe medical issues or risky health habits.
- Preferred Tobacco: Individuals who would have been placed in the "Preferred" or "Preferred Plus" category if not for their tobacco use.
- Standard Tobacco: Individuals who would have been placed in the "Standard" or "Standard Plus" category if not for their tobacco use.
Age
Age is one of the most influential factors affecting life insurance premiums. As individuals get older, the probability of dying increases, thus elevating the risk to insurers. This means that policy costs increase due to the heightened chance of a death benefit claim as applicants get older.
The older an individual is when they purchase a policy, the more expensive the premiums will be. This is because the cost of life insurance is based on actuarial life tables that assign a likelihood of dying while the policy is in force. The older an individual is, the more likely they are to become ill or die while under coverage.
In addition to age and current health, insurers also take into account an applicant's family medical history.
Gender
Actuarial data shows that women have a longer lifespan than men, meaning companies may pay out a life insurance benefit earlier for men than for women. As a result, men tend to pay more for life insurance than women.
Life Insurance Tiers: Understanding the Different Levels of Coverage
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and gender
Life insurance rates are influenced by a number of factors, including age, health, and gender. While men and women can expect to pay different rates, it's important to note that other factors typically have a bigger impact on the overall cost of coverage.
Men's life insurance rates are generally higher than women's. This is because women tend to have a longer life expectancy than men and are therefore expected to live longer. As a result, women often pay less for life insurance. On average, women pay around 24% less for life insurance than men.
However, gender is just one factor that insurance companies consider when determining rates. Medical history and lifestyle choices typically have a much larger impact on the cost of coverage. Health conditions, smoking status, occupation, and participation in risky activities are all taken into account when calculating premiums.
It's also worth noting that gender-nonconforming applicants, including transgender and non-binary individuals, may not have higher rates based solely on their gender identity. While most insurers currently require individuals to apply under one gender category, their rates will not be determined by their gender identity but rather by other factors such as health and lifestyle.
Life Insurance and Food Stamps: Compatible Benefits?
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and lifestyle
Life insurance rates are determined by a number of factors, including age, gender, health, and lifestyle. While some of these factors, like age, are beyond an individual's control, lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on the cost of life insurance.
Lifestyle factors that can affect life insurance rates include:
- Smoking status: Smokers typically pay higher premiums than non-smokers due to the increased risk of developing health issues associated with tobacco use.
- Occupation and hobbies: High-risk jobs or dangerous hobbies, such as skydiving or racing, can result in higher insurance rates. Occupations that are considered hazardous, such as working on a bomb squad or as a race car driver, will also increase premiums.
- Driving record: A history of DUIs, DWIs, or major traffic violations can lead to higher rates, as these are seen as indicators of high-risk behaviour.
- Credit history: While credit scores do not directly impact life insurance rates, a bankruptcy on your record may be considered a risk factor by insurers.
- Family medical history: A family history of serious health conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, or diabetes, can affect your premiums.
It is important to note that being honest about your lifestyle and health during the application process is crucial. Omitting relevant information or providing false information can result in denied claims or even insurance fraud.
Additionally, lifestyle choices can also help lower your life insurance rates. For example, improving your health, quitting smoking, and engaging in safety-conscious behaviours can positively impact your insurance risk classification and lead to lower premiums.
THC Use and Amica Life Insurance: What's the Verdict?
You may want to see also

Life insurance rates and policy type
Life insurance rates are determined by several factors, including age, gender, health, lifestyle choices, and the type of policy chosen. When it comes to policy types, there are two main categories: term life insurance and permanent life insurance.
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance is the most affordable option as it only covers a set number of years, usually 10 to 30, and then expires. The premiums for term life insurance are typically fixed and remain stable throughout the policy term. This means that the policyholder pays the same premium every year, regardless of their age or health status. The shorter coverage period makes term life insurance less affected by economic fluctuations, and the premiums do not increase with age.
Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, is more expensive as it covers the insured for their entire lifetime, often up to age 95 or 120. It also includes a cash value component that allows the policyholder to borrow against the policy or withdraw funds. The premiums for permanent life insurance may increase over time, especially during periods of economic uncertainty, as the insurance company adjusts for profitability. The longer coverage period and the presence of cash value make permanent life insurance more sensitive to interest rate changes and economic conditions.
In summary, term life insurance offers basic protection for a fixed period and has stable premiums, while permanent life insurance provides lifelong coverage with a cash value component but tends to be more expensive and sensitive to economic changes.
Life Insurance and Suicide in Florida: What's Covered?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, life insurance rates increase with age as health issues become more frequent and the policyholder gets closer to their life expectancy.
Women tend to pay lower life insurance premiums than men, as women tend to live longer than men.
Yes, health is a major factor that contributes to the cost of life insurance. People with pre-existing medical conditions are likely to pay higher rates.
Yes, applicants who engage in low-risk activities often pay less than those who regularly participate in high-risk roles.