The cost of car insurance varies from state to state, and several factors influence this fluctuation. Pennsylvania's average annual full-coverage car insurance is around $1,261, while South Carolina's is about $1,827. Pennsylvania's rates are close to the national average, whereas South Carolina's are 20% lower.
Pennsylvania's insurance rates are influenced by its status as a no-fault state, higher population density, and competitive insurance market. On the other hand, South Carolina's lower population density, mild weather, and low cost of living contribute to its more affordable insurance rates.
Various factors, including age, coverage level, location, credit score, and driving record, impact car insurance premiums in both states.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average annual premium for full coverage | SC: $1,261 |
| PA: $2,464 | |
| Average annual premium for minimum coverage | SC: $450 |
| PA: $512 | |
| Average monthly premium for full coverage | SC: $105 |
| PA: $205 | |
| Average monthly premium for minimum coverage | SC: $37 |
| PA: $43 |
What You'll Learn

The impact of population density on insurance rates
Population density is one of the factors that influence insurance rates. The higher the population density, the higher the insurance rates tend to be. This is because urban areas with higher traffic density and theft rates can lead to increased insurance premiums compared to rural areas.
For example, in Pennsylvania, car insurance rates vary by city. Allentown has the cheapest full coverage, while Philadelphia is the most expensive. The difference in rates between these two cities can be attributed, in part, to their population density. Philadelphia, being a larger and more densely populated city, likely has higher traffic congestion and theft rates than Allentown, which would drive up insurance rates.
Similarly, in South Carolina, population density is a factor that influences insurance rates. The state's low population density, especially outside the metropolitan area of Charleston, likely contributes to its lower insurance rates compared to other states.
In addition to population density, other factors such as the number of licensed drivers, traffic density, cost of living, and the percentage of uninsured drivers also impact insurance rates. These factors are all interconnected and influence the likelihood and severity of car accidents, which ultimately drive insurance rates up or down.
Overall, population density is a significant factor in determining insurance rates. Urban areas with higher population densities tend to have higher insurance rates due to increased traffic congestion, theft rates, and accident risks. Conversely, rural areas with lower population densities often benefit from lower insurance rates.
Vehicle Theft: Insurance Impact
You may want to see also

The effect of no-fault insurance on premiums
No-fault insurance, also known as personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, is a type of insurance that helps cover medical expenses and loss of income for you and your passengers if you're hurt in an accident, regardless of who caused the crash. While no-fault insurance can provide valuable financial protection, it's important to understand how it can impact your insurance premiums.
In general, a no-fault accident won't cause your car insurance rates to rise significantly. This is because the at-fault party's insurance provider is typically responsible for compensating you for medical expenses and vehicle repairs. As a result, your own insurance company doesn't need to pay out money, and your premiums are less likely to increase.
However, it's important to note that there are situations where your insurer may still raise your rates after a no-fault accident. For example, if the at-fault driver is uninsured or underinsured, your insurance company may need to cover your expenses through your uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. In such cases, your premiums may increase because it becomes more costly for your insurance provider to do business with you.
Additionally, if you have a history of accidents or claims, your insurer may view you as a higher risk and increase your rates after a no-fault accident. According to the Consumer Federation of America, drivers who have been involved in no-fault accidents experience an average premium increase of 10%.
It's also worth mentioning that a no-fault accident will show up on your driving record and can affect your insurance rates for a certain period. The duration may vary depending on the state and the severity of the collision.
When it comes to auto insurance rates, the location where you live plays a significant role. Each state has its own regulations, cost of living, and claim frequency, which can impact insurance premiums. Pennsylvania, for instance, is known for having moderate insurance rates due to state regulations and a competitive insurance market.
In conclusion, while no-fault insurance can provide financial protection in the event of an accident, it's important to understand that it may still have an impact on your insurance premiums. The effect of a no-fault accident on your premiums can vary depending on the circumstances, your location, and your insurance company's policies. Therefore, it's always a good idea to carefully review your insurance policy and understand the potential implications of filing a claim.
MetLife Auto Insurance: Understanding Their Roadside Assistance Offerings
You may want to see also

How age affects the cost of insurance
Age is one of the most significant factors in determining auto insurance rates. In most states, the cost of insurance is highest for teens and young adults due to their relative lack of driving experience, with rates gradually decreasing as drivers gain more experience behind the wheel. However, rates may begin to increase again for drivers in their senior years due to factors such as age-related vision or hearing loss and slowed response times.
In Pennsylvania, age does impact car insurance costs. Drivers aged 22 to 29 typically face the highest premiums, with rates decreasing as drivers mature. The average cost of car insurance for a 22-year-old in the state ranges from $543 for state minimum coverage to $1,554 for full coverage with a $1,000 deductible annually.
While age is a significant factor, it is important to note that insurance is highly personalized, and rates can vary depending on other factors such as gender, driving record, credit score, and location.
Unearned Gap Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

How credit scores influence insurance rates
Credit scores can have a significant impact on auto insurance rates, with drivers with poor credit often facing substantially higher premiums. This is because insurance companies tend to view individuals with lower credit scores as more likely to file claims, and consequently charge them more for coverage. The impact of credit scores on insurance rates varies across states, with some states prohibiting or limiting the use of credit scores in determining rates.
Insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores to assess the risk associated with insuring a particular individual. These scores are based on an individual's credit report and take into account factors such as outstanding debt, credit history length, credit mix, and payment history. A lower credit-based insurance score indicates a higher risk to the insurer, which typically results in higher premiums.
In most states, an individual's credit score can significantly influence their auto insurance rates. For example, in Pennsylvania, drivers with poor credit pay around 85% more for full coverage insurance than those with excellent credit. Similarly, in South Carolina, individuals with poor credit may pay up to 88% more for full coverage insurance than those with good credit.
However, there are a few states, such as California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan, that prohibit or limit the use of credit scores in determining insurance rates. In these states, insurance companies primarily consider factors such as driving record, location, and other characteristics when setting rates.
It is worth noting that having no credit history can also impact insurance rates. In some states, such as New Jersey and Rhode Island, insurance companies are not allowed to charge higher rates due to a lack of credit history.
Improving Credit Scores
Improving one's credit score can be a time-consuming process but can ultimately lead to reduced insurance premiums. Some strategies for improving credit scores include paying bills on time, minimizing hard credit inquiries, regularly monitoring one's credit score, maintaining old lines of credit, and keeping credit card balances low relative to credit limits.
Auto Insurance Cancellation Charges: Understanding the Costs
You may want to see also

The cheapest and most expensive insurance providers
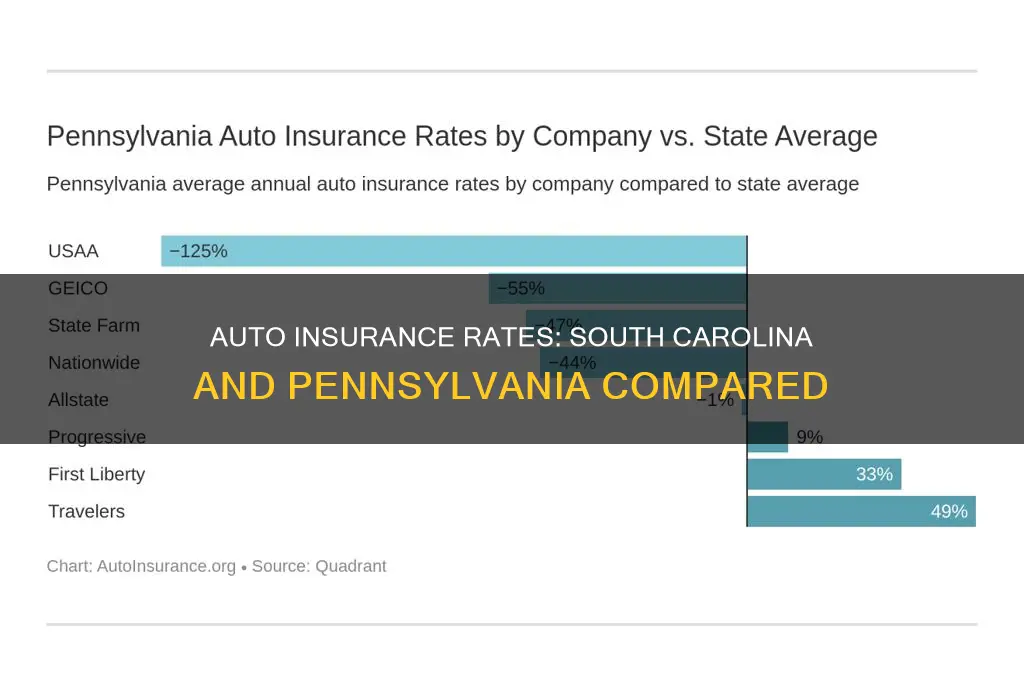
In Pennsylvania, the cheapest car insurance providers for full coverage are Travelers, Auto-Owners, and Progressive, with average annual rates of $895, $1,007, and $2,158, respectively. For minimum coverage, the cheapest providers are Travelers, Auto-Owners, and Progressive, with average annual rates of $796, $231, and $1,017, respectively.
In South Carolina, the cheapest car insurance providers for full coverage are American National, Auto-Owners, and Southern Farm Bureau, with average annual rates of $536, $1,531, and $890, respectively. For minimum coverage, the cheapest providers are American National, South Carolina Farm Bureau, and Dairyland, with average annual rates of $297, $483, and $2,158, respectively.
Auto Insurance and Pedestrian Injuries: Understanding the Coverage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The average cost of auto insurance in South Carolina is $2,278 per year for full coverage and $621 per year for minimum coverage.
The average cost of auto insurance in Pennsylvania is $2,464 per year for full coverage and $512 per year for minimum coverage.
Factors such as location, driving record, credit score, age, vehicle type, and coverage level can influence auto insurance rates in both states.
Yes, each state has its own auto insurance laws and requirements. For example, South Carolina requires drivers to have uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, while Pennsylvania mandates medical benefits coverage. It's important to review the specific requirements for each state when purchasing auto insurance.