Life insurance is a contract between an insurance company and a policyholder. In exchange for regular premium payments, the insurance company agrees to pay a sum of money to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon their death. This sum of money is known as a 'death benefit' and is designed to offer financial security to the policyholder's loved ones. There are two main types of life insurance: term insurance and permanent life insurance. Term insurance covers the policyholder for a specific time period, while permanent life insurance covers the policyholder for their entire life as long as they continue to pay premiums.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type of contract | Legally binding |
| Parties to the contract | Policyholder and insurance company |
| Purpose | Financial protection for beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder |
| Payment by policyholder | Regular premiums |
| Payment by insurance company | Lump sum known as a 'death benefit' |
| Beneficiaries | Individuals, trusts, or organisations |
| Use of payout | At the discretion of the beneficiaries |
| Types of life insurance | Term and permanent |
What You'll Learn

What is life insurance?
Life insurance is a legally binding contract between an individual and an insurance company. The individual, or policyholder, agrees to make regular premium payments to the insurance company. In exchange, the insurance company agrees to pay a sum of money, often a lump sum, to one or more named beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder. This sum is known as a 'death benefit'.
The purpose of life insurance is to provide financial security for loved ones after the policyholder's death. The death benefit can be used to cover expenses such as end-of-life costs, debts, and essential day-to-day purchases. It can also be used to leave an inheritance or support charitable causes.
There are two main types of life insurance: term insurance and permanent insurance. Term insurance covers the policyholder for a specific time period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Permanent insurance lasts for the entire life of the policyholder, as long as premiums continue to be paid. Permanent insurance is typically more expensive than term insurance but can build cash value over time, which can be borrowed against.
Life insurance policies can be customised by adding optional coverages known as riders. For example, a living benefit rider allows the policyholder to access their policy's death benefit while they are still alive, which can be beneficial if they are terminally ill and need funds to pay for medical care.
Dog Life Insurance: Is It Worth the Cost?
You may want to see also

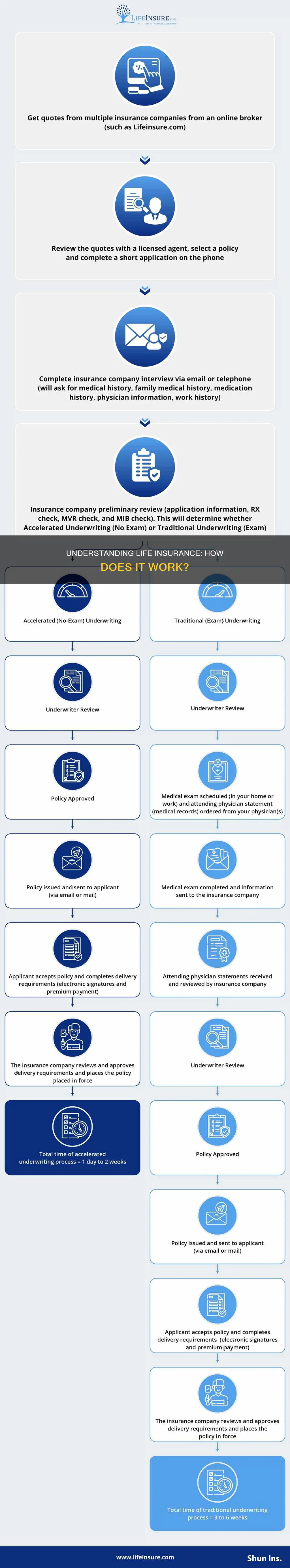
How does it work?
Life insurance is a contract between a policyholder and an insurance company. The policyholder agrees to make regular premium payments and follow the terms within the plan, and the insurance company agrees to pay out a sum of money to the policyholder's beneficiaries in the event of their death. This sum of money is known as a 'death benefit'.
The purpose of life insurance is to provide financial security to your loved ones after you die. The death benefit can be used to cover expenses such as end-of-life costs, debts, and essential day-to-day purchases. It can also be used to fund children's college education, pay estate taxes, or make charitable donations.
There are two main types of life insurance: term insurance and permanent insurance. Term insurance covers the policyholder for a specific time period (e.g. 10, 20, or 30 years), while permanent insurance lasts for the entire life of the policyholder, as long as premiums are paid. Permanent insurance is typically more expensive than term insurance but can build cash value over time, which can be borrowed against.
When purchasing life insurance, it is important to consider factors such as the amount of coverage needed, the type of policy (term or permanent), the cost of premiums, and any optional coverages or riders that may be included. Life insurance premium costs depend on factors such as the type of policy, the amount of the death benefit, the policyholder's age, health, and overall risk factors.
To receive a payout, beneficiaries must file a claim with the life insurance company, typically by providing a certified copy of the death certificate and other relevant documentation. The insurance company will then review the claim and make the payout if approved.
Life Insurance: Blood Test Requirements and Exclusions
You may want to see also

Who needs it?
Life insurance is a financial safety net for those who depend on your income, and it's a way to ensure your financial legacy lives on after you're gone. But who needs it?
Couples and Parents
If you're part of a couple, it's important to have life insurance to maintain the same quality of life if one of you passes away. This is especially true if you have young children or other dependents. The payout from a life insurance policy can help cover expenses like food, shelter, clothing, and education, giving your family financial stability during a challenging time. Even if you don't have children, a life insurance policy can help your partner cover living expenses and pay off shared debts.
Homeowners and Mortgage Holders
If you're a homeowner, a life insurance payout can be used to pay off the remaining mortgage, ensuring your beneficiaries and lender are protected. This is also a good option for those who rent and want to ensure their family can continue to live in the same home.
Business Owners and Partners
Life insurance is also recommended for business owners and partners. In the event of your death, a life insurance payout can help your business partners or heirs cover expenses such as buying out your share of the company, paying rent, or employing additional help.
Those Wanting to Leave a Financial Legacy
If you want to leave money behind for legacy purposes, life insurance is a good option. This could include grandparents who want to pay for their grandchildren's education or individuals who want to make a donation to a charity or local hospital.
Final Expenses
Funeral and burial costs can be expensive, and life insurance can help cover these final expenses, ensuring your loved ones don't have to worry about finances during an already difficult time.
Co-signers or Co-owners of Debt
If you have debts, they could pass to your spouse or any joint account holders when you die. Life insurance can help protect your loved ones from becoming responsible for paying off these debts.
Special Circumstances
There are also some less common situations where life insurance may be beneficial. For example, if you have a special-needs dependent who you care for financially, life insurance can help ensure they have the necessary resources if you pass away. Additionally, if you're a stay-at-home parent, your work as a caregiver has value, and life insurance can help your partner cover the costs of replacing these services.
In summary, life insurance is a valuable tool for financial planning and protecting your loved ones. By understanding your unique needs and goals, you can select a policy that offers peace of mind and financial security.
Life Insurance for the Elderly: Options at 80 Years Old
You may want to see also

How to choose a beneficiary
Choosing a beneficiary is an important step in owning a life insurance policy. Your beneficiary is probably the reason you have life insurance in the first place, so it's worth taking the time to make the right choice.
Who can be a life insurance beneficiary?
Almost anyone can be a life insurance beneficiary, including people, organisations, and trusts. Some common examples of life insurance beneficiaries are:
- A person, like your spouse
- Multiple people, like your children
- A charitable organisation
- A legal entity, like your company
The beneficiaries you choose must have what the insurance industry calls an "insurable interest" in your life. In other words, they must have more to lose than gain by your death, whether that's financial or otherwise.
Primary vs. contingent beneficiary
Primary life insurance beneficiaries are first in line to receive the death benefit if you die. Contingent life insurance beneficiaries, sometimes called secondary beneficiaries, will receive the death benefit if the primary beneficiary dies before you do.
Irrevocable vs. revocable beneficiaries
You cannot change an irrevocable life insurance beneficiary without the beneficiary's approval. For this reason, irrevocable designations are uncommon. However, they can be useful if you want to ensure that the death benefit goes to a specific person, such as your child.
In contrast, a revocable life insurance beneficiary can be changed, updated, added, or removed at any time.
How to choose a life insurance beneficiary
When choosing a beneficiary, start by asking yourself why you have life insurance in the first place:
- Who relies on you financially and would need help paying ongoing bills if you die?
- Who would need financial support to cover costs incurred by your death, such as funeral expenses?
- Who would you like to leave money to, regardless of whether they rely on you, such as a charity or a trust for your children?
To avoid mistakes when designating a beneficiary, be as specific as possible. If you write "spouse" or "child", the insurer might not be certain who should receive the funds, especially if you remarry or have multiple children. Make sure to include any identifying factors, such as each beneficiary's full name, Social Security number, relationship to you, date of birth, and address.
Once you've narrowed down your options, decide how much money each beneficiary would need and divide the death benefit accordingly.
Moose Membership: Life Insurance Benefits and Beyond
You may want to see also

How much does it cost?
The cost of life insurance depends on several factors, and the price will vary among applicants, insurers, and policy types. The average cost of life insurance is $26 a month, based on a 40-year-old purchasing a 20-year, $500,000 term life policy, which is the most common term length and amount sold. However, the actual cost of an average term life insurance policy depends on several factors, and the younger and healthier you are, the cheaper your premiums are likely to be.
The two biggest influences on life insurance rates are age and gender, both of which are uncontrollable factors. Generally, younger people pay less than older people as they are less likely to have health problems, and women pay less than men because they have longer life expectancies.
The length of the term selected will also determine the cost of a policy. For example, a 10-year term policy will be less expensive than a 25-year policy due to the number of years of coverage. The amount of coverage you select will also impact the cost, with more coverage resulting in higher rates.
Your health is another important factor that insurers consider when determining the cost of life insurance. They will look at your height, weight, and medical history, especially any chronic or serious illnesses you have experienced. Standard policies require a medical exam before determining your eligibility, though some life insurance policies don't require one.
Your lifestyle and hobbies can also affect the cost of life insurance. If you engage in risky activities like skydiving or have dangerous hobbies like racing cars, you may be charged a higher premium. Similarly, certain occupations, such as police officer, firefighter, pilot, or construction worker, are considered hazardous and may result in higher life insurance rates.
Tobacco use is another factor that can increase the cost of life insurance. Smokers typically pay higher rates than non-smokers due to the number of medical conditions associated with smoking, including cancer.
Other factors that can impact the cost of life insurance include your financial history, criminal record, and driving record. While your credit score won't directly affect your premium, bankruptcies or other risk factors on your credit report may increase your rate. DUIs, previous arrests, and other criminal convictions may also affect your rate or disqualify you from coverage with some insurers.
In summary, the cost of life insurance varies based on several factors, including age, gender, health, lifestyle, and the type of policy chosen. The younger and healthier you are, the cheaper your premiums are likely to be. The best way to determine your rates is to get a life insurance quote and compare rates from multiple insurers.
Freedom Life Insurance: Marketplace Approved?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance is a contract between a policyholder and an insurance company that pays out a death benefit when the insured person passes away.
In exchange for regular premium payments, your insurer will pay your beneficiaries a lump sum of money (death benefit) while covered by the policy.
There are two main types of life insurance: term and permanent. Term life insurance covers you for a set number of years, while permanent life insurance covers you for life.
The cost of life insurance depends on several factors, such as the type of policy, the amount of the death benefit, your age, health, and lifestyle.