Life insurance is a contract between a policyholder and an insurance company that pays out a death benefit when the insured person passes away. The premium rate for a life insurance policy is based on two underlying concepts: mortality and interest. A third variable is the expense factor, which covers the operating costs of selling insurance, investing the premiums, and paying claims.
The amount at risk must be known to predict the cost to each member of the group. Mortality tables are used to give the company a basic estimate of how much money it will need to pay for death claims each year. By using a mortality table, a life insurer can determine the average life expectancy for each age group.
The second factor used in calculating the premium is interest earnings. Companies invest premiums in bonds, stocks, mortgages, real estate, etc., and assume they will earn a certain rate of interest on these invested funds.
The third consideration is the expenses of operating the company, including salaries, agents' compensation, rent, legal fees, and postage. The amount charged to cover each policy's share of expenses of operation is called the expense loading. This cost area can vary from company to company based on its operations and efficiency.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Premium rate | Based on mortality, interest, and expense factor |
| Mortality | Risk of death shared by a large group of people |
| Interest earnings | Companies invest premiums in stocks, bonds, mortgages, etc. |
| Expense factor | Covers operating costs of selling insurance, investing premiums, and paying claims |
| Age | Younger individuals get better rates |
| Gender | Women tend to pay lower rates than men |
| Smoking | Smokers pay higher rates |
| Health | Healthier individuals get better rates |
| Lifestyle | Dangerous occupations and hobbies can increase rates |
| Family medical history | History of major disease in the family can increase rates |
| Driving record | History of moving violations or drunk driving can increase rates |
What You'll Learn
- Premium rates are determined by mortality, interest earnings, and expense factors
- Life insurance is based on the sharing of the risk of death by a large group
- Life insurance policies can be term or permanent
- The younger and healthier you are, the better your quotes will be
- Life insurance can be used to provide a financial safety net for loved ones

Premium rates are determined by mortality, interest earnings, and expense factors
Premium rates for life insurance are determined by three main factors: mortality, interest earnings, and expense factors.
Mortality is the first underlying concept in determining premium rates. Life insurance is based on the idea of sharing the risk of death among a large group of people. To predict the cost to each member of the group, mortality tables are used to give insurance companies a basic estimate of how much money they will need to pay for death claims each year. This allows them to determine the average life expectancy for each age group. The younger the policyholder, the lower the mortality and expense risk will be, as an older person is more likely to die than a younger one.
The second factor is interest earnings. Companies invest the premiums they receive in bonds, stocks, mortgages, and real estate, among other things, and assume they will earn a certain rate of interest on these funds.
The third consideration is the expense factor, which covers the operating costs of selling insurance, investing the premiums, and paying claims. This includes expenses such as salaries, agents' compensation, rent, legal fees, and postage. This amount, known as the expense loading, can vary from company to company based on its operations and efficiency.
Get Your Life Insurance License: Steps to Success
You may want to see also

Life insurance is based on the sharing of the risk of death by a large group
Life insurance is based on the principle of shared risk among a large group of people. The fundamental idea is that the risk of death is spread across a significant number of individuals, allowing for the prediction of costs for each group member. This system is often referred to as "mortality" in the insurance industry.
To determine the cost per member, insurance companies use mortality tables, which provide estimates of annual death claims. These tables help insurers calculate the average life expectancy for different age groups, influencing the pricing of policies accordingly.
The interest earnings on premiums invested in stocks, bonds, mortgages, and real estate are another critical factor in calculating premiums. Companies assume a certain rate of return on these investments, which contributes to covering death claims and operational expenses.
Speaking of operational expenses, they constitute the third factor influencing premium rates. This includes salaries, agent compensation, legal fees, rent, and other costs associated with running the insurance company. The efficiency of operations and the specific expenses incurred can vary from one company to another, impacting the final premium rates charged to policyholders.
Life insurance, therefore, operates on the principle of shared risk, where the costs of potential death claims are distributed across a large group, with adjustments made based on interest earnings and operational expenses. This allows insurance companies to set premium rates that reflect the predicted costs for each member of the insured group.
Life Insurance Options for Angina Patients
You may want to see also

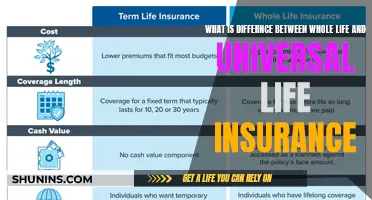
Life insurance policies can be term or permanent
There are two basic types of term life insurance policies: level term and decreasing term. Level term means that the death benefit stays the same throughout the duration of the policy. Decreasing term means that the death benefit drops, usually in one-year increments, over the course of the policy's term.
In contrast, permanent life insurance provides lifelong insurance protection. The policy pays a death benefit whenever the insured person dies, even if they live to 100 years old. There is also a savings element that will grow on a tax-deferred basis and may become substantial over time. Because of the savings element, premiums are generally higher for permanent than for term insurance. However, the premium in a permanent policy remains the same, while term premiums can go up substantially every time you renew.
There are several types of permanent insurance policies, such as whole (ordinary) life, universal life, variable life, and variable/universal life. In a permanent policy, the cash value is different from its face value amount. The face amount is the money that will be paid at death, while the cash value is the amount of money available to you. There are a number of ways that you can use this cash savings. For instance, you can take out a loan against it or you can surrender the policy before you die to collect the accumulated savings.
There are unique features to a permanent policy, such as:
- You can lock in premiums when you purchase the policy. By purchasing a permanent policy, the premium will not increase as you age or if your health status changes.
- The policy will accumulate cash savings.
- Depending on the policy, you may be able to withdraw some of the money.
You also may have these options:
- Use the cash value to pay premiums.
- If unexpected expenses occur, you can stop or reduce your premiums.
- The cash value in the policy can be used toward the premium payment to continue your current insurance protection, providing there is enough money accumulated.
- Borrow from the insurance company using the cash value in your life insurance as collateral. Like all loans, you will ultimately need to repay the insurer with interest. Otherwise, the policy may lapse or your beneficiaries will receive a reduced death benefit.
Vaping's Impact: Life Insurance and Your Health
You may want to see also

The younger and healthier you are, the better your quotes will be
Life insurance is a contract between an insurance company and a policy owner. The insurer guarantees to pay a sum of money to the policy's beneficiaries when the insured person dies. In exchange, the policyholder pays premiums to the insurer during their lifetime. The cost of life insurance is determined by the likelihood of a payout, which is calculated using mortality tables and interest earnings. The expense of operating the company is also a factor.
Age is one of the primary factors influencing life insurance premium rates, regardless of whether the policy is term or permanent. The older you are when you purchase a policy, the more expensive the premiums will be. This is because the cost of life insurance is based on actuarial life tables that assign a likelihood of dying while the policy is in force. The closer you are to your life expectancy, the more expensive it is to insure you. Typically, the premium amount increases by about 8% to 10% for every year of age.
Health is another major factor that contributes to the cost of life insurance. The underwriting process for most carriers includes a medical exam in which the company records your height, weight, blood pressure, cholesterol, and other vital metrics. In some cases, it may also require an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to check your heart. Carriers are also interested in any conditions your parents or siblings have experienced, especially if they have contributed to a premature death.
The younger and healthier you are, the better your life insurance quotes will be. This is because your age and health are two of the most important factors in determining your premium cost. The younger you are, the lower your payments. Similarly, if you improve your health through lifestyle changes or medical treatment, you may be able to get a lower premium.
In addition to age and health, other factors that can affect life insurance quotes include gender, lifestyle, family medical history, driving record, and smoking status. Women tend to pay lower premiums than men because they have a longer life expectancy. Leading a risky lifestyle, such as having dangerous hobbies or a hazardous occupation, can also increase your premium. A history of moving violations or drunk driving can also dramatically increase the cost of life insurance.
Borrowing Against Universal Life Insurance: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

Life insurance can be used to provide a financial safety net for loved ones
Life insurance is a contract between an insurance company and a policy owner. The policy owner pays premiums to the insurer during their lifetime, and in exchange, the insurance company guarantees to pay a sum of money to one or more named beneficiaries when the insured person dies. This is known as the death benefit and is usually paid as a lump sum.
- Financial protection: Life insurance is meant to help protect your family's financial future. It can help secure your family's financial stability if you pass away, mitigating the stress and burden of an already difficult time. This is especially important if you have dependents or loved ones who rely on your income.
- Income replacement: Life insurance can help replace your income and ensure your family's financial stability even when you're no longer there. This is crucial if your income covers your family's daily needs, such as housing, food, utilities, and healthcare premiums.
- Accumulating cash value: Some types of life insurance, such as whole life insurance and universal life insurance, accumulate cash value over time. This means that you can build up a savings account within your policy, which can be accessed through loans or withdrawals. This can provide a financial buffer for unexpected expenses or temporary financial needs.
- Financial stability during tough times: Life insurance can help cover funeral costs and immediate expenses, providing financial stability during difficult times. The death benefit can be used to pay for funeral expenses, medical bills, and other immediate costs, easing the financial burden on your loved ones.
- Legacy planning: Life insurance can be used for legacy planning, allowing you to leave a financial inheritance for your loved ones or support charitable causes. You can choose your beneficiaries, including charitable organizations, when selecting your life insurance policy.
- Supplemental retirement income: Life insurance, especially permanent life insurance policies, can supplement your retirement income. The cash value component of these policies can be borrowed against or used to buy an annuity, providing a stream of retirement income.
By purchasing life insurance, you can ensure that your loved ones will have the financial resources they need to maintain their standard of living and cover any necessary expenses in the event of your death.
Life Insurance Surrender: Taxable Proceeds?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The premium rate for a life insurance policy is based on the concepts of mortality and interest. The amount at risk must be known to predict the cost to each member of the group. Mortality tables are used to give the company a basic estimate of how much money it will need to pay for death claims each year. The second factor used in calculating the premium is interest earnings. Companies invest your premiums in bonds, stocks, mortgages, real estate, etc., and assume they will earn a certain rate of interest on these invested funds. The third consideration is the expenses of operating the company. The amount charged to cover each policy's share of expenses of operation is called the expense loading.
There are two primary types of life insurance: term and permanent. Term life insurance provides coverage for a certain period, usually between 10 and 30 years. Permanent life insurance, such as whole life insurance or universal life insurance, can provide lifetime coverage and usually includes the ability to accumulate cash value, which can be accessed while the policyholder is still alive.
Life insurance provides a financial safety net for your loved ones if you pass away. It can be used to replace lost income, pay off debts, cover funeral and burial costs, fund children's education, and more. Life insurance can also offer tax advantages, as death benefits are typically not taxable, and the cash value component of permanent life insurance policies grows tax-deferred.
If you have someone who depends on you financially, you should consider getting life insurance. This includes individuals with spouses, children, or other family members, as well as business owners who want to ensure their business can continue operating after their death.