The cost of auto insurance varies depending on a number of factors, including age, gender, location, driving record, and the type of car being insured. The average cost of car insurance in the US is $193 per month for full coverage and $53 for minimum coverage. The cheapest car insurance is $30 a month from Geico. However, the cost of auto insurance can be as high as several thousand dollars a year, depending on the factors mentioned above. It is important to shop around and compare quotes from multiple insurance companies to get the best rate.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Average monthly cost of car insurance in the U.S. | $193 for full coverage |
| $53 for minimum coverage | |
| Average cost of car insurance in the U.S. per year | $2,311 for full coverage |
| $640 for minimum coverage | |
| Cheapest car insurance | $30 a month from Geico |
| Factors that affect the cost of car insurance | Personal characteristics like age, gender and marital status |
| The coverage you choose | |
| Your driving record | |
| Your location | |
| Your credit score | |
| Your car insurance history | |
| Your car make and model |
What You'll Learn

How much does car insurance cost by state?
The cost of car insurance varies from state to state, with several factors influencing the price. The national average rate for full coverage car insurance is $1,718 per year, according to a June 2024 analysis by NerdWallet. However, the cost of car insurance in each state can differ significantly, with some states having much higher or lower rates than the national average. Here is a breakdown of the average cost of car insurance in different states:
The Most Expensive States for Car Insurance:
Florida, Louisiana, Texas, Rhode Island, and Kentucky are among the states with the highest average annual cost of full coverage car insurance. Florida tops the list with an average rate of $3,067 per year, followed by Louisiana at $3,037, and Texas at $2,567. These states often have higher rates due to factors such as frequent claims, high population density, and costly repairs.
The Cheapest States for Car Insurance:
On the other hand, Wyoming, Vermont, New Hampshire, Idaho, and Ohio are among the states with the lowest average annual cost of full coverage car insurance. Wyoming has the lowest rate at $972 per year, followed by Vermont at $1,082, and New Hampshire at $1,119. These states tend to have lower rates due to factors such as cheaper cost of living, lower accident rates, and less traffic congestion.
Factors Affecting Car Insurance Rates by State:
The cost of car insurance in each state is influenced by various factors, including accident and claim frequency, the cost of labour and vehicle parts, vehicle theft rates, road conditions, and state regulations. Additionally, personal factors such as age, driving record, credit score, and vehicle type can also impact the cost of car insurance. It's important to note that car insurance rates can change over time, so it's always a good idea to compare rates and shop around for the best deal.
Gap Insurance: VW Loan Standard?
You may want to see also

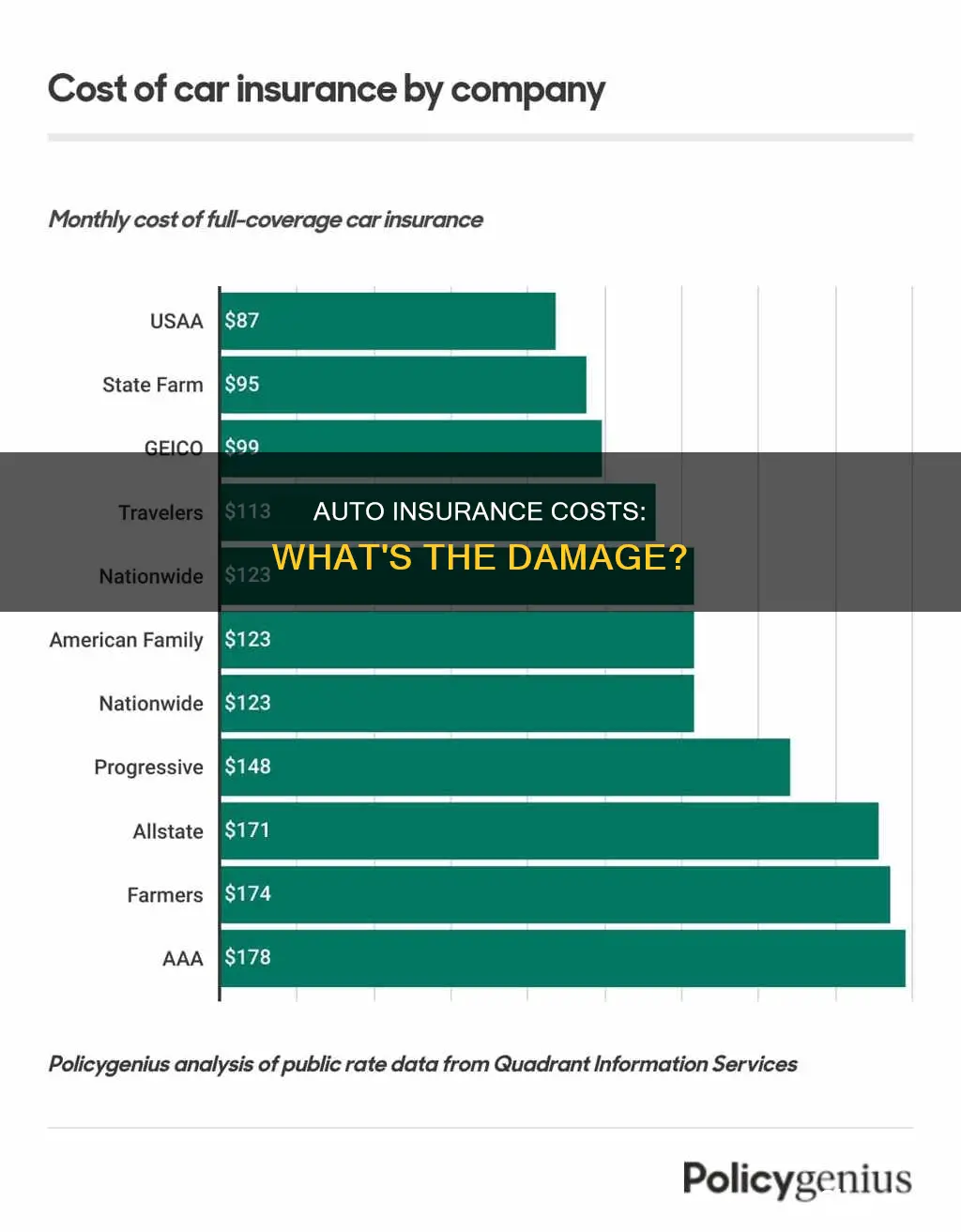
How much does car insurance cost by company?
The cost of car insurance varies depending on the company you choose, as well as other factors such as your age, gender, driving history, and location. Here is a breakdown of the average cost of car insurance by company:
USAA
USAA is a popular choice for military members, veterans, and their families, as it offers some of the lowest rates on the market. Their average annual rate for full coverage is around $1,300 to $1,400, but it's important to note that their policies are only available to a specific group of people.
Erie
Erie is another affordable option, with average annual rates ranging from $1,500 to $1,600 for full coverage. They are widely available and known for their competitive pricing.
Geico
Geico is a well-known insurance company that often offers low premiums across the country. Their average annual rate for full coverage is around $1,700.
Progressive
Progressive is a good option for high-risk drivers, and their rates are generally competitive. Their average annual rate for full coverage is around $1,800.
State Farm
State Farm is the largest auto insurer in the country, and they offer a wide range of coverage options. Their average annual rate for full coverage is around $1,900.
Allstate
Allstate is one of the more expensive options, with an average annual rate for full coverage of around $3,4000.
It's important to note that these rates are averages and may not reflect the exact cost of your policy. The best way to determine the cost of car insurance for your specific situation is to get quotes from multiple companies and compare their offers. Additionally, you can consider bundling your home and auto insurance or taking advantage of various discounts to lower your premiums.
UK Vehicle Insurance: Am I Covered?
You may want to see also

How much does car insurance cost by age?
The cost of car insurance varies depending on the age of the driver. In general, younger and older drivers pay more for car insurance than those in their 20s to 60s. This is because younger and older drivers are considered higher risk.
Car Insurance Costs for Teenagers
Teens are considered some of the riskiest drivers to insure. Statistically, drivers aged 16 to 19 are almost three times more likely to be involved in fatal car accidents per mile driven than any other age group. As a result, insurers charge more to insure teen drivers to offset the higher costs associated with teen driving claims.
The average cost of car insurance for a 16-year-old is $3,192 per year for minimum coverage and $3,192 per year for full coverage. For a 17-year-old, the cost drops slightly to $2,930 for minimum coverage and $2,823 for full coverage.
Car Insurance Costs for Young Adults
Car insurance costs continue to decrease as drivers gain more experience behind the wheel. By the age of 25, drivers might notice a significant reduction in their premiums.
The average cost of car insurance for a 21-year-old is $1,217 per year for minimum coverage and $1,217 per year for full coverage.
Car Insurance Costs for Adults
Throughout adulthood, provided that drivers have a history of safe driving and no insurance claims, premiums generally continue to drop as drivers gain more experience.
Car Insurance Costs for Seniors
As drivers reach their senior years, premiums can start to increase again. This is due to risk factors such as age-related slowed response times and vision or hearing loss, which can make seniors more likely to get into accidents.
The average cost of car insurance for a 60-year-old is $1,896 per year for minimum coverage and $1,582 per year for full coverage. For a 75-year-old, the cost increases to $2,082 for minimum coverage and $1,882 for full coverage.
Uber Vehicle Insurance: What You Need
You may want to see also

How does gender affect car insurance pricing?
Several factors, including gender, influence car insurance pricing. In most states, insurance companies are allowed to consider gender when setting rates. Men are generally considered riskier to insure than women, and this is reflected in their insurance rates. Men tend to pay more for car insurance, especially at younger ages, due to their higher likelihood of engaging in risky driving behaviours and being involved in car accidents. However, the gender gap in insurance rates narrows with age, and women may pay slightly higher premiums later in life, although the reason for this is not clear.
Gender and Car Insurance Pricing
Historically, men have paid more for car insurance than women, as insurance companies view them as higher-risk drivers. Data from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) supports this perception, showing that men are more likely to be involved in fatal crashes, with a higher number of deaths in car accidents each year. According to a 2018 CDC study, the rate of fatal car accidents for men aged 16 to 19 was nearly double that of their female counterparts. This risk factor contributes to higher insurance rates for young men.
Gender Gap in Insurance Rates
The gender gap in insurance rates is most pronounced among younger drivers. Teenage boys pay the highest insurance rates of all, with quotes significantly higher than those of girls of the same age. For example, a sample male driver in his teens may receive a quote that is $328 more per year than a female driver of the same age. This disparity reflects the increased risk associated with young male drivers.
However, as drivers age, the gender gap in insurance rates narrows. After the age of 25, the difference in insurance premiums between men and women becomes negligible, with rates stabilising for both genders. While women continue to have safer driving records overall, their rates may increase slightly compared to men by the age of 35, although the reason for this slight hike is not well understood.
State Regulations on Gender-Based Pricing
It is important to note that not all states permit gender to impact insurance rates. Several states, including California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, North Carolina, and Montana, have explicitly forbidden insurance companies from considering gender when setting rates. In these states, insurers must rely on other factors to determine premiums. Additionally, some states are pushing for more inclusive practices by offering a third option on insurance applications to allow transgender and non-binary individuals to self-identify.
Factors Other Than Gender Affecting Insurance Rates
While gender plays a role in car insurance pricing, it is essential to recognise that other factors also influence rates. These factors include age, driving record, location, vehicle make and model, and credit history. Safe driving practices and maintaining a clean driving record can help individuals of all genders obtain more affordable insurance rates.
Uninsured Motor Vehicle Insurance: What's Covered?
You may want to see also

How does driving record impact the cost of car insurance?
A person's driving record can have a significant impact on the cost of their car insurance. Insurance companies rely on historical data to assess the level of risk associated with insuring a driver. A clean driving record with no accidents or violations generally results in lower insurance premiums. Conversely, a record marred by accidents, traffic tickets, or other infractions can lead to increased rates.
Accidents and Insurance Claims
A history of accidents, particularly those that are deemed to be the driver's fault, signals a higher risk to insurance providers. Drivers with a track record of accidents are more likely to file insurance claims, which translates into increased costs for the insurer. As a result, insurance companies may perceive these drivers as a higher liability and adjust their premiums accordingly.
Traffic Violations and Moving Offenses
Traffic violations, such as speeding tickets, reckless driving, or running red lights, are red flags for insurers. These infractions indicate a disregard for traffic laws and responsible driving behaviour. Insurance companies view these violations as indicators of increased risk and may raise premiums in response. Multiple violations can have a cumulative effect, further amplifying the impact on insurance rates.
Driving under the Influence (DUI) or Driving While Intoxicated (DWI)
A DUI or DWI conviction is a serious offense that significantly impacts insurance premiums. Such convictions signal a high level of risk and demonstrate irresponsible behaviour behind the wheel. Insurance companies may respond by substantially increasing premiums or, in some cases, refusing coverage altogether due to the elevated risk associated with these offenses.
Insurance Points and Surcharge Systems
In some jurisdictions, insurance companies use a point-based system to assess a driver's risk. Insurance points are assigned for accidents, violations, and other driving-related offenses. Accumulating points can result in premium surcharges, leading to increased insurance rates based on the number of points on a driver's record. The severity and frequency of offenses determine the number of points assigned.
How to Mitigate the Impact of a Poor Driving Record
While past driving infractions can have a lasting impact on insurance premiums, there are several steps that drivers can take to reduce their effect over time:
- Defensive driving courses: Completing a defensive driving course can demonstrate a commitment to safe driving and may qualify drivers for insurance discounts.
- Period of good behaviour: Maintaining a clean driving record for an extended period can gradually improve insurance rates, as insurers consider more recent driving history as a positive indicator.
- Shop around for quotes: Comparing quotes from multiple insurance providers can be beneficial for drivers with less-than-perfect driving records. Different companies may have varying policies and rates for drivers with infractions.
- Improve your credit score: In some states, insurance companies use credit scores as a factor when determining premiums. Improving credit scores can indirectly help lower insurance costs.
Removing Vehicles from Root Insurance
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The cost of car insurance for a new driver depends on several factors, including age, gender, location, and the type of car being insured. On average, car insurance for a new driver can range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars per year.
There are a few ways to get cheaper car insurance. One way is to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers and choose the one that offers the best rate. Another way is to bundle your car insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners or renters insurance. Additionally, improving your credit score and driving record can also help lower your car insurance premiums.
The cost of car insurance is influenced by various factors, including age, gender, marital status, credit score, driving record, location, and the type of car being insured. These factors are used by insurance companies to assess the risk of insuring a particular driver and set the premium accordingly.
Full coverage car insurance typically includes comprehensive and collision coverage, in addition to the state-mandated minimum liability coverage. It offers more protection in the event of an accident, but it is also more expensive than minimum coverage. Minimum coverage car insurance only meets the legal requirements of the state and may not provide sufficient financial protection in the event of a major accident.







