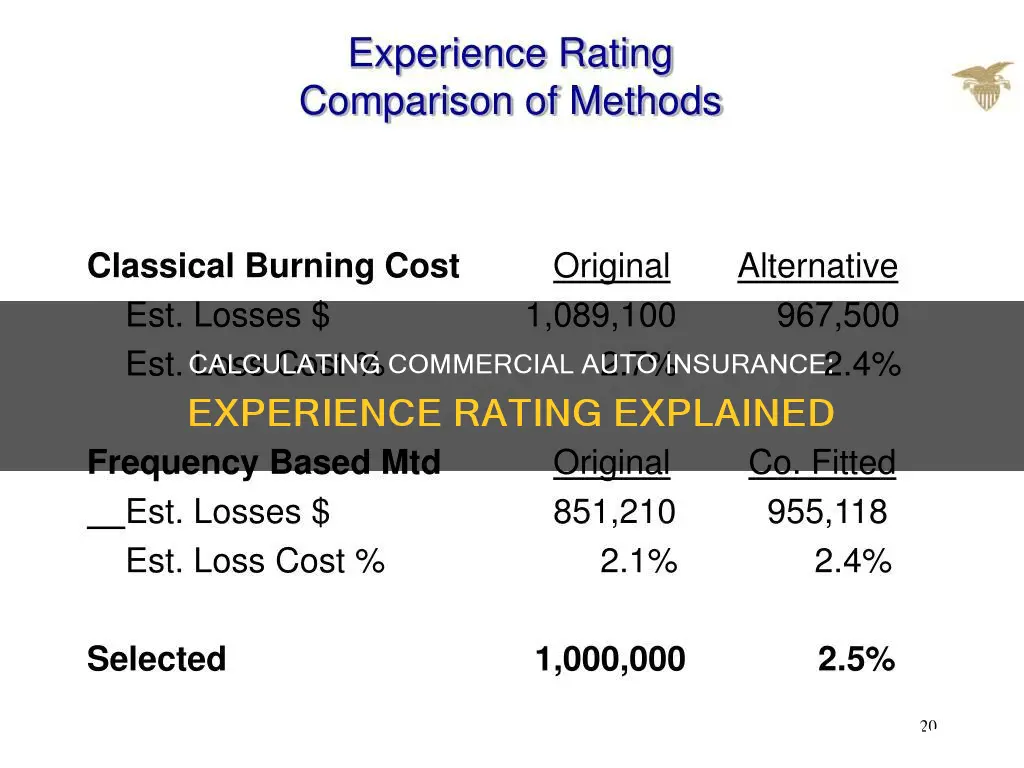
Experience rating is a method used by insurance providers to evaluate the past results of workers' compensation insurance and to determine future policy premiums. It compares the actual loss experience of the insured with the loss experience of other similar insured parties. This helps insurance companies determine the likelihood of a policyholder filing a claim and adjust their premiums accordingly. Experience ratings are calculated by comparing the historical loss of similar businesses and setting a benchmark for the experience modifier, which is then used to increase or decrease premiums. This article will specifically discuss how to calculate experience ratings for commercial auto insurance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To calculate the experience modification factor |
| Data | Loss experience of the insured compared to similar insured parties |
| Usage | Used to calculate premiums for workers' compensation and liability policies |
| Calculation | Based on previous loss experience and industry averages |
| Modifier | A numerical value applied to the premium, can be less than, greater than, or equal to one |
| Premium adjustment | Higher for riskier policyholders, lower for those with fewer claims |
| Incentive | Encourages policyholders to improve risk management practices |
| Timeframe | Based on the three years prior to the most recent expired policy period |
What You'll Learn

Calculating experience modifiers
An experience rating is a calculation used by insurance providers to compare an insured party to other insured parties with similar traits. This helps to determine and assign a current premium, taking into account the insured party's previous claims. The idea is that past loss experience will determine future loss experience. For example, a small-sized auto repair shop would be compared to other small-sized auto repair shops.
Experience ratings are most commonly used in workers' compensation insurance but are also used in other insurance sectors such as commercial auto liability. They help insurance providers identify high-risk policyholders and ensure they are collecting enough premiums to cover future claim costs.
Experience modifiers are used to determine whether premium rates will increase, decrease or remain the same based on a company's loss history. The experience modifier is calculated annually and is usually effective from the date the policy started.
The experience modifier is the quantifiable aspect of the experience rating that insurers use to increase or decrease premiums in relation to the average. If the average experience modifier is 1, companies with fewer historical losses may have an experience modifier of less than 1, multiplying their premiums by a lower rate. Conversely, a history of losses will push the modifier higher than 1.
For example, if a company has a relatively good history of workers' compensation claims compared to similar companies in their state, their experience modifier might be 0.90. The manual premium for their workers' compensation insurance based on payroll might be $10,420. But, because of their good experience rating, their standard premium is reduced to $9,378 – a saving of 10% on their annual premium.
Auto Insurance in Columbia, TN: How Much Does It Cost?
You may want to see also

How experience rating affects premiums
An experience rating is a calculation used by insurance providers to compare an insured party's loss experience to that of similar insured parties. This helps insurance companies determine the likelihood of a policyholder filing a claim and adjust their premiums accordingly.
When it comes to commercial auto insurance, an experience rating can affect premiums in several ways. Insurance companies will consider the number of claims made by the policyholder in the past and compare it to the number of claims typically made by similar businesses. If a business has a higher number of claims compared to its peers, its experience rating will be higher, and its premium will increase. On the other hand, if a business has fewer claims than similar companies, its experience rating will be lower, resulting in a lower premium.
The severity and frequency of incidents also play a role in determining the experience rating. More frequent and severe accidents or incidents will lead to higher experience ratings and premiums. Conversely, less frequent and less severe incidents will result in lower experience ratings and premiums.
Experience ratings also take into account the total cost of losses incurred across all claims. Higher costs will lead to an increased experience rating and premium, while lower costs will have the opposite effect. Additionally, factors such as payroll figures and the number of employees can influence the experience rating and, consequently, the premium.
It's important to note that experience ratings are not solely based on a policyholder's history of loss. They are calculated by comparing historical loss data from similar businesses and setting a benchmark. This benchmark is then used to determine the experience modifier, which is applied to the manual premium to calculate the standard premium. A company with a good experience rating (fewer historical losses) may have an experience modifier of less than 1, resulting in a lower premium. Conversely, a company with a higher experience rating (greater historical losses) will have an experience modifier greater than 1, leading to a higher premium.
Gap Insurance: Comprehensive Coverage?
You may want to see also

How experience rating helps insurers
An experience rating is a rating method that calculates the amount of loss experienced by an insured party compared to the amount of loss experienced by similar insured parties. This method is used to adjust premium rates, typically for workers' compensation and liability policies, to accurately reflect the risk posed by a policyholder.
Experience ratings help insurers in several ways. Firstly, they assist insurers in determining the likelihood of an insured party filing a claim. By comparing the loss experience of an insured party to that of similar insured parties, insurers can identify whether certain classes of policyholders are more prone to claims and, therefore, more risky to insure. This information is valuable for insurers when assessing the risk associated with a particular policyholder.
Insurers can then use experience ratings to adjust future premiums accordingly. If a policyholder is found to have a higher rate of claims than similar policyholders, insurers will increase future premiums to account for the expected rise in payout losses. Conversely, if a policyholder has a lower rate of claims, their premiums may be reduced. This adjustment of premiums based on experience ratings allows insurers to more accurately reflect the level of risk posed by individual policyholders.
Additionally, experience ratings provide an incentive for policyholders to improve their risk management practices. By charging higher premiums for riskier policyholders, insurers motivate these individuals or businesses to implement better safety procedures and improve conditions to reduce the likelihood of future claims. For example, a construction company that is considered high-risk for workers' compensation claims can improve its workplace safety measures to lower its premium.
Experience ratings also help insurers develop an experience modification factor, which refers to the adjustment level of the premium. This factor is calculated based on the experience rating and is applied to the insured's premium. By considering the experience modification factor, insurers can further refine their assessment of the risk associated with a particular policyholder.
Auto Insurance: Who Pays for Window Repairs?
You may want to see also

Experience rating and risk management
Experience rating is a method used by insurance companies to evaluate the risk associated with a particular policyholder. It is based on the idea that a policyholder's past loss experience is indicative of their future loss potential. By comparing a policyholder's loss history to that of similar insured parties, insurers can determine the likelihood of future claims and adjust premiums accordingly. This helps to ensure that premiums accurately reflect the risk level of the insured party.
Insurers use experience ratings to incentivize policyholders to improve their risk management practices. By charging higher premiums to risky policyholders, insurers encourage them to implement better safety procedures and workplace conditions, thereby reducing the likelihood of future claims. This is especially important for businesses carrying workers' compensation insurance, as higher premiums can cripple their balance sheets.
Experience ratings are calculated by comparing the historical loss data of similar businesses in the same industry. This data is then averaged to set a benchmark for the experience modifier. The experience modifier is the quantifiable aspect of the experience rating that insurers use to increase or decrease premiums. If the average experience modifier is 1, a company with fewer historical losses may have an experience modifier of less than 1, resulting in a lower premium. Conversely, a company with a high number of losses will have an experience modifier greater than 1, leading to a higher premium.
The experience rating formula for workers' compensation insurance is as follows:
> (Total Payroll / 100) x Experience Modifier = Total Workers' Compensation Insurance Premium)
For example, a company with a payroll of $300,000 and an average experience modifier of 1 would have a total premium of $3,000. However, if the company had a good experience rating and an experience modifier of 0.90, their total premium would be reduced to $2,700.
Experience ratings are typically based on the three years of loss experience prior to the most recent expired policy period. This allows insurers to evaluate past results and determine future policy premiums. By using experience ratings, insurance companies can incentivize businesses to improve their risk management practices and safety procedures, leading to a reduction in the number of claims.
Does GEICO Cover Windshield Claims?
You may want to see also

Experience rating and safety procedures
In the context of commercial auto insurance, an insurance company will evaluate the claims and losses associated with the policies they underwrite. They will pay close attention to whether certain classes of policyholders are more prone to filing claims, making them riskier to insure. For example, a large-sized construction company with a history of frequent claims will likely be considered a higher risk than a similar-sized company with fewer claims.
The experience rating is then used to adjust future premiums accordingly. If a policyholder has a higher-than-average loss experience, their premium will increase to cover the expected rise in payout losses. Conversely, if their loss experience is better than average, their premium may be reduced. This incentivizes policyholders to improve their risk management practices and safety procedures, which can help lower their premium.
Safety procedures play a crucial role in this process. By implementing effective safety measures and improving workplace conditions, businesses can reduce the likelihood of claims and, consequently, lower their insurance premiums. For instance, a construction company can develop comprehensive safety protocols for its workers, reducing the risk of accidents and subsequent workers' compensation claims.
It's important to note that experience rating is typically based on the three years prior to the most recent expired policy period. This means that insurance companies will take into account a business's loss experience over a relatively short period when determining their experience modification factor and setting premiums. Therefore, businesses should continuously focus on improving their safety procedures to maintain favourable experience ratings and insurance rates.
By understanding the relationship between experience rating and safety procedures, businesses can actively work towards mitigating risks and creating a safer work environment. This not only benefits their employees but also helps them secure more favourable insurance terms, contributing to their long-term financial stability.
Oregon Auto Insurance: Valid in California?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An experience rating is a calculation used mainly by insurance providers within worker’s compensation insurance. It compares an insured party to other insured parties with similar traits to calculate and assign a current premium.
Experience ratings help insurance companies determine which customers are more likely to file claims, which creates losses for them. To balance this out, they charge a higher premium to customers that have a higher risk of filing claims.
An experience modifier is the quantifiable aspect of Experience Rating that insurers use to increase or decrease premiums in relation to the average. If the average experience modifier is 1, companies with a good Experience Rating may have a modifier of less than 1, multiplying their premiums by a lower rate.