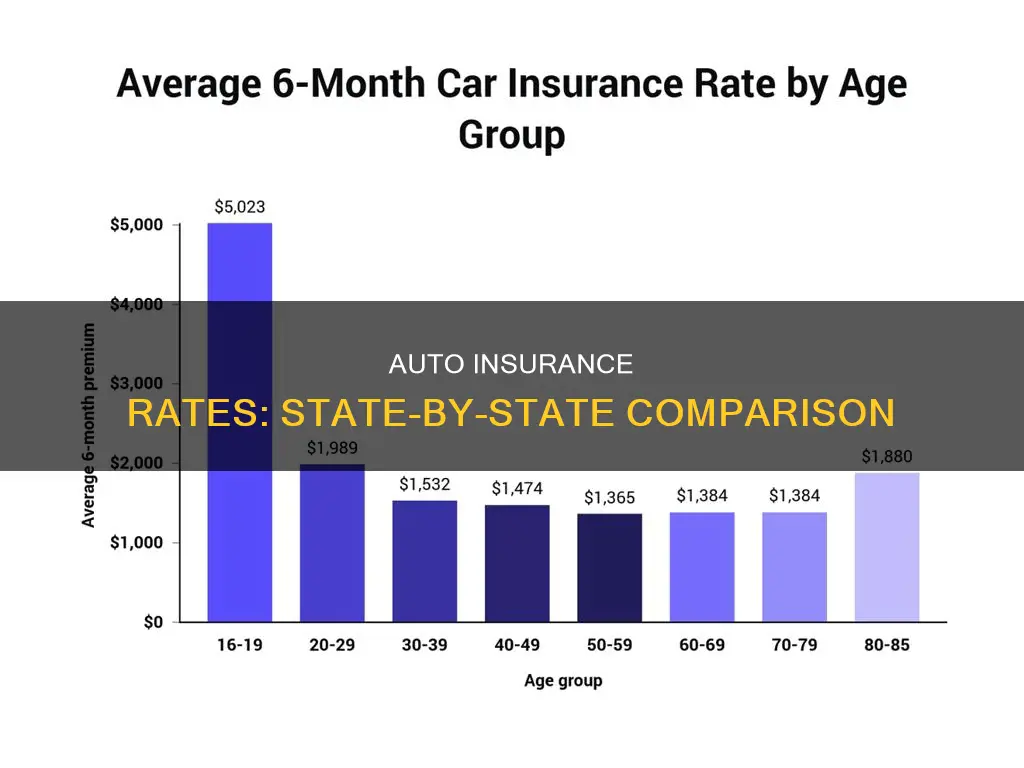
Auto insurance rates vary drastically from state to state. The national average annual cost for a full-coverage policy is $1,895, but the rates in your state will depend on your location, driving record, the type of car you drive, desired coverage types, and age.
Louisiana, Florida, California, Michigan, and Colorado are the most expensive states for car insurance in the U.S. Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Idaho, and Ohio are the cheapest states for car insurance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| States with the most expensive car insurance | New York, Florida, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, and Maryland |
| States with the cheapest car insurance | Idaho, Vermont, Ohio, Maine, and Iowa |
| States with the highest full-coverage car insurance rates | Louisiana, New York, Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Nevada |
| States with the highest minimum liability car insurance rates | New York, Nevada, Florida, Louisiana, and New Jersey |
| States with the lowest full-coverage car insurance rates | Maine, Vermont, Hawaii, Idaho, and Ohio |
| States with the lowest minimum liability car insurance rates | Wyoming, Vermont, South Dakota, Hawaii, and Iowa |
What You'll Learn

No-fault states vs. fault states
No-fault states and fault states have different ways of handling insurance claims after a car accident. Currently, there are 12 no-fault states and the remaining states, along with Washington, D.C., are considered at-fault or tort states.
In a no-fault state, each driver files a claim with their own insurance company to cover their injuries, regardless of who is at fault. This is known as Personal Injury Protection (PIP) and is mandatory in no-fault states. The at-fault party is still responsible for paying for everyone's property damage. No-fault states can still determine liability after an accident, and the responsible party may be liable for property damage and medical expenses that exceed a certain threshold.
On the other hand, in an at-fault state, the insurance of the driver who caused the accident pays for both injuries and damage. The at-fault driver's insurance typically covers the other driver's injuries, damaged property, and sometimes compensation for other damages such as pain and suffering.
No-fault states tend to have higher insurance costs compared to at-fault states due to factors such as claims being paid regardless of fault, encouraging fraud, and possible exaggerated injuries. Additionally, drivers in no-fault states are required to purchase additional coverage in the form of PIP, which can increase the overall cost of insurance.
Insurance Total Loss: What's Next?
You may want to see also

Population density
For example, New York, one of the most densely populated states, has the highest insurance rates in the country, with an average monthly premium of $410. Other densely populated states like Florida, Louisiana, and California also rank among the most expensive states for car insurance.
In contrast, states with lower population density, such as Maine, Vermont, and Idaho, tend to have cheaper insurance rates. The fewer drivers on the road in these states result in reduced accident rates and insurance claims, leading to more affordable insurance premiums. Maine, for instance, has an average premium of $93 per month for full coverage, which is significantly below the national average.
Additionally, population density influences insurance rates at the ZIP code level. Insurers assign risk levels to specific ZIP codes based on factors such as traffic volume, accident frequency, crime rates, and theft data. As a result, two drivers living in different areas of the same state can experience significantly different insurance rates due to variations in population density and associated risk factors.
Auto Insurance Rates: Factors and Impact
You may want to see also

Weather conditions
Impact of Weather Conditions on Insurance Rates
The frequency and severity of weather-related events can have a substantial impact on auto insurance rates. States that experience more frequent and intense weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, hailstorms, and tornadoes, tend to have higher insurance rates. For example, Florida, Louisiana, and Texas, which are prone to hurricanes and severe storms, often see higher insurance costs. In contrast, states with milder weather, such as Vermont, Ohio, and Maine, typically have lower insurance rates.
Claims and Insurance Rates
The number of weather-related claims in a state can significantly influence insurance rates. When natural disasters strike, there is usually a surge in property damage claims, and insurers may raise rates across the board to compensate for their losses. States with a higher frequency of claims due to weather events will generally have higher insurance rates.
Comprehensive Coverage and Weather Events
Comprehensive auto insurance is crucial for protecting against weather-related damage. It covers a wide range of perils, including natural disasters, fallen objects, theft, and accidents involving animals. Areas prone to extreme weather events often have higher comprehensive insurance rates because insurers anticipate more claims. However, even if you live in an area with milder weather, comprehensive coverage can still be beneficial, as it provides financial peace of mind in the event of unexpected weather-related damage.
Seasonal Weather Conditions
Seasonal weather conditions, such as snowy and icy roads during winter, can also impact insurance rates. States that experience harsh winters with treacherous driving conditions will likely have higher insurance premiums. This is because the risk of accidents and vehicle damage increases during these periods.
Unpredictable Weather and Additional Coverage
Weather can be unpredictable, and it's essential to consider additional coverage options to bridge any gaps in your policy. For example, roadside assistance can be invaluable if you get stuck in the snow or mud, while rental reimbursement can help cover the cost of a rental car while your vehicle is being repaired after weather-related damage. These additional coverages can provide peace of mind and help you manage unexpected situations.
Impact of Weather-Related Claims on Rates
Filing a weather-related claim generally doesn't affect your insurance rates, as these events are beyond your control. However, if you have multiple claims on your policy, a comprehensive claim may contribute to a rate increase. It's important to remember that the number of claims, rather than the cause, can influence your insurance costs.
Auto Insurance and Utility Bills: Understanding the Difference
You may want to see also

Cost of living
The cost of living is a significant factor in determining auto insurance rates by state. States with a high cost of living tend to have higher insurance rates, as the cost of repairs and labour is typically higher in these areas. For example, California's sky-high cost of living is a contributing factor to its above-average insurance costs. Similarly, the low cost of living in Alaska helps keep insurance rates relatively low.
The cost of living is also linked to population density, as urban areas tend to have higher living costs. This is reflected in insurance rates, with states like New York, Florida, and Pennsylvania—which have large urban populations—ranking among the most expensive for insurance. Conversely, states with sparse populations and low costs of living, like Idaho, Vermont, and Ohio, tend to have cheaper insurance.
In addition to the cost of living, other factors that influence insurance rates include road conditions, the number of licensed drivers, traffic density, weather conditions, and local claims history. These factors collectively contribute to the variability in insurance rates across different states.
Strategies for Success in Auto Insurance Sales
You may want to see also

Crime rates
For example, Louisiana, Florida, and California have some of the highest auto insurance rates in the country, partly due to high crime rates, severe weather, and a high number of uninsured motorists. On the other hand, states like Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont have the cheapest auto insurance rates, benefiting from lower population density and fewer car insurance claims.
In addition to crime rates, other factors that influence auto insurance rates include road conditions, the number of licensed drivers, traffic density, cost of living, weather conditions, and local claims history.
Past Auto Insurance: How to Find Out Yours
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The factors that affect auto insurance rates by state include the state's insurance requirements, the number of auto insurance claims, the cost of car insurance claims, and the frequency of lawsuits in the state.
Unless you live in New Hampshire or Virginia, a minimum amount of car insurance is required in your state if you're operating a car on the roadway.
Auto insurance rates by state can change due to various factors such as inflation, higher repair costs, and natural disasters.
The states with the cheapest auto insurance rates include Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Ohio, and Iowa.
The most expensive states for auto insurance include New York, Florida, Louisiana, Pennsylvania, and Maryland.







