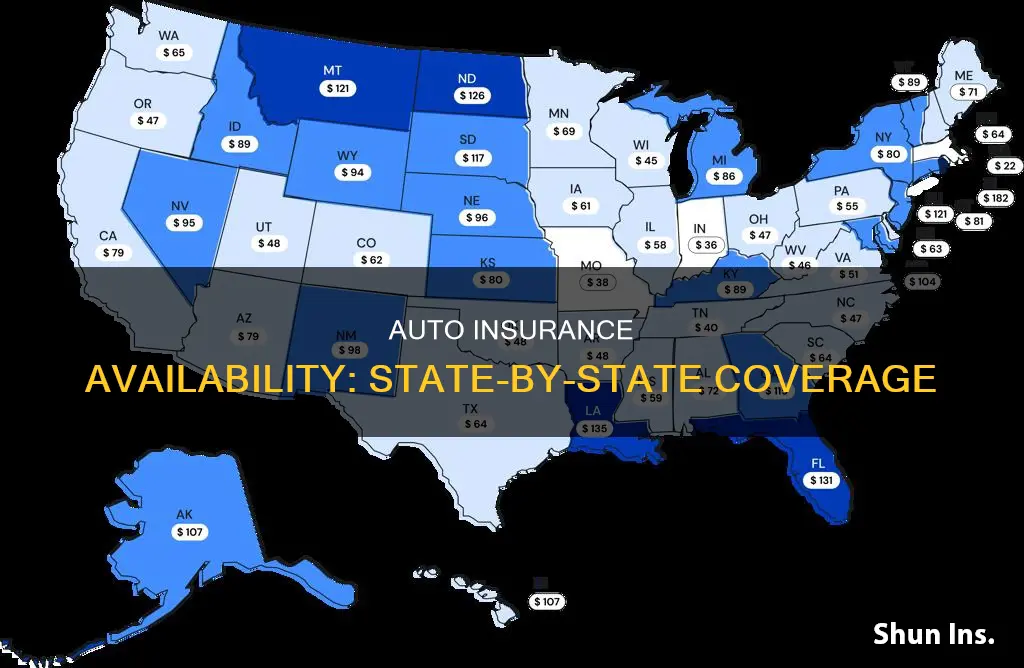
Auto insurance is a legal requirement in almost every state in the US. While the exact requirements vary from state to state, most states mandate a minimum amount of liability coverage, which includes bodily injury and property damage coverage. Other types of coverage, such as personal injury protection, uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, and collision coverage, may also be required in some states. The cost of auto insurance also varies depending on factors such as age, gender, driving record, location, and the type of vehicle.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| States without mandatory car insurance | New Hampshire and Virginia |
| Average annual full-coverage car insurance rates | $1,460 (Maine) to $8,232 (New York) |
| Average annual minimum-liability car insurance rates | $303 (Wyoming) to $2,221 (New York) |
| Average annual full-coverage car insurance rates for 20-year-old drivers | $1,260 (women) to $1,420 (men) |
What You'll Learn

Minimum auto insurance requirements vary by state
Auto insurance requirements differ from state to state, with each state setting its own minimum coverage requirements. While nearly all states have minimum requirements for liability coverage, these can vary significantly. In most cases, there is a minimum requirement for both bodily injury liability and property damage liability.
For example, in Arkansas, the minimums are $50,000 for bodily injury and liability, and $25,000 for property damage. In contrast, in California, the minimum liability coverage limits are 15/30/5, meaning up to $30,000 for all persons injured in an accident, subject to a limit of $15,000 for one individual, and $5,000 coverage for property damage.
In addition to liability coverage, some states also require other types of coverage, such as uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage and personal injury protection (PIP). For instance, Virginia requires uninsured motorist coverage, while Maine mandates medical payments coverage.
When choosing an auto insurance policy, it's important to understand the minimum requirements in your state and compare offerings from different insurance companies to ensure you're getting the coverage you need.
Factors Affecting Auto Insurance Rates
Several factors can influence auto insurance rates, including location, driving history, credit score, and the type of vehicle insured. The number of licensed drivers, traffic density, the percentage of uninsured drivers, and local claims history can also impact rates. Additionally, state laws specifying minimum insurance requirements can affect the cost of coverage.
No-Fault vs. At-Fault States
It's important to understand the difference between no-fault and at-fault (or tort) states when it comes to auto insurance. In a no-fault state, each party must typically file a claim with their own insurance company to cover medical expenses after an accident, regardless of who is at fault. On the other hand, in an at-fault state, the driver responsible for the accident is liable for paying for damages and medical expenses, and the not-at-fault driver is not required to file a claim with their insurer.
There are currently 12 no-fault states: Florida, Hawaii, Kansas, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, and Utah.
Gap Insurance: Who Qualifies?
You may want to see also

New Hampshire and Virginia don't require car insurance
While almost every state in the US requires drivers to have auto insurance, New Hampshire and Virginia are notable exceptions. However, this does not mean that residents of these two states can drive without any financial responsibility for their vehicles.
In Virginia, drivers who choose not to have auto insurance must pay a $500 uninsured motor vehicle fee when they register or renew their car registration. This money goes into an uninsured motorist fund, which helps to reduce insurance premiums for those who do have coverage. Uninsured drivers who do not pay this fee will have their registration cancelled and their driving privileges suspended.
In New Hampshire, drivers must provide proof of financial responsibility. This means that they need to show that they can pay the costs incurred by another driver if they are found to be at fault for an accident. If they are unable to do so, they will be required to purchase auto insurance.
Although New Hampshire and Virginia do not require drivers to have auto insurance, it is still highly recommended that residents of these states purchase coverage to protect themselves financially in the event of an accident.
North Carolina's Auto Insurance Conundrum: Understanding the No-Fault System
You may want to see also

Auto insurance rates differ by state
Secondly, the number of auto insurance claims in a state can impact rates. States with a higher frequency of severe weather events, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, or flooding, tend to have higher insurance costs. For example, Florida's extreme weather conditions contribute to higher insurance rates. Additionally, states with more congested urban areas and higher traffic densities often experience more accidents, leading to increased insurance claims and rates, as seen in Connecticut compared to Iowa.
Thirdly, the cost of car repairs and medical care varies across states, and this is reflected in insurance rates. States with higher repair and medical costs will generally have higher insurance rates since insurance companies need to pay out more for claims.
Fourthly, the frequency of lawsuits in a state can influence insurance rates. States with a higher number of litigious drivers tend to have costlier insurance. Louisiana, for instance, has a high rate of bodily injury claims and lawsuits, contributing to its expensive insurance rates.
Finally, location-specific factors such as population density, crime rates, and road conditions can also impact insurance rates. For example, rural states like South Dakota tend to have cheaper insurance due to lower accident risks and a smaller number of uninsured drivers. In contrast, states with large urban areas, such as New York, often have higher insurance rates due to increased congestion and accident risks.
Insuring Electric Cars in Massachusetts
You may want to see also

Average car insurance rates differ by state
The cost of car insurance varies significantly from state to state. The national average annual cost for a full-coverage policy is $1,895, but this can be as low as $1,460 in Maine, and as high as $8,232 in New York.
Factors Affecting Car Insurance Costs
There are a number of factors that affect the cost of car insurance, including:
- Population density: Urban drivers generally pay more for auto insurance than those in rural areas.
- Crime rate: Areas with higher crime rates tend to have higher insurance premiums.
- Number of licensed drivers: The more drivers there are, the higher the chance of accidents, which leads to higher premiums.
- Weather conditions: Severe weather can cause damage to vehicles and make driving conditions more hazardous, increasing the likelihood of accidents.
- State insurance minimums: Each state has different insurance requirements, which can affect the cost of coverage.
- Personal factors: Age, gender, driving record, and credit history can all impact the cost of car insurance.
States with the Highest Car Insurance Rates
The states with the highest average annual full-coverage car insurance rates are:
- Louisiana
- New York
- Michigan
- Pennsylvania
- Nevada
States with the Lowest Car Insurance Rates
The states with the lowest average annual full-coverage car insurance rates are:
- Maine
- Vermont
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Ohio
Smart Strategies to Secure Affordable 20/40 Auto Insurance
You may want to see also

Auto insurance is required by law in most states
The purpose of auto insurance is to provide financial protection in the event of a car accident. While the specific coverages offered by insurance companies can vary, most policies include liability coverage, which protects you if you're at fault in an accident. This typically includes bodily injury liability, which covers medical expenses for those injured in the accident, and property damage liability, which covers damage to another person's property.
In addition to liability coverage, some states also require additional types of coverage. For instance, some states mandate personal injury protection (PIP), which covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault in the accident. Other states may require uninsured and/or underinsured motorist coverage to protect you if you're in an accident with a driver who has insufficient or no insurance.
While collision and comprehensive coverage are not mandated by any state, many lenders and leasing companies require these coverages to protect their investment. Collision coverage pays for repairs to your vehicle if it's damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Comprehensive coverage, on the other hand, covers damage to your car from non-collision incidents, such as weather events, falling objects, or vandalism.
It's worth noting that auto insurance requirements can change over time, and it's the driver's responsibility to ensure they have the minimum required coverage for their state. Failure to meet the legal requirements can result in fines, license suspension, and other penalties.
Auto Insurance Costs in North Carolina: What to Expect
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, but it is required in almost every state. The only two states that don't require auto insurance are New Hampshire and Virginia.
Each state sets its own minimum coverage requirements. In many states, the minimum amount of liability insurance covered by law for bodily injury is $25,000 and $50,000 for property damage.
If you are caught driving without auto insurance, you may face penalties including fines, license suspension, vehicle impoundment, or legal consequences. Additionally, you will be financially vulnerable in the event of an accident.
The cost of auto insurance varies depending on factors such as age, driving history, type of vehicle, coverage limits, and location. On average, full-coverage auto insurance costs around $1,460 to $8,232 per year, while minimum-coverage policies cost around $303 to $2,490 per year.







