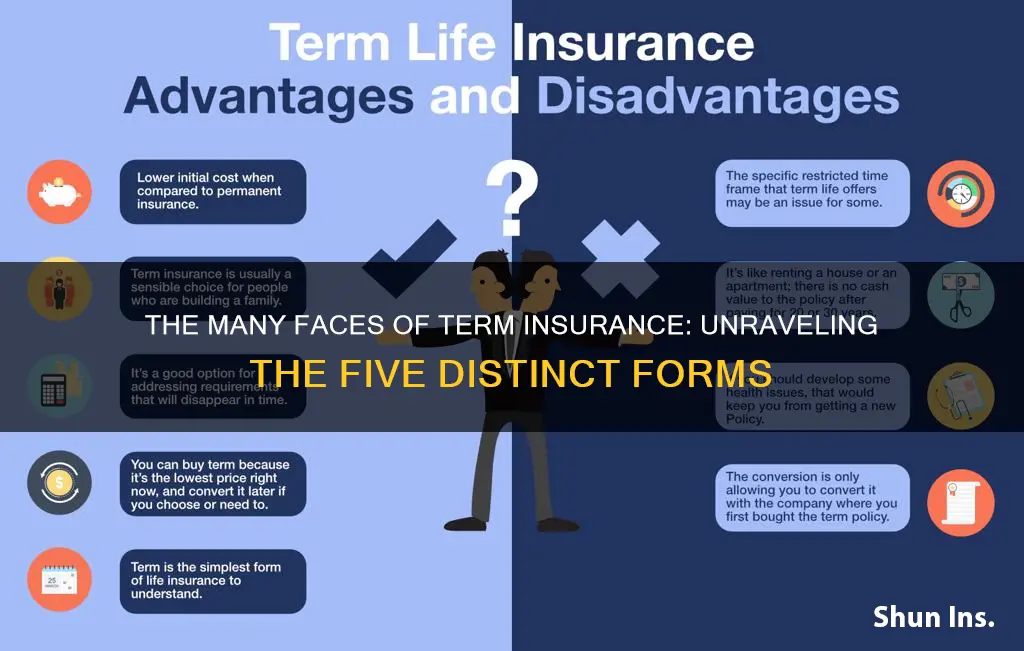
Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific period of time. There are two basic varieties: level term and decreasing term. Level term insurance policies have a fixed monthly payment and a death benefit that remains the same throughout the policy term. On the other hand, decreasing term insurance policies have a death benefit that declines over time, typically in one-year increments.
In addition to these two main types, there are also a few other less common forms of term insurance. Yearly renewable term (YRT) policies are one-year policies that can be renewed annually without providing evidence of insurability. Convertible term life insurance allows policyholders to convert their term insurance into whole life or universal life insurance. Finally, term insurance with a return of premium (TROP) feature will refund the total premiums paid if the policyholder survives the policy term.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Level Term Insurance, Yearly Renewable Term (YRT) Insurance, Decreasing Term Insurance, Term Insurance with Return of Premium (TROP), Convertible Term Insurance |
| Features | Affordable, High Life Cover, Flexibility in Premium Payments, Life Cover, Additional Add-ons, Tax Benefits |
| Coverage | Coverage for a specific period of time, beneficiaries receive a death benefit if the insured person dies during the policy term |
| Premium | Level premiums, increasing premiums |
| Conversion | Some term policies can be converted to permanent insurance |
What You'll Learn

Level Term Insurance
However, one of the drawbacks of level term insurance is that it expires. If the policyholder still needs coverage by the time their level term policy nears expiration, they will need to get a new policy, likely at a higher cost. Life insurance becomes more expensive to buy as the policyholder ages due to increased insurance risk.
Understanding the Convertibility Factor in Term Insurance: Unlocking Flexibility
You may want to see also

Increasing Term Insurance
While increasing term insurance can be a good option for those who want to hedge against inflation or know they will need increased coverage in the future, it is generally more expensive and complicated than comparable level term life insurance policies. The premiums for increasing term policies are higher than those for level term policies because of the potential for a larger death benefit later in the term.
One alternative to increasing term insurance is to use a rider to add more coverage to an existing policy. Another option is to purchase a supplemental level term life insurance policy, which can provide additional coverage at a lower cost.
Policybazaar's Term Insurance: A Safe Bet for Long-Term Financial Security?
You may want to see also

Decreasing Term Insurance
The predominant use of decreasing term insurance is for personal asset protection. Small business partnerships also use this type of insurance to protect indebtedness against startup costs and operational expenses. In the case of small businesses, if one partner dies, the death benefit proceeds from the decreasing term policy can help to fund continuing operations or retire the remaining debt for which the deceased partner is responsible.
Decreasing term policies are sometimes required by certain lenders to guarantee that the loan will be repaid if the borrower dies before the loan matures. For example, a small business may borrow a substantial sum from a bank, with a certain amount to be repaid each year for a set number of years. The bank may ask the business owner to take out a decreasing term policy that mirrors the amortization schedule of the loan.
Decreasing term life insurance is ideal for those who expect their beneficiaries to need less financial support as time passes. It is a viable way to protect against significant shorter-term expenses. This type of insurance lowers your death benefit over time, reducing the cost of your coverage.
However, the main drawback is that the death benefit declines over time, which is why it costs less than standard term life or other policies. Additionally, decreasing term life may not provide sufficient coverage if unexpected expenses arise towards the end of the policy's term.
Maximizing Long-Term Health Insurance Savings: Strategies for the Savvy Consumer
You may want to see also

Term Insurance with Return of Premium (TROP)
TROP is suitable for unmarried individuals with dependent parents or siblings, married couples without children, and married couples with children. It ensures that their loved ones are financially secure in the event of their death and that they receive a refund of their premiums if they survive the policy term.
TROP offers guaranteed returns on the total premium paid, excluding any additional premiums paid for add-ons or riders. It also provides tax benefits, allowing policyholders to claim deductions on their premiums under Section 80C of the IT Act and tax exemptions on both maturity and death benefits under Section 10 (10D).
Policyholders can choose from various premium payment options, including monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, and annual payments. TROP also offers flexible payout options, allowing policyholders to receive their maturity benefit in a lump sum, monthly instalments, or a combination of both.
Overall, TROP is a valuable option for those seeking life insurance coverage and a savings component. It provides financial protection for loved ones and the opportunity to receive a refund of premiums if the policyholder survives the policy term.
Securing Short-Term Rental Insurance: Navigating the Path to Comprehensive Coverage
You may want to see also

Convertible Term Insurance
However, convertible term policies have an extra feature that lets individuals switch some or all of their coverage to permanent life insurance. This means that the coverage could last the entire life of the insured and build cash value, provided that the premiums are paid. Importantly, the insured would not need to pass a health exam to make the conversion.
Most term life insurance policies are convertible. They can be exchanged for, or converted to, permanent policies issued by the same insurance company. The term policy will usually state whether it is convertible, along with any time limits on making the move. If the policy doesn't include this information, the insured can call the insurer or talk to a financial professional about their options.
When a term policy is converted to a permanent policy, the premium will probably increase. Permanent life insurance generally costs more than term life insurance because it never expires, as long as premiums are paid. The insurance company bases the price of the new permanent coverage on how old the insured is when they convert.
The Fine Print of Renewable Term Life Insurance: Understanding Expiry and Renewal Clauses
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The five forms of term insurance are level term insurance, yearly renewable term insurance, decreasing term insurance, term insurance with return of premium, and convertible term insurance.
Level term insurance is the most common type of term insurance, offering a fixed sum assured throughout the policy's duration. Premiums remain constant, providing policyholders with predictable costs.
Convertible term insurance allows policyholders to convert their term policy into an endowment or whole life insurance policy at a later stage. This flexibility is beneficial for individuals whose needs may evolve over time.
Yearly renewable term insurance policies are one-year policies that can be renewed annually without providing evidence of insurability. The premiums for these policies increase each year as the insured person ages, making them potentially expensive over time. Level term insurance, on the other hand, offers fixed premiums for specific durations such as 10, 20, or 30 years.







