There are many different types of insurance, and many different questions you might want to ask about them. For example, you might want to ask about health insurance, life insurance, or insurance for your home, car, or business.
If you're thinking about getting health insurance, you might want to ask about the monthly cost, whether your current doctors are covered, whether routine examinations are covered, and how the company handles disputes over claims.
If you're thinking about getting life insurance, you might want to ask about the different types of coverage available, how much it will cost, and whether it will provide any living benefits.
If you're thinking about getting home or car insurance, you might want to ask about your deductible and premium, and whether your policy offers enough protection.
What You'll Learn

What is my deductible?
Understanding your insurance deductible is crucial, especially when it comes to filing a claim. A deductible is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for a covered service before your insurance plan starts to pay. For example, if you have a $2,000 deductible, you will need to pay the first $2,000 of covered services yourself. After you meet your deductible, you typically pay a fixed amount for a covered service, and your insurance company covers the rest.
It's important to note that deductibles vary depending on the type of insurance. For instance, in health insurance, you may have a separate deductible for certain services, like prescription drugs. Family plans often have both individual and family deductibles. On the other hand, car insurance deductibles are usually associated with collision, comprehensive, uninsured motorist, and personal injury protection coverages. Unlike health insurance, car insurance deductibles are not annual; you pay your deductible every time you file a claim.
When choosing a deductible, you typically have the option of selecting a low or high deductible. A low deductible leads to higher insurance rates, while a high deductible results in lower rates. It's essential to consider your financial situation when deciding on a deductible. Make sure you understand your potential out-of-pocket expenses and choose a deductible that aligns with your budget.
Additionally, some insurers offer disappearing deductible programs, where your deductible decreases or is waived if you go a certain period without a claim or violation. This is another factor to consider when selecting an insurance plan and understanding your deductible options.
Unraveling the Complexities of Insurer Annual Billing: Maximum Charges and Their Implications
You may want to see also

What is my premium?
An insurance premium is the price you pay for an insurance policy. The amount you pay is determined by the type of insurance you buy, such as health, life, renters, auto, or homeowners insurance. Premiums are typically paid monthly, semi-annually, or annually, depending on the policy.
Health Insurance Premium
The amount you pay for health insurance each month is known as a health insurance premium. This is billed monthly and must be paid by the policyholder regardless of whether they use any healthcare services. The more comprehensive the coverage, the more expensive the premium. For example, a health insurance policy with a $1,000 deductible will be pricier than one with a $5,000 deductible.
Car Insurance Premium
Car insurance premiums are determined by a variety of factors, including your age, driving record, claims history, vehicle, and the amount of coverage you buy. The more coverages you carry, the higher your car insurance premium will be. Additionally, newer, faster, and more expensive cars have higher premiums.
Life Insurance Premium
Insurers typically use your age and medical history when calculating life insurance premiums. Other factors, such as your credit history, the amount of coverage you buy, and your employment status, can also impact the price.
Renters Insurance Premium
The price of renters insurance premiums is based on specific details, such as the value of your belongings, whether the building has a burglar alarm, and your credit score in most states.
Homeowners Insurance Premium
Homeowners insurance premiums are based on a variety of factors, such as the building's location and value, your credit score, claims history, and the amount of coverage you want to buy.
How to Lower Your Insurance Premium
You can lower your insurance premium by reducing your coverage or increasing your deductible. However, this may not always be a good choice, as it increases your risk. Another way to lower your premium is to bundle your insurance policies. For example, if you have your auto, home, and life insurance policies with one company, you will likely qualify for a discount.
Additionally, building healthy habits can help lower your health insurance premium. For instance, some employers may provide a discount on health insurance if you quit smoking, get a yearly physical, or exercise regularly.
It is important to note that insurance premiums vary depending on the insurance company and your personal circumstances. Shopping around and comparing prices and policies can help you find the best option for your needs.
Pregnancy: Pre-Existing Condition?
You may want to see also

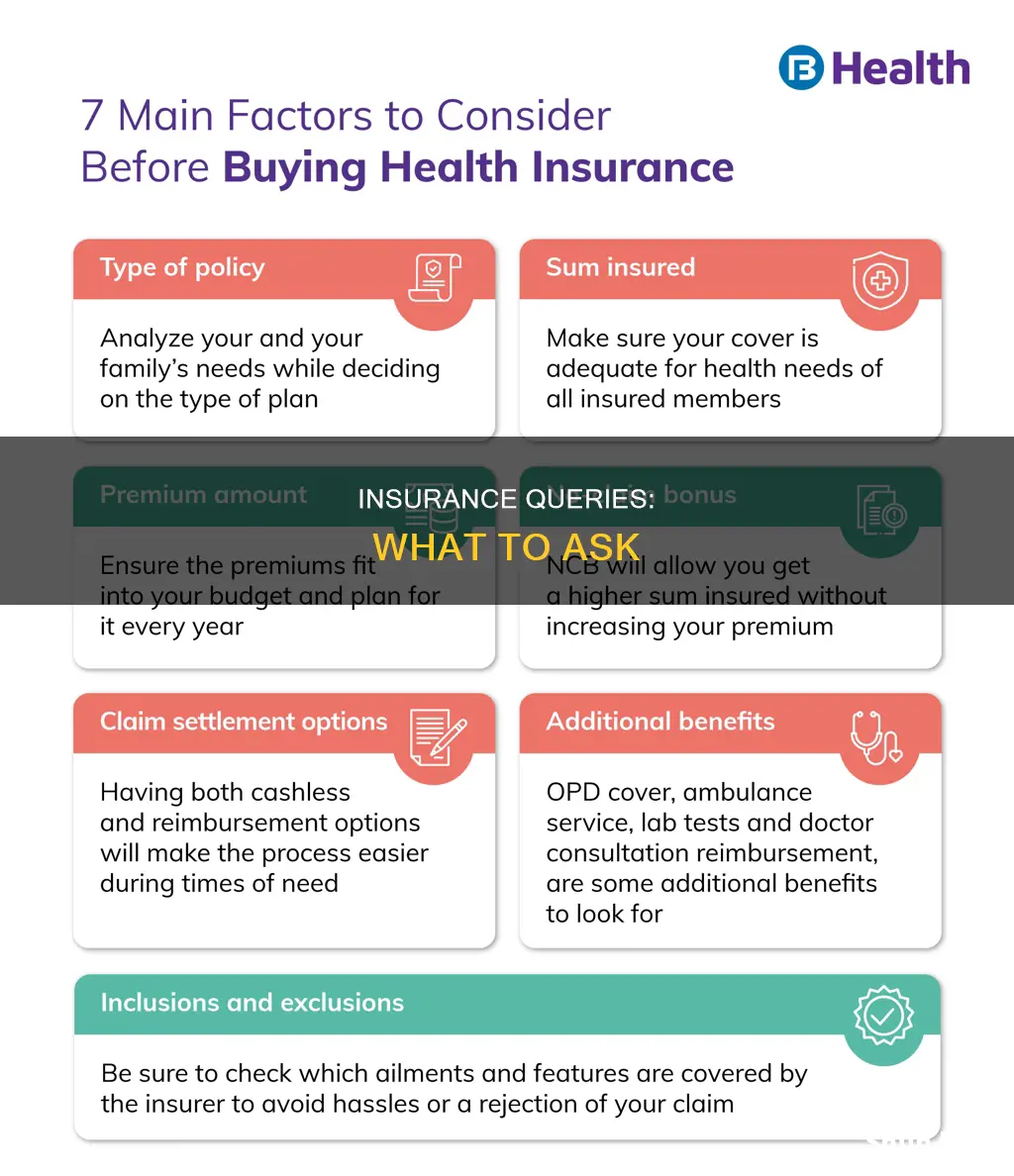
What type of plan is it?
When choosing an insurance plan, it is important to understand the different types of plans on offer. There are three main types of health insurance plans: indemnity health plans, managed care systems, and health maintenance organizations (HMOs).
Indemnity health plans, also known as fee-for-service plans, allow you to pay a percentage of the medical costs, while the insurance company covers the remaining percentage. You are usually allowed to choose your own doctors with this type of plan.
Managed care, on the other hand, includes health maintenance organizations (HMOs) and preferred provider organizations (PPOs). With an HMO, you or your employer pays a fixed monthly fee for health services, but you can only visit doctors who are under contract with the HMO. PPOs offer a discount for using physicians within the plan, but you may go to a doctor outside the PPO system for a higher price.
Another type of insurance plan is a life insurance plan. There are several types of life insurance policies, including term life, whole life, and universal life, each designed to fit specific needs and budgets. Term life insurance offers coverage for a certain number of years, while whole life insurance provides coverage for a lifetime.
Additionally, when considering health insurance, it is worth noting that there are also exclusive provider organizations (EPOs) and point-of-service (POS) plans. EPOs have lower monthly premiums than PPOs, but require you to stay within the provider network. POS plans offer the flexibility to choose between in-network and out-of-network providers, but out-of-network services come with higher costs.
When deciding on an insurance plan, it is crucial to understand the different types available, weigh their features, and select the one that best aligns with your requirements and financial situation.
Supplemental Insurance: Understanding the Added Layer of Protection
You may want to see also

What happens if I get in a car accident?
Getting into a car accident can be a stressful and disorienting experience. Here is a detailed guide on what to do if you get into a car accident:
Immediate Actions:
- Stay calm and check for injuries: Ensure that you, your passengers, and anyone else involved in the accident are safe and uninjured.
- Move vehicles out of traffic: If possible, move your car to the side of the road or a safe location away from oncoming traffic. Use hazard lights or road flares to warn other drivers.
- Call the police: Dial 911 and wait for the police to arrive. Provide them with the necessary information, including driver's license and insurance details. Get the name and badge number of the responding officer and ask how to obtain a copy of the police report.
Information Exchange:
- Exchange information: Collect and share names, contact details, insurance information, license plate numbers, and vehicle models with the other driver(s) involved.
- Document the scene: Take pictures of the accident scene from multiple angles, capturing vehicle damage, injuries, and the surrounding environment. If there are witnesses, politely ask for their contact information.
Reporting and Claims:
- Report the accident to your insurance company: Inform your insurer about the accident as soon as possible. Stick to the facts and avoid making any admissions or accusations.
- File a claim: You can choose to file a claim with your insurance company or the other driver's insurer. They will typically need basic information and photos of the damage to open a claim.
Additional Considerations:
- Seek medical attention: Even if you don't feel injured, it's advisable to get checked by a medical professional. Some injuries may not be apparent immediately but can be documented and treated early.
- Save documentation: Keep all receipts and documents related to the accident, including medical expenses and repair costs, to support your insurance claim and seek full compensation.
- Understand fault and liability: Depending on where you live, the determination of fault can impact how damages are handled. Consult with an attorney to understand your rights and options.
Social Insurance Programs: A Safety Net
You may want to see also

What life insurance benefits are guaranteed?
Life insurance provides a range of benefits, some of which are guaranteed. Here is a detailed overview:
Guaranteed Benefits
Life insurance guarantees a death benefit to the policy owner when the insured person dies. This payout is usually tax-free and can be used to cover final expenses, such as funeral costs, medical bills, and estate settlement costs. The death benefit also ensures that dependents will have money for living expenses, including rent, mortgage payments, and groceries.
Additional Benefits
Life insurance can also provide benefits during the policyholder's lifetime. Some policies offer a cash value component, similar to a savings account, which the policyholder can use to take out loans or pay premiums. This cash value grows tax-deferred and can supplement retirement savings.
Furthermore, life insurance may provide coverage for chronic and terminal illnesses through accelerated benefits riders, which allow early access to the death benefit. Long-term care riders can also help pay for nursing home or assisted living expenses.
Considerations
While life insurance offers these guaranteed benefits, it's important to note that certain conditions may apply. For example, graded death benefits in guaranteed issue life insurance policies may result in reduced payouts if the insured person dies within the first few years of the policy. Additionally, policy loans and withdrawals can reduce the death benefit and cash values.
It's always essential to carefully review the terms and conditions of a life insurance policy to understand the specific benefits, guarantees, and limitations offered.
Insurance MDHS: Change Form Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are eight different categories of homeowner's insurance in the US, each covering different aspects of your home, natural disasters, and contents. If you own a condo or mobile home, your policy will be different.
You need to conduct an inventory of the items in your home, especially valuable pieces, and the cost to replace them. Your insurance policy should cover all of these possessions.
Ask an agent about your deductible and ensure it works within your financial situation. By choosing a higher deductible, you may be able to lower your premiums.
Ask about the process and timeline for an adjuster to inspect the damage, how many estimates you will need, whether they work with a network of repair shops, and if they will provide a rental car.







