Actual Cash Value (ACV) is a term used by insurance companies to determine the current market value of a vehicle. It is calculated by subtracting depreciation from the original purchase amount. This value is used by auto insurance companies to estimate the value of a vehicle on the market and to determine how much to reimburse a policyholder if their car is totaled. The ACV of a car is typically lower than the amount originally paid for it.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | The actual cash value (ACV) of a car is its current market value, taking into account depreciation. |
| Calculation | ACV = Replacement cost – Depreciation. |
| Depreciation calculation | Depreciation = (Remaining useful life / Expected lifetime) x Replacement cost. |
| Factors considered | Mileage, make, year, model, interior, exterior, location, wear and tear, accident history, and vehicle options. |
| Use in insurance | Insurers use ACV to determine how much to reimburse a policyholder if their car is totaled. |
| Total loss | A vehicle is considered a total loss if the cost of repairs exceeds a certain percentage of the vehicle's ACV. This threshold varies by state and insurer. |
| Comparison to replacement cost | ACV is different from replacement cost value, which is the cost to replace an insured item with a new one. ACV policies are generally cheaper than replacement cost policies. |
What You'll Learn

ACV vs replacement cost
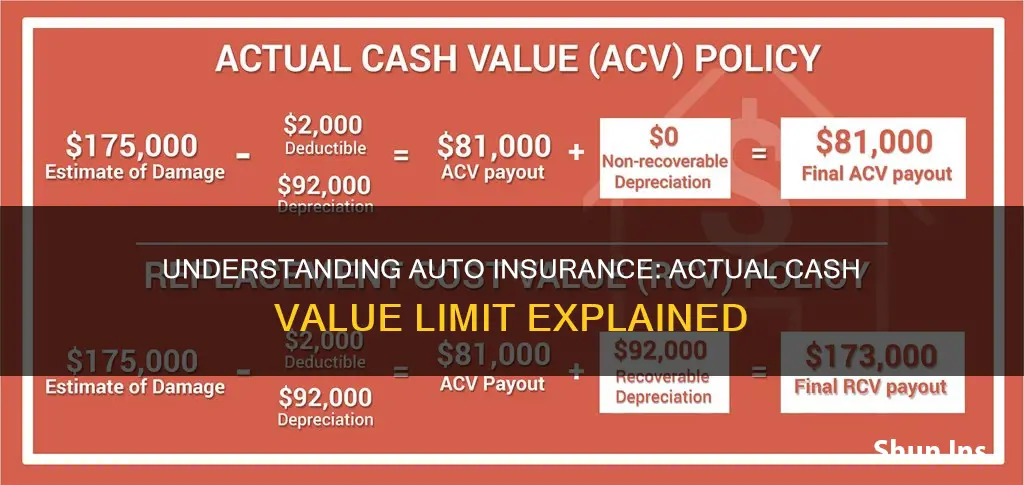
When it comes to auto insurance, actual cash value (ACV) and replacement cost value (RCV) are two different methods used by insurance companies to determine how much they will pay out for damaged or stolen property.
Actual Cash Value (ACV)
ACV is the amount paid to replace your property, taking depreciation into account. In other words, ACV is the replacement cost minus depreciation. Insurance companies calculate depreciation based on factors such as the age, wear and tear, and overall lifespan of the property. For vehicles, ACV is the market value or the amount the car would have sold for on the used car market. ACV is the standard level of coverage provided by comprehensive car insurance policies.
Replacement Cost Value (RCV)
RCV, on the other hand, is the amount paid to replace your property without considering depreciation. It is the full cost of replacing the property with a similar version at the current market price. RCV is not always available for car insurance, and opting for it will likely result in a higher premium.
ACV vs RCV
The choice between ACV and RCV depends on your budget, risk tolerance, and personal preference. ACV is generally more affordable, but RCV offers more coverage. If you want to limit your financial risk and are willing to pay a higher premium, RCV could be a better option. However, if you are looking for a cheaper policy, ACV may be more suitable.
Auto Owners: Competitive Insurance Rates?
You may want to see also

How is ACV calculated?
The actual cash value (ACV) of a car is calculated by subtracting depreciation from the original cost of the vehicle. This is because the ACV of a car is its current market value, which is always less than what it would cost to replace it.
Determining depreciation can be challenging, as there is no exact formula for calculating it. However, there are a few steps you can take to calculate the ACV of your car.
First, research your vehicle online and determine what it would cost to replace it with a similar vehicle of the same year, make, model and trim level. Once you have this figure, you can then deduct an amount for wear and tear, as well as any past claims or damage that has not been repaired.
Online depreciation calculators can also be used to estimate depreciation. These calculators will gather information about your vehicle and then calculate depreciation. As there is no exact formula for calculating depreciation, you should use multiple calculators and average the results to get a more accurate number.
It's important to note that ACV is not the same as replacement cost value. Replacement cost value is the cost to replace an insured property with something similar, and it does not take depreciation into account.
When calculating ACV, insurers will also take into account a variety of factors such as the vehicle's age, mileage, and any past accidents or unrepaired weather issues. They will also look at what comparable vehicles have sold for in your area to help them determine a fair market value for your car.
Accident Forgiveness: Standard Practice or Rare Privilege?
You may want to see also

How does ACV affect insurance costs?
When buying auto insurance, it's important to understand how your insurance company calculates payouts in the event of damage or a total loss. This is where Actual Cash Value (ACV) comes in.
ACV is the amount your vehicle is worth in its current condition, factoring in depreciation. It's the amount you could reasonably expect to get for it if you sold it today. When determining the ACV of a car, insurance companies consider factors such as the vehicle's year, make, model, mileage, wear and tear, and accident history.
Now, let's explore how ACV affects insurance costs:
Impact on Premium Costs
ACV policies typically have lower premiums than replacement cost value (RCV) policies. This is because ACV policies provide lower compensation in the event of a claim. By choosing an ACV policy, you may benefit from more affordable insurance premiums. This is advantageous if you're looking to save money on your insurance costs.
Payout in the Event of a Total Loss
In the unfortunate event that your vehicle is declared a total loss, the ACV will significantly impact the payout you receive. Insurance companies will reimburse you for the ACV of your vehicle, minus any applicable deductible. This means that you will receive the market value of your car at the time of the loss, taking into account depreciation. The higher the ACV, the higher the payout you can expect to receive.
Negotiating Power
Understanding ACV gives you leverage when negotiating with your insurance company. If you disagree with their valuation of your vehicle, you can conduct your own research and present comparable sales data to support a higher ACV. By demonstrating that your vehicle is worth more than their initial estimate, you may be able to negotiate a higher payout.
Impact on Loan Repayment
If you have an outstanding loan on your vehicle, the ACV payout may not be sufficient to cover the remaining balance. In such cases, gap insurance can be invaluable. Gap insurance helps pay the difference between the ACV payout and the amount you still owe to the lender or leasing company. This type of insurance is worth considering to protect yourself from being upside down on your loan after a total loss.
In summary, ACV directly affects insurance costs by determining the payout you will receive in the event of a total loss. It also influences your premium costs, with ACV policies typically carrying lower premiums than RCV policies. Understanding ACV and its impact on your insurance coverage is crucial when purchasing auto insurance and can help you make more informed decisions about your policy.
Insuring Your Vehicle: Year-Round Necessity
You may want to see also

When is a vehicle considered a total loss?
A vehicle is considered a total loss when the cost of repairing it to its pre-damaged state is higher than the vehicle's actual cash value (ACV). ACV is the amount the car is worth in its current condition, taking into account depreciation and the local market. The threshold for "totaling" a vehicle varies by state and insurer.
When determining whether a vehicle is a total loss, insurance companies consider several factors, including:
- The specific condition of the vehicle. Can it be repaired safely, and will it cost more to repair than the vehicle is worth?
- State laws, which often dictate that a vehicle must suffer a specific percentage of damage before it can be deemed a total loss.
If your vehicle is considered a total loss, you will need to file a total loss claim with your insurance company. They will likely ask for your vehicle's title and license plate, as well as the contact information for your lienholder, if applicable. The insurance company will then determine the ACV of your vehicle, which will be used to calculate your payout.
ACV or Replacement Cost: Understanding Mercury Auto Insurance's Payout Options
You may want to see also

Can you negotiate ACV?
Yes, you can negotiate the Actual Cash Value (ACV) of your car with your insurance company. This is because the ACV of your car is not set in stone and is open to interpretation.
To negotiate the ACV of your car, you should first independently determine its value. You can do this by using online tools such as Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds, or by getting an estimate from a qualified mechanic. It is important to know what your car is worth so that you can push for a higher settlement if you think the insurance company's offer is too low.
You should also find out how your insurance company defines ACV and how they arrived at their valuation. This will help you to provide your own counter-estimate and negotiate a better payout.
Additionally, you can look for comparable vehicles for sale in your local area and use their prices as an indication of your car's ACV. You can also point out any value-adding features of your vehicle, such as low mileage, excellent exterior and interior condition, and any enhancements you've made.
It is important to stay involved and communicate with your insurance company throughout the process. Don't be afraid to counter their offer and ask for a better deal, but always remain polite and firm.
If you are unable to reach an agreement with the insurance company, you may consider hiring an attorney or a public adjuster to help with the negotiation. However, this may incur additional costs, and there is no guarantee that you will receive a higher settlement.
Auto Accident Claims: Navigating the Insurance Maze
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The actual cash value (ACV) of a car is what it’s worth in its current condition, or the amount you could reasonably expect to get for it if you sold it today. The ACV of a car is calculated as the amount paid for the vehicle minus depreciation.
Depreciation is figured by establishing an expected lifetime of an item and determining what percentage of that life remains. This percentage, multiplied by the replacement cost, provides the actual cash value.
Auto insurance companies use ACV to estimate the value of a vehicle on the market. Insurance companies use ACV to determine how much to reimburse a policyholder if their car is totaled.
To compute the ACV of your car, you will need to subtract depreciation from the original purchase price. You can search for your car’s depreciation rate or depreciated value online or use an actual cash value calculator.







