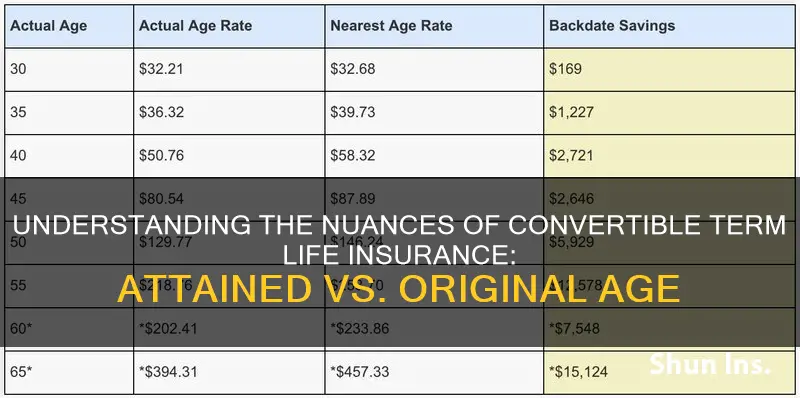
When it comes to insurance, there are two types of age calculations: attained age and original age. Attained age refers to the age of the insured person on a given date, usually the date of conversion from a term policy to a whole life insurance policy. It is one of the most common methods used by insurance companies to price their plans, with premiums based on the policyholder's age at enrollment. On the other hand, original age refers to the age of the insured when the term insurance was first acquired, and is used as a basis for premiums when converting to a whole life insurance policy. While the original age method results in lower annual premiums, it often requires a lump-sum payment to make up for the difference in cost between the term and whole life policies.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Attained age is the age at which the beneficiary of an insurance policy can receive benefits or withdraw funds. |
| Use | Attained age is most commonly used to refer to the age of an insured person on a given date. |
| Calculating Pricing | Attained age can be used to calculate pricing for insurance policies that set payments according to the policyholder's age, called an attained-age policy. |
| Attained-Age Policy | An attained-age policy is a policy in which premiums are based on your age at enrollment. |
| Attained-Age Rating | Attained-age rating is among the most common pricing methods in the United States. |
| Convertible Insurance | A type of life insurance that allows the policy owner to change a term policy into a whole or universal policy without a health qualification. |
| Convertible Insurance Premium | The permanent policy will have higher premiums. |
| Attained Age Premium | More expensive cost of insurance on a yearly basis. |
| Original Age Premium | Less expensive on a yearly basis. |
What You'll Learn
- Convertible term insurance allows for conversion to whole life insurance without a health test
- The conversion of term insurance to whole life insurance is a simple process
- The attained-age method bases insurance premiums on the age of the insured at the time of conversion
- The original-age method bases insurance premiums on the age of the insured when term insurance was first acquired
- Term insurance is the cheapest life insurance policy available

Convertible term insurance allows for conversion to whole life insurance without a health test
Convertible term insurance is a type of temporary term life insurance that can be turned into permanent life insurance without the need for a new health screening. This allows the policyholder to buy low-cost temporary coverage now while keeping the option to buy lifelong coverage later.
The conversion can happen as long as the policy conditions have been maintained, including making payments on time. While permanent life insurance carries higher premiums than term insurance, it also provides benefits such as lifelong coverage, level premiums, and tax-free cash value accumulation.
The biggest reasons in favour of converting to a whole life policy from a term policy are to preserve life insurance coverage for an individual's entire life and to preserve a favourable underwriting rating after a decline in health. By purchasing a convertible term life insurance policy when the insured person is young and healthy, they give themselves the ability to convert at a later time when they have more money without having to worry about their health rating.
The cost of convertible insurance is higher than that of traditional term policies, and premiums will increase if and when the conversion is carried out. The permanent policy will have the same value as the term policy, but the premiums will be higher. Convertible insurance is more expensive than a term life insurance policy for the same amount of coverage because there is a built-in cost for the option of being able to make the conversion without a medical exam.
The attained age method for calculating insurance premiums bases the premiums on the age of the insured at the time of conversion, resulting in a more expensive cost of insurance annually. The original age method bases the premiums on the age of the insured when the term insurance was first acquired, resulting in a less expensive policy annually but requiring a lump-sum payment upfront.
Supplemental Insurance: Understanding Its Role and Relationship with Short-Term Coverage
You may want to see also

The conversion of term insurance to whole life insurance is a simple process
- Check if your current term policy has a conversion option and ensure that you meet the conversion requirements. The time frame that companies allow for policyholders to convert varies. Some will allow it at any point, while others will carry a conversion period limit.
- Find out if your conversion includes a medical exam requirement, in case you have underlying health issues that could make getting a new policy problematic.
- Speak with your insurance agent or a financial professional to get expert advice on whether a conversion is in your best interest, based on your current life situation.
- Decide if converting to whole life makes sense from a budgeting standpoint. Whole life policies are more expensive and sometimes significantly more, so you don't want to convert to a policy you can't afford.
- Ask about converting in stages. You might have the option to convert in instalments if that better meets your needs.
- Complete a conversion application, working with your agent if needed, to help you answer any questions along the way.
- Choose how you want to be billed for premiums. Based on your preferences, it may make sense to be billed annually instead of monthly or quarterly.
- Consider setting up automatic withdrawals to ensure you don't let your policy lapse.
- Double-check who you want as beneficiaries for the policy.
- Sign and submit the application.
The effective date will vary by insurer, but you should ask when the policy will go into effect to have full clarity on this important final step.
The Dark Side of Short-Term Insurance: Uncovering the Hidden Pitfalls
You may want to see also

The attained-age method bases insurance premiums on the age of the insured at the time of conversion
When it comes to convertible term life insurance, there are two methods used to calculate the cost of converting to a permanent life insurance policy: the attained-age method and the original-age method. This answer will focus on the attained-age method and how it affects insurance premiums.
The attained-age method bases insurance premiums on the age of the insured person at the time of conversion. In other words, the premium is calculated based on how old the policyholder is when they decide to convert their term policy to a permanent one. This usually results in a more expensive premium than the original-age method.
For example, let's consider a healthy 30-year-old man who purchases a $500,000 25-year term life insurance policy for $25 per month. At age 50, he decides to convert $100,000 of his term policy to a whole life insurance policy. Due to the attained-age method, the premium for his new whole life policy is now $118 per month, a significant increase from his original term policy.
The attained-age method takes into account the increased risk associated with insuring an older individual. As people age, their life expectancy decreases, and the likelihood of health issues and premature death rises. Insurance companies factor these risks into their pricing, resulting in higher premiums for older individuals.
It's important to note that while the attained-age method may result in higher premiums, it also offers the advantage of not requiring a lump-sum payment upfront, unlike the original-age method. The original-age method calculates premiums based on the age when the term insurance was first acquired, resulting in lower yearly costs but often requiring a substantial upfront payment to account for the difference in cost between term and whole life insurance.
The decision to use the attained-age method or the original-age method depends on the policyholder's financial situation and long-term goals. By opting for the attained-age method, policyholders avoid the immediate financial burden of a lump-sum payment but accept higher annual premiums. Ultimately, the choice between the two methods should be guided by careful consideration of the potential costs and benefits of each option.
Medigap and Supplemental Insurance: Understanding the Difference
You may want to see also

The original-age method bases insurance premiums on the age of the insured when term insurance was first acquired
When it comes to insurance, there are two methods for calculating premiums: the attained-age method and the original-age method. The original-age method bases insurance premiums on the age of the insured when term insurance was first acquired. This means that the premium price will be calculated as if the insured person took out the whole life policy at the age they were when they were issued their term policy.
The benefit of the original-age method is that the yearly cost of insurance will be lower. However, to compensate for this, the insured person will usually have to pay a lump sum upfront. This is the difference in price between the term policy and what the premium payments would have been if a whole life policy had been taken out instead.
The reason for this upfront payment is that the original-age method allows the insured person to lock in a lower premium by pricing the policy as if they were still the age they were when they first took out their term insurance. As age is a major factor in the price of life insurance, this can result in significant savings. However, insurance companies will usually require this upfront payment to make up for the lower yearly cost of insurance they will receive.
Due to the cost of converting a policy based on the original-age method, most insurers either don't offer this method or require conversion within 5 years of buying term insurance. Despite this, the original-age method can still be a valuable option for those looking to lock in lower insurance premiums by pricing their policy based on their age when they first acquired term insurance.
Exploring Healthcare Choices: Beyond Short-Term and ACA Insurance Plans
You may want to see also

Term insurance is the cheapest life insurance policy available
Term insurance is also the simplest type of policy, which makes it the easiest to sell. It was the earliest policy type sold over the Internet, with much more competition among insurers, which drives down prices.
Term insurance is a good option for those who can't afford a cash-value policy but still want to guarantee their insurability later when they can afford it.
Term life insurance is usually the cheapest type of life insurance policy; the cost of whole life insurance can be significantly higher. With that in mind, here are some of the cheapest companies for a 20-year, $500,000 term life insurance policy covering super preferred applicants:
- Corebridge Financial (formerly AIG Life)
- Banner Life
- Lincoln Financial
- SBLI
- Symetra
- Prudential
- Protective Life
Term life insurance is also the cheapest option for seniors, with companies like Protective offering relatively cheap rates.
Term life insurance is also the cheapest option for people with pre-existing conditions. Legal & General America, which also does business as Banner Life and William Penn, has some of the longest term lengths and most competitive life insurance rates available, even for people with a history of medical conditions.
Term life insurance is also the cheapest option for families. Corebridge Financial (formerly AIG Life & Retirement) offers cheaper rates and a quicker turnaround time than some of its competitors.
Term life insurance is also the cheapest option for smokers. Corebridge Financial offers some of the cheapest rates on the market for both male and female smokers.
Term life insurance is also the cheapest option for young people. Transamerica offers affordable rates for almost every age, and you can even skip the medical exam if you fall under a certain age or coverage amount.
Term life insurance is also the cheapest option for people considered overweight. Pacific Life offers some of the lowest rates for term life insurance across age brackets.
Term Insurance for Non-Resident Indians: Exploring Eligibility and Benefits
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Attained age is the age of the insured person on a given date, usually the age at which they can receive benefits or withdraw funds. Original age is the age of the insured person when they first acquired the term insurance.
The younger the insured person is, the less expensive the insurance premium will be.
Using original age for the conversion process can save the insured person money on later premiums. However, to use original age, the insured person will usually have to pay a lump sum upfront to preserve that age calculation.







