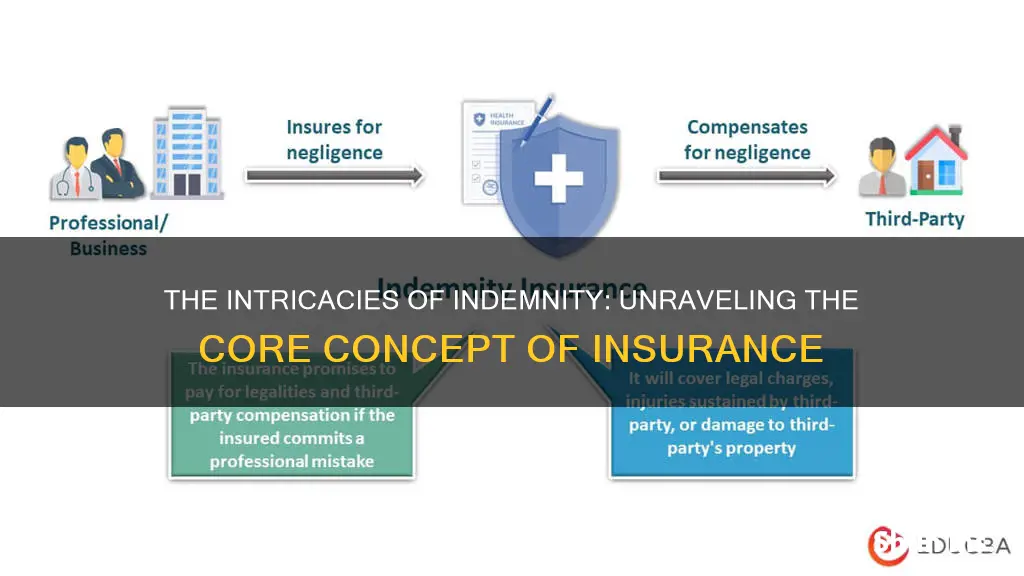
Indemnity is a contractual agreement between two parties, wherein one party agrees to compensate the other for any losses or damages incurred. In the context of insurance, indemnity refers to the principle of compensating an insured party for damages or losses up to a certain limit, usually the amount of the loss itself. This type of insurance is designed to protect professionals and business owners from financial losses due to events such as misjudgment, malpractice, or negligence. Indemnity insurance can cover legal fees, settlements, and other expenses resulting from a claim.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A contractual obligation to compensate an individual or business for damages or losses they experience |
| Type of agreement | Contractual agreement between two parties |
| Parties involved | One party (the indemnitor) agrees to pay for potential losses or damages caused by the other party (the indemnitee) |
| Examples | Auto insurance, homeowners insurance, pet insurance, health insurance, business insurance, malpractice insurance, errors and omissions insurance |
| Payment mode | Cash, repair or replacement of damaged property |
| Applicability | Insurance in which the payment to insureds is tied closely to a specific replacement cost, fair-market value, or reimbursement |
What You'll Learn

Indemnity insurance can protect against claims of negligence or malpractice
Indemnity insurance is a type of insurance policy that compensates an insured party for unexpected damages or losses, usually up to the amount of the loss itself. It is a comprehensive form of insurance compensation for damage or loss. Indemnity insurance is also referred to as professional liability insurance.
Indemnity insurance is designed to protect professionals and business owners when they are found to be at fault for a specific event, such as misjudgment or malpractice. Certain professionals are required to carry indemnity insurance, including those in the medical field. For example, doctors, surgeons and other healthcare professionals often have malpractice insurance to protect them from claims that their treatment resulted in physical or mental harm to patients.
Indemnity insurance can also protect against claims of negligence. For instance, if a client accuses a business of negligence, making an error, or missing a deadline that causes them to lose money, they may seek damages. Indemnity insurance can help cover court costs and fees regardless of the outcome, and can help cover settlements if the insured is found at fault, up to the policy limit.
In the case of malpractice, indemnity insurance can cover the legal defence and damages that the insured is required to pay. It is invaluable for any professional who provides advice or a service.
The Intricacies of Insurance Twisting: Unraveling the Practice and Its Impact
You may want to see also

Indemnity insurance can cover legal fees
Indemnity insurance is a type of insurance policy that compensates the insured party for unexpected damages or losses, usually up to the amount of the loss itself. Indemnity insurance covers the costs of an indemnity claim, including court costs, fees, and settlements. This includes legal fees incurred by the insured party in the event of a lawsuit.
Indemnity insurance is a supplemental form of liability insurance that is specific to certain professionals or service providers. It is designed to protect professionals and business owners when they are found to be at fault for a specific event, such as misjudgment or malpractice. Certain professionals are required to carry indemnity insurance, including those involved in financial and legal services, such as financial advisors, insurance agents, accountants, mortgage brokers, and attorneys.
In addition to malpractice insurance, other common types of indemnity insurance include auto insurance, homeowners insurance, pet insurance, health insurance, and business insurance. Indemnity insurance can also cover court costs, fees, and settlements in addition to an indemnity claim.
For example, if a physician works for a hospital, they may be required to sign an indemnity agreement that holds the hospital harmless. The physician indemnifies the hospital so that the hospital cannot be the target of any lawsuits brought as a result of the physician's actions. Therefore, the physician may require medical malpractice insurance, which is a form of indemnity insurance, to protect themselves from potential patient lawsuits.
Unraveling the Mystery: Exploring the Cash Value Potential of Term Insurance
You may want to see also

Indemnity insurance can be tax-deductible
Indemnity insurance is a type of insurance policy that compensates the insured party for unexpected damages or losses. It is a comprehensive form of insurance compensation for damage or loss. It amounts to a contractual agreement between two parties in which one party agrees to pay for potential losses or damage caused by the other party.
Indemnity insurance is often beneficial in protecting finances, especially in the event of a potential lawsuit. For example, if a client suffers a loss, they can file a civil claim. In response, the professional's indemnity insurance will pay for litigation costs as well as any damages awarded by the court. Indemnity insurance covers the costs of an indemnity claim, including court costs, fees, and settlements.
In the United States, the IRS considers insurance costs for a business as eligible for a write-off, so professional indemnity insurance usually qualifies as a business expense and can be deducted from tax returns.
It is important to note that not all insurance policies are based on indemnity. Indemnity applies when the payment to the insured is closely tied to a specific replacement cost, fair-market value, or reimbursement. Life insurance, for example, is not considered indemnity because it is impossible to determine the value of a human life.
Understanding Renewable Term Insurance: Unraveling the Benefits and Mechanics
You may want to see also

Indemnity insurance can be required by law
Indemnity insurance is a type of insurance policy that compensates an insured party for unexpected damages or losses, usually up to the amount of the loss itself. It is a comprehensive form of insurance compensation for damage or loss and is based on a contractual agreement between two parties. In this arrangement, one party agrees to pay for potential losses or damage caused by the other party. Indemnity insurance is often required by law in certain situations, such as when buying or selling property, operating a business, or providing professional services.
When purchasing property, indemnity insurance can protect against issues with planning permission, access, legal challenges, and chancel repair liability. It offers buyers protection against the costs of fixing problems that may be revealed during the conveyancing or survey processes. For example, if the seller cannot provide planning permission documentation for an extension, the buyer can take out indemnity insurance to cover any loss of value or legal claims that may result.
Businesses may also be legally required to have indemnity insurance, particularly in industries with a high risk of liability claims. This includes general liability, workers' compensation, commercial auto, and commercial umbrella liability insurance. Indemnity insurance can protect businesses from financial loss due to property damage, legal expenses, automobile injuries, workplace illnesses, and other unforeseen events.
Certain professionals, such as those in the medical, legal, and financial fields, may be legally mandated to carry indemnity insurance. Medical malpractice insurance, for instance, is required in some states and protects medical practitioners from civil claims arising from negligence. Similarly, professionals in the legal and financial sectors may need indemnity insurance to cover potential claims of negligence, malpractice, or failure to perform.
In summary, indemnity insurance is a critical form of protection for individuals, businesses, and professionals. By having indemnity insurance, individuals and organizations can safeguard themselves from financial loss and legal liabilities arising from unexpected events or claims of negligence. The requirement to have indemnity insurance varies depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the activities involved.
Understanding Direct Term Insurance: Unraveling the Basics of This Pure Protection Plan
You may want to see also

Indemnity insurance can be purchased to protect against accidental death
Indemnity insurance is a type of insurance policy that compensates the insured party for unexpected damages or losses, usually up to the amount of the loss itself. It is a contractual agreement between two parties, wherein one party agrees to compensate the other for any damage or loss incurred. This type of insurance is designed to protect professionals and business owners from financial loss and legal entanglements due to misjudgment, negligence, or malpractice.
When considering indemnity insurance for protection against accidental death, it is crucial to carefully review the terms and exclusions of the policy. While it can provide financial peace of mind for loved ones in the event of an unexpected death, it is important to understand the specific circumstances under which benefits will be paid. Additionally, certain professions and individuals working in hazardous environments may find this type of insurance particularly relevant.
Overall, indemnity insurance for accidental death can be a valuable addition to existing insurance coverage, providing further protection and peace of mind. However, it is important to assess your specific needs and existing coverage to determine if this type of insurance is necessary for your situation.
The Policyholder's Shield: Unraveling the Provision that Safeguards Insured Terms
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Indemnity insurance is an agreement between two parties in which one party is responsible for compensating the other for any losses or damages they may incur. It is a form of protection against indemnity claims.
In a legal context, indemnity may refer to an exemption from liability for damage.
Indemnity insurance can refer to auto insurance, homeowners insurance, pet insurance, health insurance, and business insurance.







