Life insurance is a contract that ensures financial protection for your loved ones in the event of your death. The death benefit, or payout, is given to beneficiaries, who can use it to cover funeral costs, manage living expenses, and pay off remaining debts. The cost of life insurance depends on several factors, including age, gender, health, hobbies, occupation, and criminal history. A unit of coverage refers to a life insurance policy's base death benefit amount. For example, if one unit of coverage is $1,000, and you buy a policy for 15 units, your death benefit will be $15,000. The cost of each unit depends on the insurance company and the policyholder's risk factors.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Unit of coverage | $1,000 |
| Premium per unit | $9.95 |
| Death benefit per unit | Varies based on age, gender, and other factors |
| Premium per unit | Fixed amount |
| Death benefit per unit | Varies based on risk factors |
What You'll Learn
- Unit pricing: $9.95 per unit, with the death benefit per unit varying based on age, gender, etc
- Death benefit: the amount paid out to beneficiaries after the policyholder's death
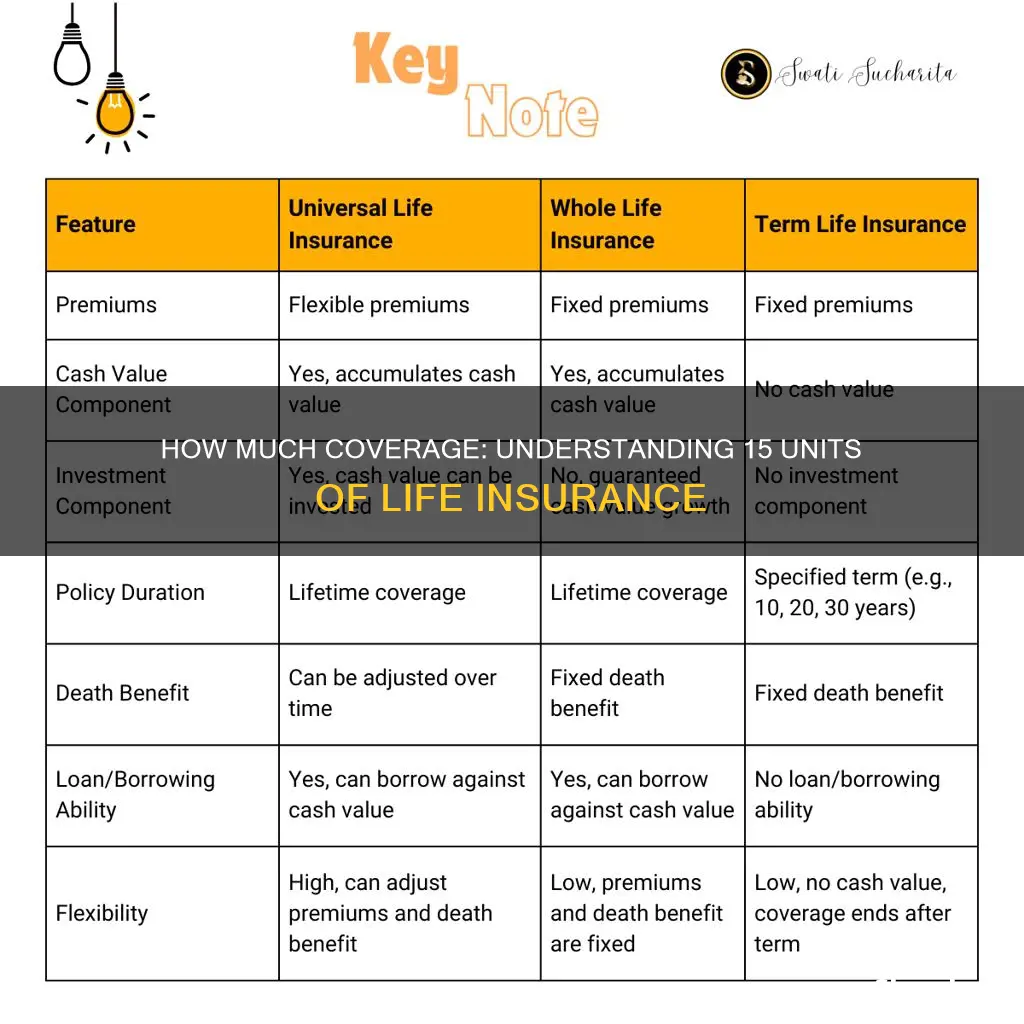
- Whole life insurance: permanent coverage with an investment component
- Term life insurance: coverage for a set number of years, no cash value
- Guaranteed acceptance: no medical exam, health questions, or rate increases

Unit pricing: $9.95 per unit, with the death benefit per unit varying based on age, gender, etc
The unit pricing of life insurance is a crucial aspect of understanding the overall cost of your policy. While the monthly or annual premium payments are more commonly discussed, the unit price is essential to calculating the total expense.
In the context of life insurance, the unit price refers to the cost per unit of the death benefit. The death benefit is typically priced out in $1,000 units, so a $250,000 death benefit would equate to 250 units. The unit price, in this case, would be the cost you incur for each of those 250 units.
For example, Colonial Penn offers a unit system where each unit costs $9.95 per month. The death benefit per unit varies based on age and gender. A 66-year-old male, for instance, would receive $846 in life insurance from a single $9.95 unit, while a 65-year-old female would get $1,000 in coverage. The older the insured individual is, the lower the death benefit per unit tends to be.
It's important to note that the unit price is not a standard rate for everyone. Insurance companies assess factors such as age, gender, lifestyle, and health to determine the unit price for an individual. Generally, younger people are considered less risky and, therefore, pay lower unit prices than older individuals. Additionally, men tend to have shorter lifespans and are viewed as more likely to engage in dangerous jobs or lifestyles, resulting in higher unit prices for male policyholders.
While unit pricing is not often discussed during the insurance shopping process, it is a valuable piece of information for calculating the true cost of your insurance policy. By understanding the unit price and the number of units your death benefit comprises, you can make more informed decisions about your life insurance coverage.
Depression and Life Insurance: Eligibility and Exclusions
You may want to see also

Death benefit: the amount paid out to beneficiaries after the policyholder's death
The death benefit is the primary reason why someone purchases a life insurance policy. It is the amount of money paid out to beneficiaries after the policyholder's death. The amount of the death benefit is set in the terms of the contract and chosen by the policyholder, who make regular premium payments. The premium payments will increase as the amount of the death benefit increases. Generally, the younger and healthier you are, the lower your premiums will be.
The death benefit can be paid out as a lump sum or in installments. The policyholder can allocate different percentages to different beneficiaries. The death benefit is typically tax-free, but you should consult a tax professional if you have any questions.
In most cases, the beneficiaries of a death benefit are the policyholder's partner, children, or other close loved ones, but any person or organisation can be named as a beneficiary.
There are several types of death benefits:
- All-cause death benefit: This is the typical death benefit for standard life insurance policies. The policy will pay out no matter how the policyholder passes away, except in the rare case that their cause of death is specifically excluded by the policy.
- Accidental death benefit: This type of death benefit only pays out to beneficiaries in the event of a car crash, drowning, or another accident that results in a fatality.
- Accidental death and dismemberment: This type of policy pays out for qualifying accidental fatalities as well as for accidents that cause qualifying major injuries such as the loss of a limb, paralysis, or blindness.
Colonial Penn's life insurance policy is based on a unit system. Each unit costs $9.95 per month, and the amount of life insurance coverage per unit depends on the age and gender of the policyholder. For example, a 66-year-old male would receive $846 in life insurance from a single unit.
Using Life Insurance for a Loan: Is It Possible?
You may want to see also

Whole life insurance: permanent coverage with an investment component
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides coverage for the entire life of the insured. It is characterised by level premiums, meaning the amount paid every month remains unchanged, and a savings component, known as the cash value, which functions similarly to a retirement savings account. The cash value typically earns a fixed rate of interest, which accumulates on a tax-deferred basis. This means that any interest earned is not taxed as long as the funds remain in the policy.
The cash value can be utilised in several ways. It can be withdrawn or borrowed against, used as collateral for a loan, or surrendered for the entire available cash value (with the policy being terminated). Withdrawals up to the value of the total premiums paid are generally tax-free. However, if the withdrawal exceeds this amount and dips into investment gains, taxes will apply. Additionally, any outstanding loans or withdrawals will reduce the death benefit paid out to beneficiaries.
Whole life insurance is particularly suitable for high-net-worth individuals who have already maximised their contributions to tax-advantaged accounts, as it provides an additional avenue for tax-deferred savings. It is also beneficial for those with lifelong financial dependents, such as parents caring for children with disabilities, as it offers lifelong coverage and financial stability. Furthermore, the cash value component makes whole life insurance a form of "forced savings," which can assist in paying estate taxes without dipping into other accounts.
Despite its advantages, whole life insurance may not be the best option for everyone. The premiums tend to be significantly higher compared to term life insurance due to the accumulation of cash value and lifelong coverage. The cash value also takes time to grow, and the rate of return is often lower than what could be achieved through other investments. Additionally, policyholders have limited flexibility to adjust the premium or death benefit.
Finding Life Insurance After a Loved One's Death
You may want to see also

Term life insurance: coverage for a set number of years, no cash value
Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that offers coverage for a set number of years, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years, with options available for longer periods. It is designed to provide financial protection for a specified term and guarantees payment of a death benefit to the insured's beneficiaries if the insured person dies during that period. Term life insurance is particularly attractive to young people with children as it offers substantial coverage at a low cost.
One of the key characteristics of term life insurance is that it does not accumulate cash value. Unlike permanent life insurance policies, term life insurance does not have a savings component. This means that there is no cash value that can be withdrawn or borrowed against during the policy's term. The policy only has value if the insured person passes away during the specified term, in which case the beneficiaries will receive the death benefit. If the policy expires before the insured person's death or they outlive the policy term, there is no payout.
The cost of term life insurance is based on factors such as the policy's value, the insured person's age, health, and life expectancy. The insurance company will consider various factors, including age, gender, health, driving record, smoking status, occupation, and hobbies, to determine the premium. Term life insurance is generally the cheapest type of life insurance available due to its limited coverage period and lack of cash value.
When considering term life insurance, it is important to note that the premiums may increase if the policy is renewed after the initial term. Additionally, term life insurance may not be suitable for those seeking lifelong coverage or looking to accumulate cash value through their policy. In such cases, permanent life insurance, including whole life insurance and universal life insurance, may be more appropriate.
In summary, term life insurance provides coverage for a specified number of years and guarantees a death benefit if the insured person passes away during that term. It is a cost-effective option for those seeking temporary coverage, especially for young families. However, it does not offer cash value, and the coverage ends if the insured person outlives the policy term.
Life Insurance Payouts: Taxable to C-Corps?
You may want to see also

Guaranteed acceptance: no medical exam, health questions, or rate increases
Guaranteed acceptance life insurance is a type of whole life insurance policy that does not require a medical exam, health questions, or rate increases. This means that applicants are not asked about their health or medical history, and their acceptance is guaranteed regardless of any pre-existing conditions. The benefit amount and premium rate are locked in once the policy is issued, and the coverage can last for the entire lifetime of the insured individual.
The main advantage of guaranteed acceptance life insurance is that it provides coverage for individuals who may otherwise have difficulty obtaining life insurance due to their health status. The application process is simple and convenient, and in many cases, a policy can be purchased online. This type of insurance is also flexible, allowing individuals to choose their payment frequency (monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually). Additionally, the coverage amount can be scaled up or down, typically within a range of $2,000 to $25,000.
However, there are some drawbacks to guaranteed acceptance life insurance. Firstly, these policies are generally more expensive than typical term or whole life insurance policies because the insurer assumes a higher risk without access to the applicant's health information. Secondly, there is usually a two- to three-year waiting period for the full benefits to take effect. If the insured individual passes away during this waiting period due to a non-accidental cause, the beneficiaries will not receive the full death benefit but will instead be refunded the premiums paid, plus interest.
Guaranteed acceptance life insurance is best suited for individuals who want to cover final expenses, such as funeral or burial costs, rather than providing a large death benefit. It is recommended that individuals explore other options, such as simplified issue life insurance, if they are seeking a more affordable option with a wider range of coverage.
Funeral Expenses: Life Insurance Payouts Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A unit of life insurance coverage refers to the base death benefit amount of a policy. For example, if one unit of coverage is $1,000 and you buy a policy for one unit, your death benefit is $1,000.
Insurance companies use units of coverage to determine the death benefit amount or premium. The unit of coverage is often set at a fixed death benefit amount, commonly $1,000, but this can vary by insurer.
The number of units you need depends on the amount of financial support you want to leave your family. Factors to consider include funeral and burial expenses, income replacement, and debt repayment.
The cost of life insurance is influenced by various factors, including age, gender, health, lifestyle, and risk factors such as smoking or engaging in risky activities.
Term life insurance covers an individual for a set number of years and does not accumulate cash value, while whole life insurance covers an individual for their entire life and includes an investment component that builds cash value over time.