Private health insurance is any health insurance plan that is not run by the federal or state government. Private insurance can be purchased from an employer, a state or federal marketplace, or a private marketplace. Private health insurance plans are designed to split the cost between the insurer and the insured, making medical care more affordable. In the US, around 60% of the population has private health insurance, with the majority receiving coverage through employer-sponsored plans. Private health insurance is more flexible than public insurance, giving policyholders more options for doctors or medical facilities. However, it tends to be more expensive and requires the payment of monthly or yearly premiums.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Health insurance plans that are not run or funded by the federal or state government |
| Providers | Private insurance companies, health insurance agents, or online brokers |
| Purchased from | Employers, state or federal marketplace, or a private marketplace |
| Purpose | Split the cost of medical care between the insured and the insurer to make it more affordable |
| Cost-sharing methods | Deductibles, copays, and coinsurance |
| Opposite of | Public insurance plan |
| Examples of public insurance plans | Medicaid, Medicare, Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) |
| Types | Indemnity plans, Preferred provider organization (PPO) plans, Health maintenance organization (HMO) plans, Long-term care (LTC) insurance, Medigap insurance plans, Medical savings accounts (MSAs) |
What You'll Learn
- Private insurance is provided by private companies and is often offered by an employer
- It can be purchased individually or as a group
- It is more flexible than public insurance, giving policyholders more options
- It is more expensive than public insurance
- It is intended to protect beneficiaries from high healthcare costs

Private insurance is provided by private companies and is often offered by an employer
Private health insurance can be purchased in a few different ways. It is often provided as an employment benefit, with around 49% of Americans receiving their health insurance through their employer. Employer-sponsored health insurance is typically more generous than public healthcare insurance programs, and it is subsidised by the government through the tax code. However, workers who receive employer-sponsored insurance may be paid less in wages as a result of the insurance premiums paid by the employer.
Private health insurance can also be purchased directly from health insurance companies, local health insurance brokers, or online health insurance marketplaces. This is known as an individual health insurance plan, and it is usually more expensive than group policies. These plans are typically purchased by individuals who are not employed or are self-employed, or who are new hires at a company and must wait for the company's coverage to take effect.
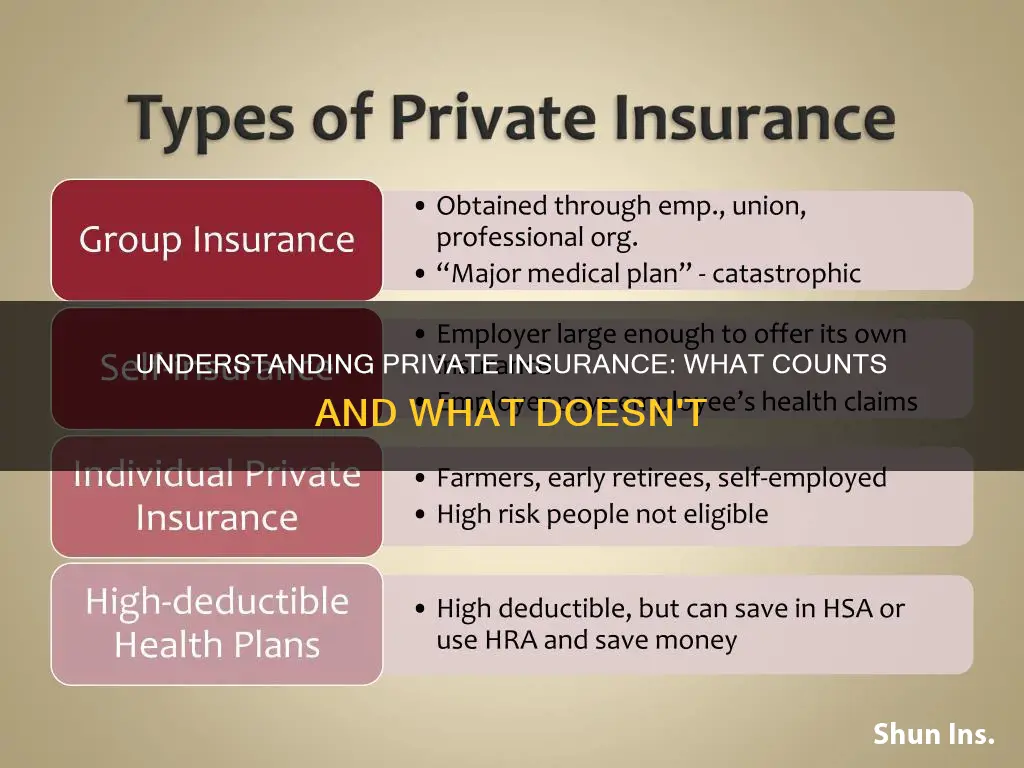
There are several different types of private health insurance plans, including indemnity plans, preferred provider organisation (PPO) plans, health maintenance organisation (HMO) plans, and long-term care (LTC) insurance. Indemnity plans allow beneficiaries to choose any physician or hospital, while PPO plans offer a list of approved physicians and hospitals from which beneficiaries must choose in order to receive the maximum benefit. HMO plans usually have no deductible, but beneficiaries are charged a small co-payment for each visit. LTC insurance is intended to cover the cost of long-term nursing home or home health care.
MassHealth: Private Insurance or Public Option?
You may want to see also

It can be purchased individually or as a group
Private health insurance plans can be purchased by individuals or groups. They are provided by private companies and are often offered by employers or other organisations with which the policyholder is affiliated.
Private insurance plans can be purchased from a variety of sources, including your employer, a state or federal marketplace, or a private marketplace. They can also be bought through private health insurance companies, health insurance agents, or online brokers.
If you are buying private health insurance as an individual, you can purchase it directly from health insurance companies, local health insurance brokers, or online health insurance marketplaces. Individual health insurance plans are usually more expensive than group insurance plans and may have additional coverage restrictions. However, they tend to be more flexible than group policies, giving policyholders more options for which doctor or medical facility to visit.
Group insurance plans are mostly offered by large employers, although some are available through voluntary associations. They are typically more generous than public healthcare insurance programs. Since 2015, Obamacare has mandated that all employers with over 50 full-time employees should provide affordable health coverage to their employees.
Harvard Pilgrim and Taylor Benefits: Private Insurance Options
You may want to see also

It is more flexible than public insurance, giving policyholders more options
Private insurance is more flexible than public insurance, offering policyholders a wider range of options. Private health insurance plans can be purchased from a variety of sources, including employers, state or federal marketplaces, or private marketplaces. This flexibility allows individuals to choose the most suitable option for their needs and preferences.
One significant advantage of private insurance is the freedom it provides in choosing healthcare providers. Private insurance policyholders can select any doctor or medical facility they prefer, whereas public insurance plans often restrict policyholders to a limited network of medical service providers. This restriction is due to many medical establishments not accepting government-sponsored health insurance plans. With private insurance, individuals can maintain continuity of care with their preferred healthcare providers, ensuring they receive treatment from trusted and familiar sources.
Private insurance also offers a broader selection of plans and a wider network of providers to choose from. This variety enables policyholders to find a plan that best suits their specific needs and budget. The competition among private insurance companies further encourages them to provide attractive benefits and services to stand out in the market. As a result, policyholders have more options to customize their coverage according to their unique requirements.
Additionally, private insurance plans often include supplemental coverage options that cater to specific needs. These can include dental and vision insurance, accident supplements, critical illness insurance, and more. Such supplemental coverage options provide policyholders with the flexibility to enhance their overall health coverage and ensure they are protected against a wide range of potential health concerns.
The flexibility of private insurance also extends to its portability. Private health insurance plans often allow employees to transfer their health insurance coverage from one employer to another when they change jobs. This portability feature ensures that individuals can maintain continuous health coverage even when transitioning between jobs, providing valuable peace of mind and security.
In summary, private insurance offers greater flexibility than public insurance by empowering policyholders with more options. From choosing healthcare providers to selecting specialized coverage plans, private insurance provides individuals with the ability to customize their health coverage according to their unique needs and preferences. This flexibility, combined with the variety of supplemental coverage options available, makes private insurance a popular choice for those seeking comprehensive and adaptable health insurance solutions.
EmblemHealth: Private Insurance, Public Benefits
You may want to see also

It is more expensive than public insurance
Private health insurance is more expensive than public insurance. This is because private insurance plans are not funded by the government. Instead, they are purchased from private companies, either by employers or individual consumers. While employer-sponsored insurance is partially paid for by the employer, employees will still need to pay a monthly premium. For those who purchase private insurance as individuals, the cost is often much higher.
The cost of private health insurance has been rising steadily over the past two decades, largely due to the increasing cost of healthcare in the United States. The rising costs have caused many employers to reduce or drop health insurance as an employee benefit. This has resulted in a growing number of uninsured Americans, particularly those who are self-employed, work part-time, or hold low-wage jobs.
The high cost of private health insurance is also due to the fact that it is not subsidized by the government in the same way that public insurance is. While some people may qualify for financial assistance or tax deductions, private insurance typically requires the policyholder to pay a monthly or yearly premium, which can be unaffordable for some.
In addition, individual private health insurance plans tend to be more expensive than group policies. They may also have additional coverage restrictions and higher deductibles. This means that the policyholder must pay a larger portion of the cost out-of-pocket before the insurance company will cover any expenses.
Overall, the higher cost of private health insurance compared to public insurance can be attributed to a variety of factors, including the lack of government funding, rising healthcare costs, and the structure of individual and group plans.
Unicare Private Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

It is intended to protect beneficiaries from high healthcare costs
Private health insurance is any health insurance plan that is not run by the federal or state government. Private insurance can be purchased from an employer, a state or federal marketplace, or a private marketplace. In the US, around 60% of the population has private health insurance, with a little over half of the population covered by employer-sponsored plans.
Private health insurance plans are intended to protect beneficiaries from high healthcare costs. They are designed to split the cost of medical care between the insured person and the insurer, making healthcare more affordable. This cost-sharing takes the form of deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
For example, most private insurance plans have a deductible, which is an amount of money that the insured person is required to pay on each claim made on the insurance policy. After the deductible has been met, the insurance plan will then cover a percentage of the remaining costs, known as coinsurance. The percentage of health care charges covered by the insurance company is usually between 70-90%. The insured person is then responsible for paying the remainder of the bill.
Private insurance plans also often require the payment of a premium, which is the amount paid by the policyholder for their insurance coverage. Premiums are typically payable on a monthly basis. The cost of private health insurance varies and depends on factors such as age and location. Generally, individual policies are more expensive than group policies.
Blue Cross Blue Shield Massachusetts: Private Insurance Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Private insurance is any health insurance plan that is not run by the federal or state government. Private insurance is provided by private companies and is often provided by an employer or other organisation with which the policyholder is affiliated.
Private insurance includes employer-sponsored plans, which cover about half of the American population. It can also be purchased by individuals directly from health insurance companies, local health insurance brokers, or online health insurance marketplaces.
Private insurance plans are designed to split the cost of healthcare between the insured and the insurer, making medical care more affordable. These cost-sharing methods come in the form of deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
Private health insurance covers a little more than half of the US population. According to the Kaiser Family Foundation, 49% of Americans get their health insurance through employer-sponsored insurance.







