Auto insurance rates are influenced by a variety of factors, some of which are within the policyholder's control, while others are not. The cost of auto insurance is determined by factors such as age, gender, driving history, location, vehicle type, and credit score. The type of coverage and deductible selected, as well as the insurance company, also impact the cost. Additionally, factors like inflation, rising repair costs, and an increase in claims can contribute to higher insurance rates. Understanding these factors can help individuals estimate their auto insurance costs and explore ways to lower their premiums.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Driving record | A history of accidents, DUI, or other instances of poor behaviour on the road will result in higher rates |
| Age | Younger, less experienced drivers pay higher rates |
| Gender | Women tend to pay less than men |
| Credit score | A higher credit score will result in lower rates |
| Car | More expensive cars, cars with high repair costs, and cars with a history of accidents will result in higher rates |
| Location | Insurance rates vary depending on the state and ZIP code |
| Coverage amount | Higher coverage amounts and lower deductibles will result in higher rates |
| Discounts | Insurers offer a variety of discounts, such as for good driving, being a student, or having safety equipment in the car |
What You'll Learn

Your age and driving experience
The cost of car insurance is influenced by several factors, with age and driving experience being key considerations. Younger and less experienced drivers are generally considered riskier to insure due to their higher likelihood of making a claim. This perception is based on statistical data and accident trends, indicating that drivers under 25 are more prone to accidents. As a result, they often face higher insurance premiums.
In contrast, older drivers with more experience behind the wheel tend to enjoy lower insurance rates. This is because insurance companies view them as less risky, assuming that their extensive driving history has likely led to the development of safer driving habits. The decrease in premiums can be particularly noticeable after the age of 25, as insurers reward a proven track record of safe driving.
However, it's important to note that age isn't the sole factor influencing insurance rates. Other factors, such as gender, credit score, driving record, and the type of car, also come into play when determining insurance premiums. Additionally, as drivers reach their senior years, insurance rates may start to creep up again due to factors like vision or hearing loss and slower response times, which can increase the risk of accidents.
While age and experience play a significant role in determining insurance costs, it's always a good idea to shop around for insurance providers and take advantage of any available discounts to help mitigate the financial burden, especially for younger drivers.
Geico Renters and Auto Insurance: Bundling Benefits
You may want to see also

Your vehicle's safety rating
Crashworthiness and Crash Testing
The NHTSA and IIHS perform crash tests to assess how well a vehicle protects its occupants in a collision. These tests include frontal crashes, side barrier crashes, side pole crashes, and rollover resistance tests. The results are rated using a 5-star system by the NHTSA, with more stars indicating a safer vehicle. The IIHS uses ratings such as Poor, Marginal, Acceptable, and Good. Insurers consider these ratings when determining premiums, as safer vehicles are less likely to result in costly injury claims.
Safety Features and Technology
In addition to crash performance, insurance companies also consider the safety features and technology equipped in your vehicle. Modern driver-assistance technologies, such as forward-collision warning, lane departure warning, crash imminent braking, and dynamic brake support, can help prevent accidents or reduce their severity. Vehicles with advanced safety features are often viewed as lower-risk by insurers, potentially leading to lower insurance rates.
Vehicle Size and Weight
The size and weight of your vehicle also play a role in insurance costs. Generally, larger and heavier vehicles, like minivans and small SUVs, tend to be safer than smaller cars in a crash. As a result, insurance rates for these vehicles may be lower. Additionally, vehicle size can impact the likelihood and severity of accidents, with smaller cars sometimes sustaining more damage in collisions.
Safety Ratings and Insurance Premiums
When insurance companies assess the risk associated with a particular vehicle, they consider its safety ratings and crash test results. A vehicle with a higher safety rating, indicating better crash performance and effective safety features, is likely to be offered lower insurance rates. Conversely, a vehicle with a lower safety rating may result in higher insurance premiums due to the increased potential for injury and damage in an accident.
It's important to note that while safety ratings are a significant factor, other variables also influence insurance rates, including your driving record, age, gender, credit score, and location. By understanding how your vehicle's safety rating impacts your insurance, you can make informed choices when purchasing a vehicle and potentially reduce your auto insurance costs.
Auto Insurance: Keeping Adult Children Covered
You may want to see also

Your location and mileage
The location and mileage of a driver play a significant role in determining auto insurance rates. The annual mileage of a driver is a crucial factor that insurance companies consider when calculating insurance costs. On average, Americans drive approximately 13,000 miles per year, and this distance is used as a benchmark by insurance companies to set their rates.
Insurance companies often categorise drivers into three mileage brackets: low, average, and high mileage. Low mileage is typically defined as driving less than 7,500 miles per year, or less than 20 miles per day. Average mileage falls between 7,500 and 15,000 miles annually, while high mileage exceeds 15,000 miles per year. Drivers in the high mileage category tend to pay higher insurance rates due to the increased likelihood of accidents.
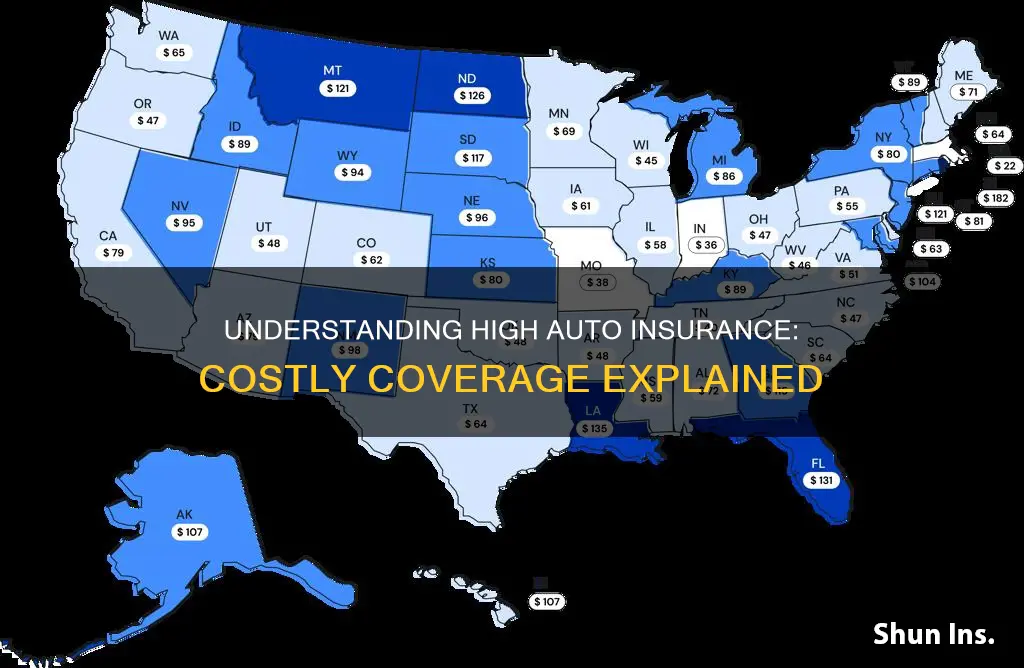
Location also influences insurance rates, as certain states or areas may have higher accident rates or more expensive repair costs. For example, in California, insurers weigh mileage more heavily when determining premiums, resulting in a 30% price gap between drivers travelling 10,000 and 30,000 miles per year.
Additionally, longer commutes can lead to higher insurance rates, as they increase the time spent on the road and the likelihood of accidents. Insurance companies may also offer low-mileage discounts to drivers who maintain a low annual mileage, helping them save on their insurance costs.
It is worth noting that insurance companies use various methods to verify a driver's annual mileage, including odometer readings, telematics devices, and data from third-party sources such as auto maintenance shops.
State Farm Auto Insurance: Flat Tire Coverage and Support
You may want to see also

Your insurance coverage choices
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is required in almost every state and is the main component of car insurance. It covers the injuries, deaths, and property damage you cause to others in an accident, but only up to your policy's limits. The minimum required liability coverage varies by state, and it is important to ensure you have adequate coverage to protect your assets. Liability coverage limits are typically presented in a format such as "25/50/15," where the first number represents the maximum payout per person, the second number is the maximum payout per accident, and the third number is the maximum payout for property damage.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for damage to your own vehicle in an accident. It is considered first-party coverage and will cover the cost of repairs or replacement of your vehicle. If the repair costs exceed the vehicle's value, your insurance company may declare it a total loss and provide you with a cheque for its value. Collision coverage is particularly important if you own a new or relatively new vehicle.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage is another form of first-party coverage that protects your vehicle from non-accident-related damage. It covers incidents such as theft, vandalism, or adverse weather conditions. For example, if your car is stolen or damaged in a storm, comprehensive coverage will help pay for the repairs or replacement.
Medical or Personal Injury Protection
Medical payments coverage, also known as MedPay, covers reasonable medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of who is at fault in the accident. Personal Injury Protection (PIP) offers similar coverage but with higher policy limits and more comprehensive benefits, including lost wages, funeral costs, and more. PIP is available in states with no-fault laws, and it is advisable to take advantage of this coverage if you reside in one of those states.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
Uninsured and underinsured motorist coverage are typically sold together. This coverage protects you if you are injured by a driver who does not have insurance or has insufficient insurance to cover your damages. It is especially important in states with a high percentage of uninsured drivers.
Other Optional Coverages
In addition to the core coverages mentioned above, there are several other optional coverages you may want to consider, depending on your specific needs. These include extended coverage, guaranteed auto protection (GAP) insurance, mechanical breakdown coverage, and OEM endorsement for original equipment manufacturer parts.
When choosing your insurance coverage, it is important to find a balance between adequate protection and affordability. Consider your financial situation, assets, and liquidity when deciding on coverage limits and deductibles. Additionally, remember to shop around, compare policies, and look for applicable discounts to ensure you get the best value for your money.
Insurance Surcharge Doubled After Accident
You may want to see also

Your credit score
The specific factors that contribute to your credit-based insurance score vary by insurer, but some common factors include payment history, length of credit history, types of credit, and credit utilisation. A good credit score can result in lower insurance premiums as insurers view you as a lower-risk customer. Conversely, a poor credit score can significantly increase your insurance costs. For example, drivers with poor credit may pay up to 88% more for full coverage car insurance compared to those with good credit.
While credit-based insurance scores are widely used, there are some states that prohibit or limit their use. California, Hawaii, Massachusetts, and Michigan are among the states that do not allow insurance companies to factor in credit scores when determining auto insurance rates. In these states, insurance rates are primarily based on driving records, location, and other characteristics.
It's important to note that getting insurance quotes or shopping around for better rates does not negatively impact your credit score. Insurance companies typically perform a "soft pull" of your credit information, which does not affect your credit score. Therefore, you can explore various insurance options without worrying about any adverse effects on your creditworthiness.
Auto Insurance in Minnesota: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The cost of auto insurance is influenced by factors such as your driving record, age, gender, location, credit score, vehicle type, and insurance coverage options.
A poor driving record, including accidents, driving violations, and a history of claims, will result in higher auto insurance rates. A DUI conviction or at-fault accident will significantly increase your premiums.
Yes, younger and less experienced drivers tend to pay higher auto insurance rates. Insurance companies generally charge higher rates for drivers in their 20s, with rates gradually decreasing as drivers gain more experience.
Location plays a significant role in determining auto insurance rates. Insurance premiums vary by state, ZIP code, and neighborhood. Rural drivers typically pay less than those in cities, and some states have higher average insurance costs due to factors like accident history and the number of uninsured drivers.
To lower your auto insurance rates, consider improving your driving record, choosing a vehicle that is cheaper to insure, increasing your deductible, comparing quotes from multiple insurers, and taking advantage of discounts offered by insurance companies.







